Carduus acanthoides
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 2: Primary Noxious Weed Seeds
Regulation Notes:
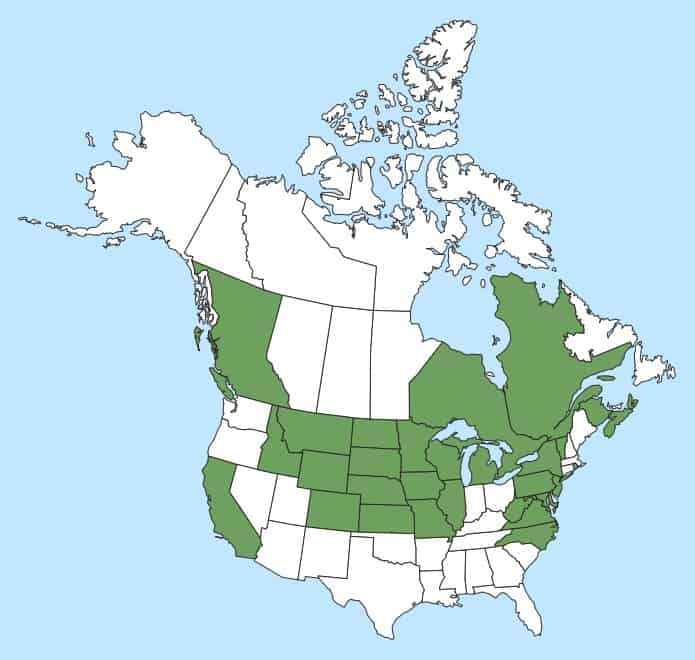
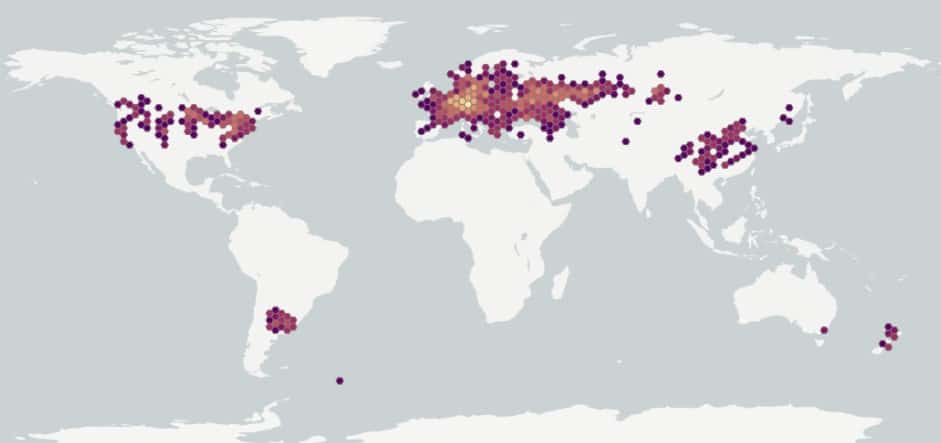
Distribution :
Répartition :
Native to northern Africa, temperate Asia, and most of Europe. Introduced to North America, Argentina, Uruguay, New Zealand, and beyond its native range in Europe (USDA-ARS 2020). Occurs across the continental United States, with the exception of some southwestern and southeastern states (Kartesz 2015). Occurs in Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick and Newfoundland and Labrador (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Cultivated fields, pastures, rangelands, roadsides and disturbed areas (Desrochers et al. 1988; Darbyshire 2003).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual or Biennial
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Achene
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
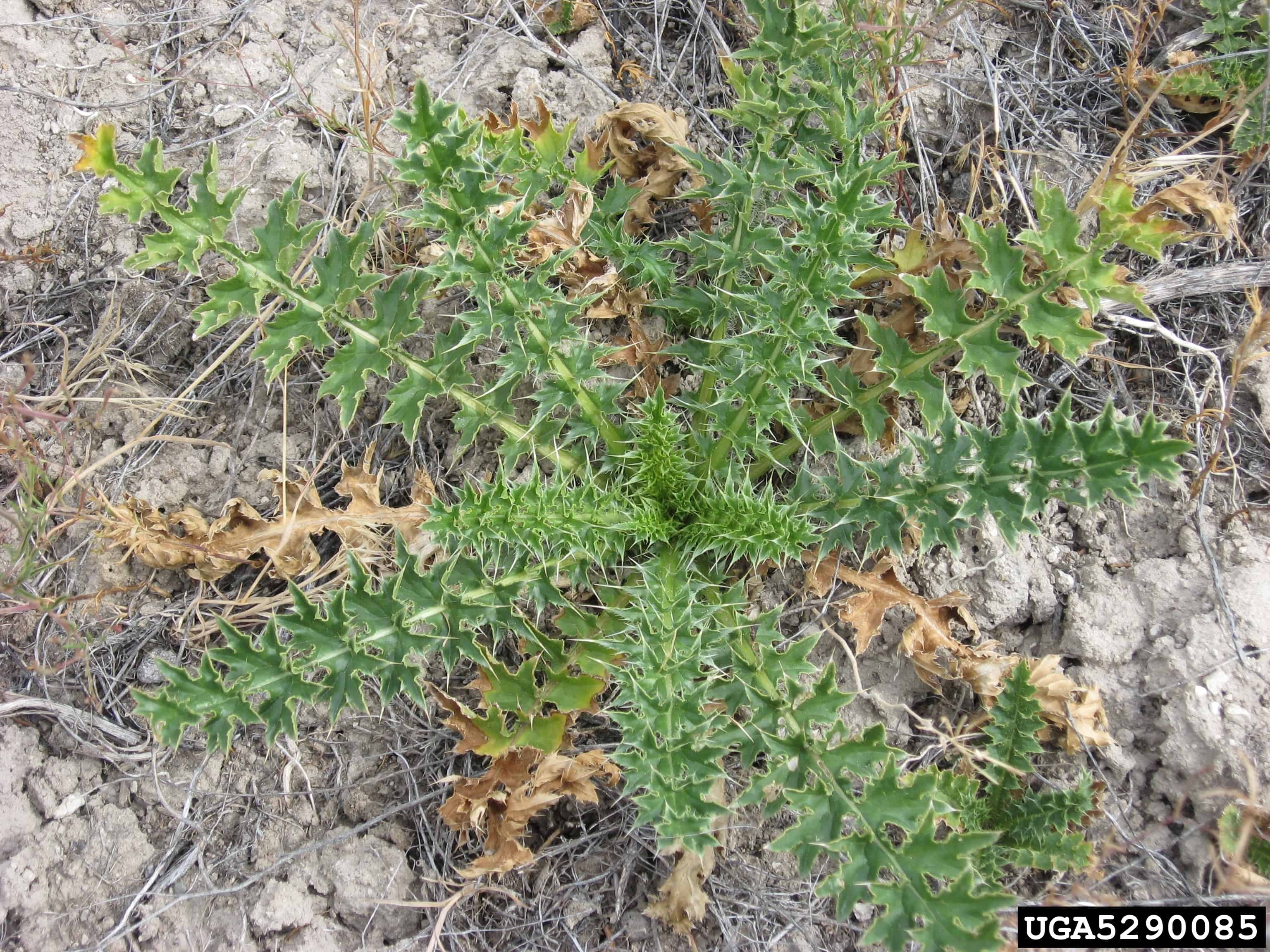
C. acanthoides was first recorded on the east coast of North America in the late 19th century, possibly arriving in ship’s ballast (Desrochers et al. 1988). It may form dense stands on disturbed sites and invade native and restored grasslands (BC MAFF 2002).
.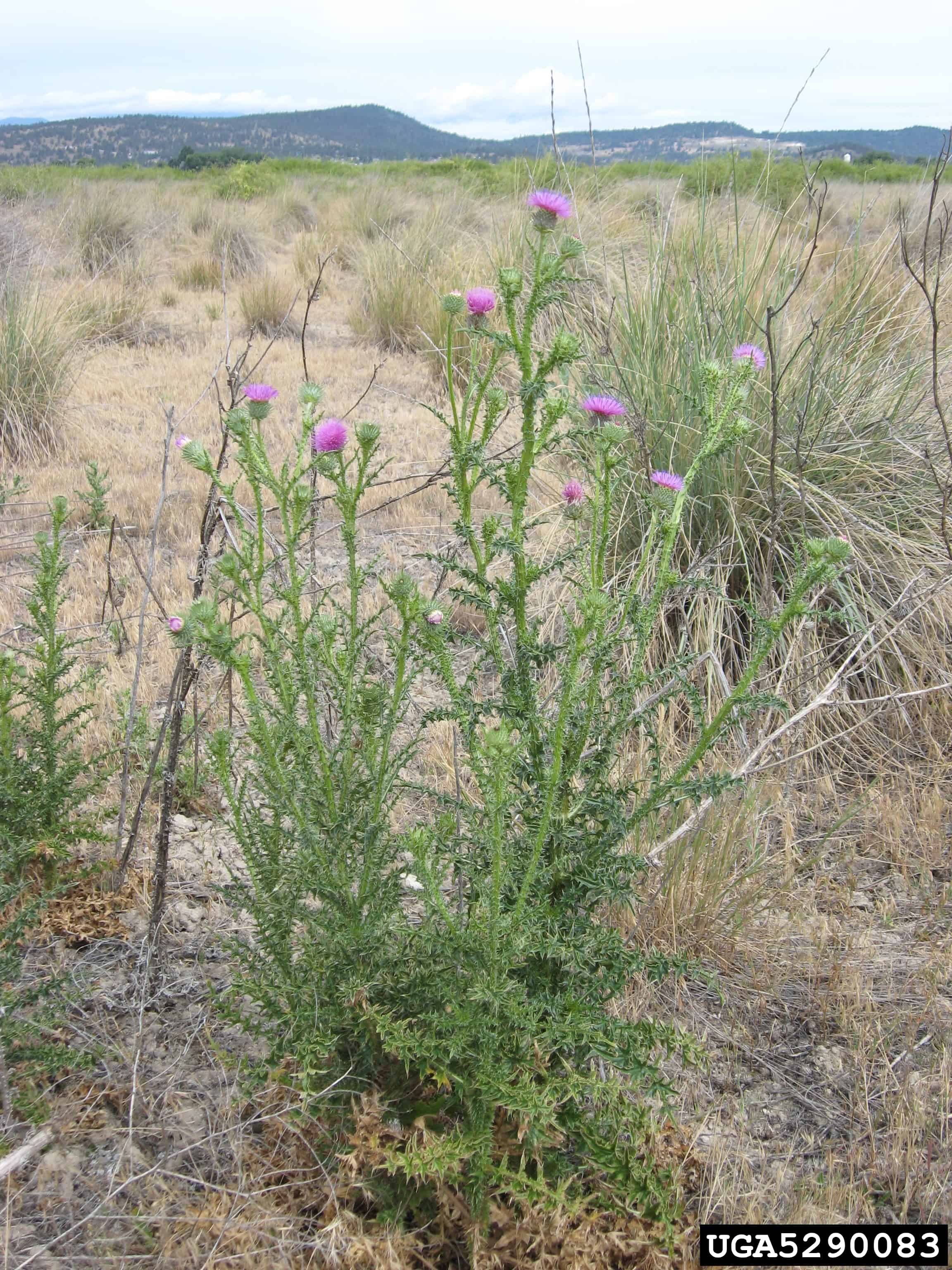
Carduus acanthoides plant (Todd Pfeiffer, Klamath County Weed Control, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
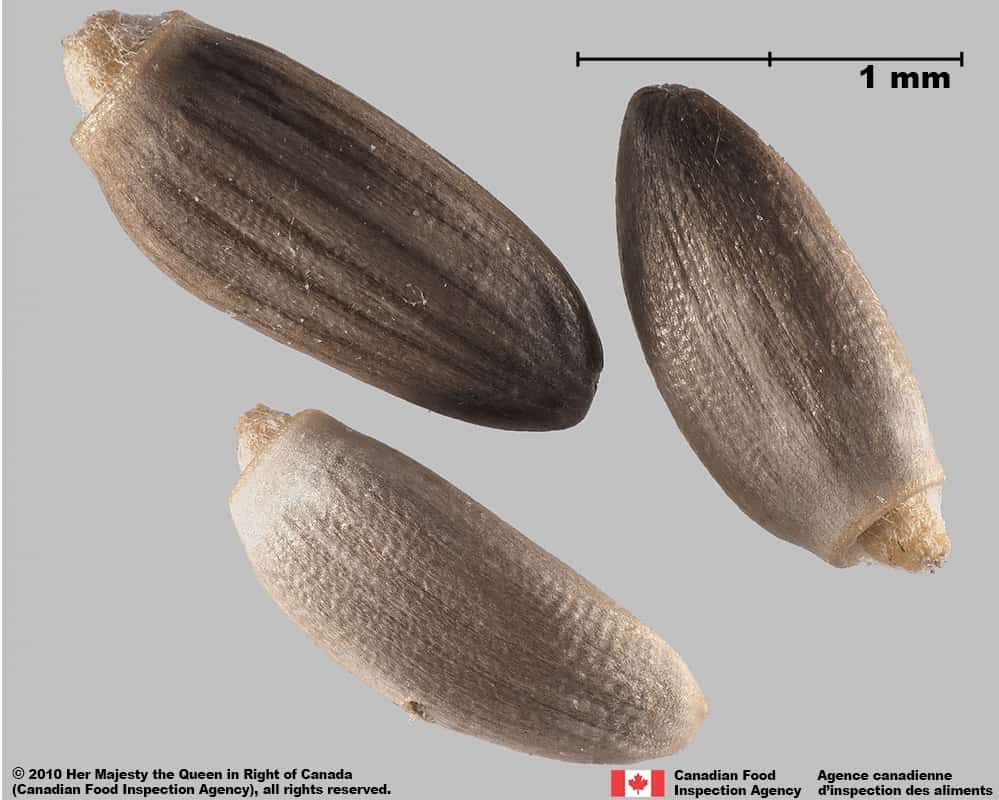
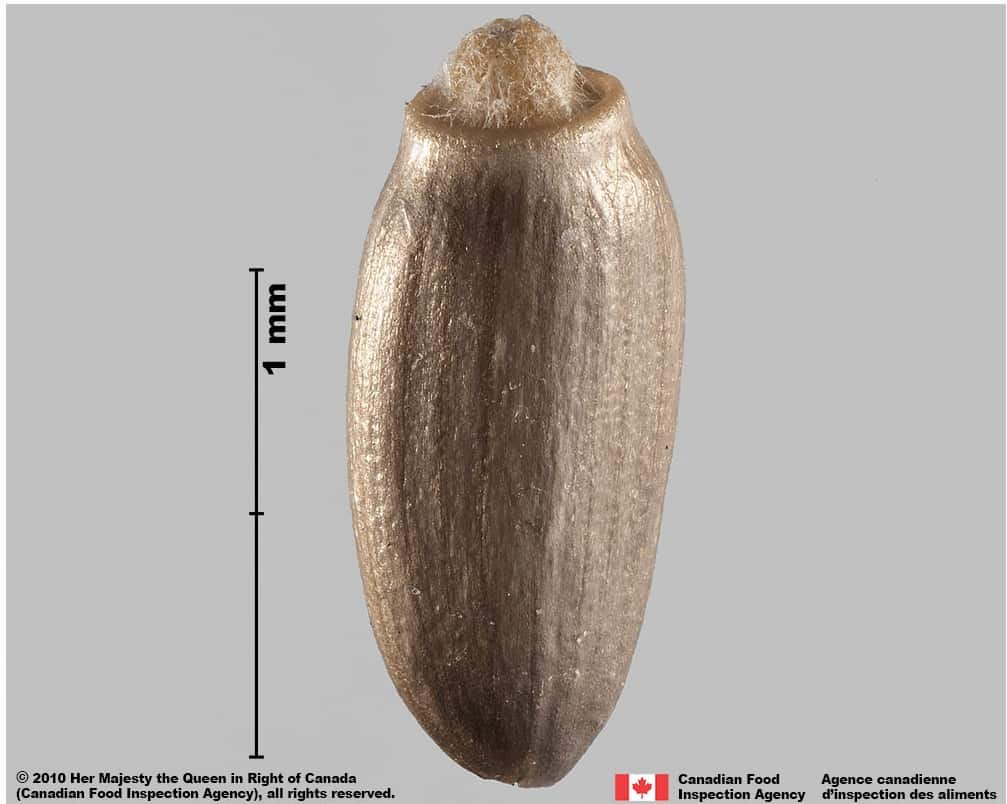
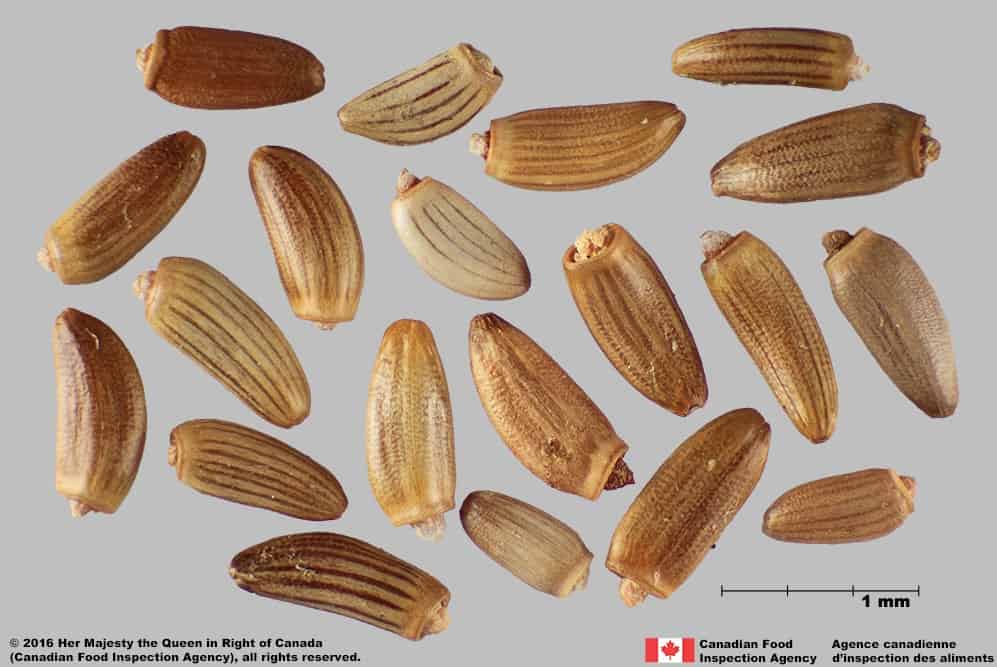
Achene
Size
- Achene length*: 2.4 – 3.5 mm; width: 1.2 – 1.4 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 achenes in a normal range of this species using specimen measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Achene is elongated oval or oblong shaped, straight or slightly curved in long side view
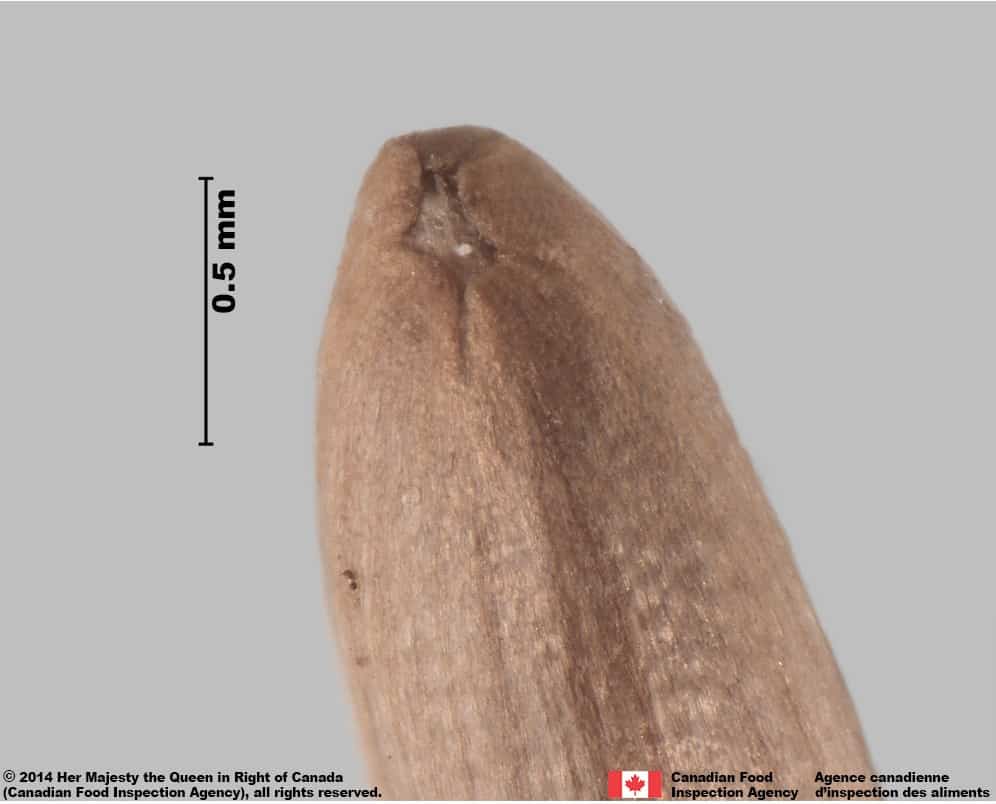
- One end narrow and rounded, the other wider and truncate
- Generally compressed laterally
Surface Texture
- Achene surface is roughened by transverse wrinkles
Colour
- Achene may be light grey, light brown, brown, or orange brown
- Often pink, grey or light brown at achene’s narrow end
- Surface pattern of dark coloured longitudinal stripes
Other Features
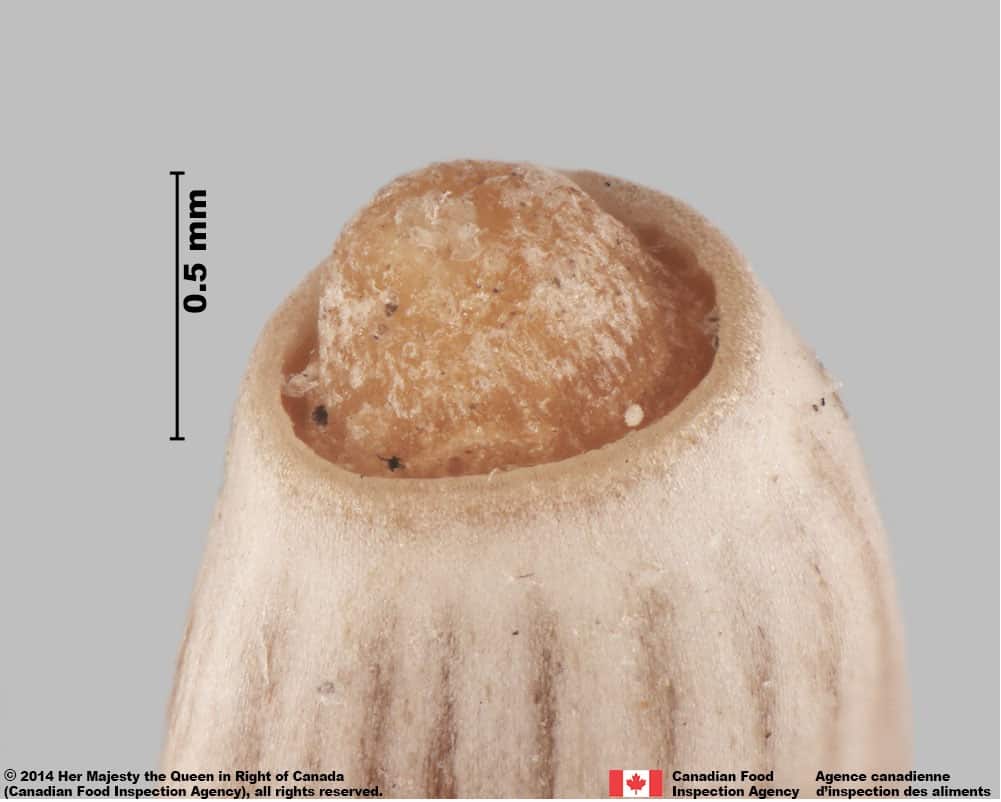
Pappus
- A thin, white, hair-like pappus up to 1.5 cm (eFloras 2020) may be attached to the achene
- Pappus is removed during processing
Achene end with pappus
- The style peg at the pappus end of achene is generally short and thick
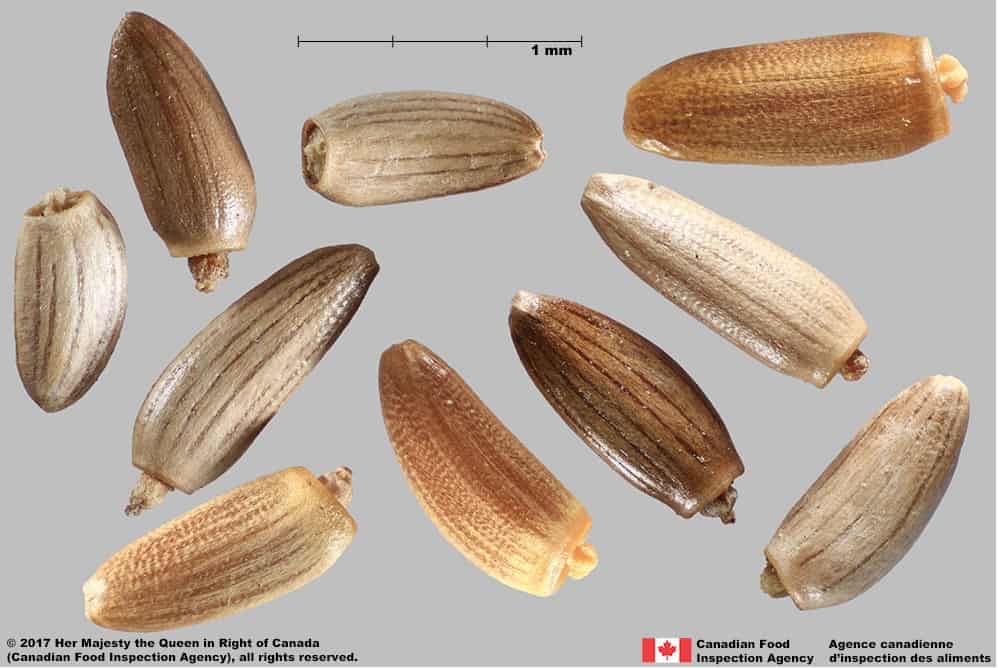

Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) achenes
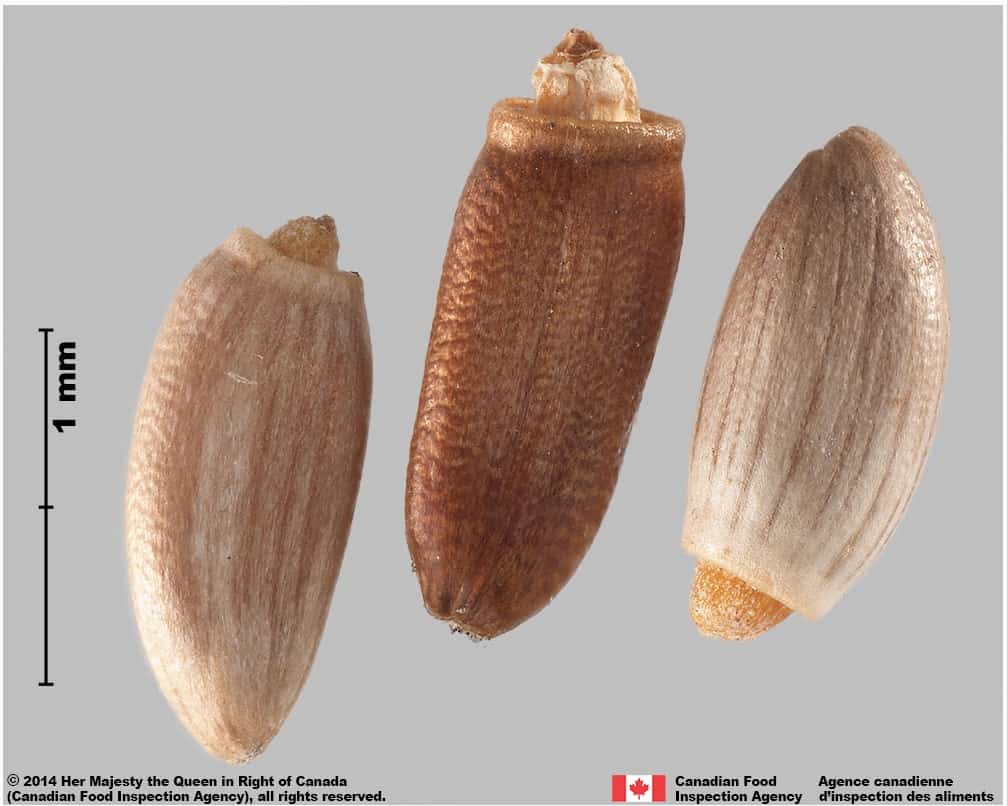






-
Seed
Size
- Seed similar to achene size
Shape
- Seed is oblong
Surface Texture
- Seed is smooth
Colour
- Seed is light yellow
Other Features
- Seed coat thin, whitish coloured, adhering to the fruit wall
-
Embryo
Size
Embryo fills the seed
Shape
- Embryo is spatulate, axial position
Endosperm
- Endosperm is absent, nutritive tissue stored in the cotyledons
Other Features
- Cotyledons are soft-textured
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
The achenes of Carduus acanthoides look similar to other Carduus species, they are distinguished by the light grey colour, wrinkled surface, and the grey, pink or brown narrow end.
Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Flowers/Inflorescence
- Flowers are tubular and purple, rarely white or cream coloured (Desrochers et al. 1988)
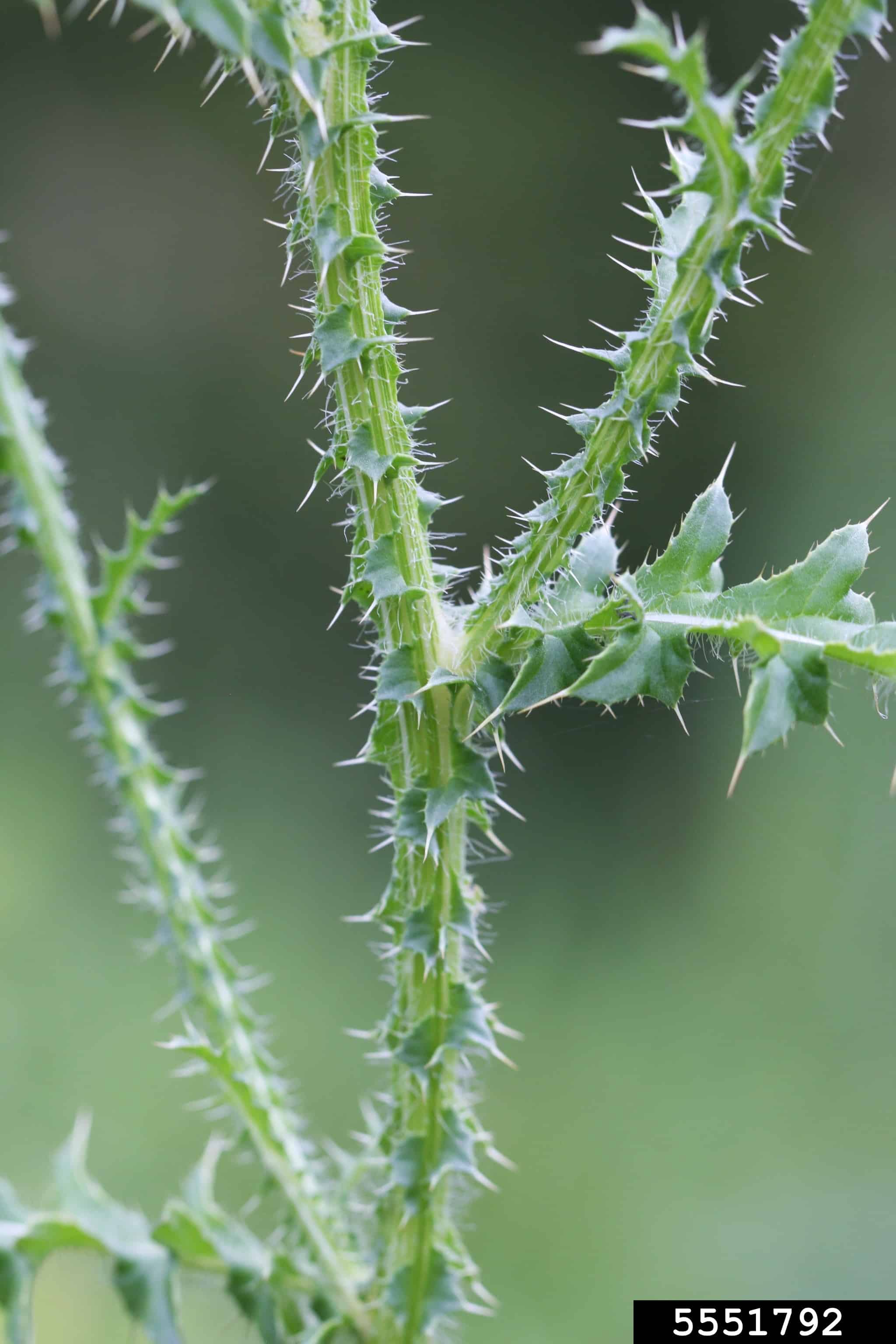
Vegetative Features
- Mature flower heads are round and held upright on the stem (Desrochers et al. 1988) and are 10.0 – 20.0 mm diameter (eFloras 2020)
- The involucral bracts are smooth or with cobweb hairs, the tips curve away from the flower head (eFloras 2020).

Carduus acanthoides flowers (Todd Pfeiffer, Klamath County Weed Control, Bugwood.org)




Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
Carduus nutans L. (nodding thistle)
C. nutans achenes are generally narrower (width*: 0.9 – 1.5), the surface is smooth with a varnish-like coating and a yellow narrow end. C. acanthoides has a brown or pink narrow end and a wrinkled surface.
Immature C. nutans achenes may have a wrinkled surface similar to C. acanthoides, but the achene will be yellowish coloured, especially at the narrow end.
*Note: minimum and maximum of 20 achenes in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces

Carduus nutans
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) achenes
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) achenes
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) achenes
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) achene
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) top of achene
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Carduus acanthoides

Carduus acanthoides
Asteraceae
Spiny plumeless thistle (Carduus acanthoides) bottom of achene
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans
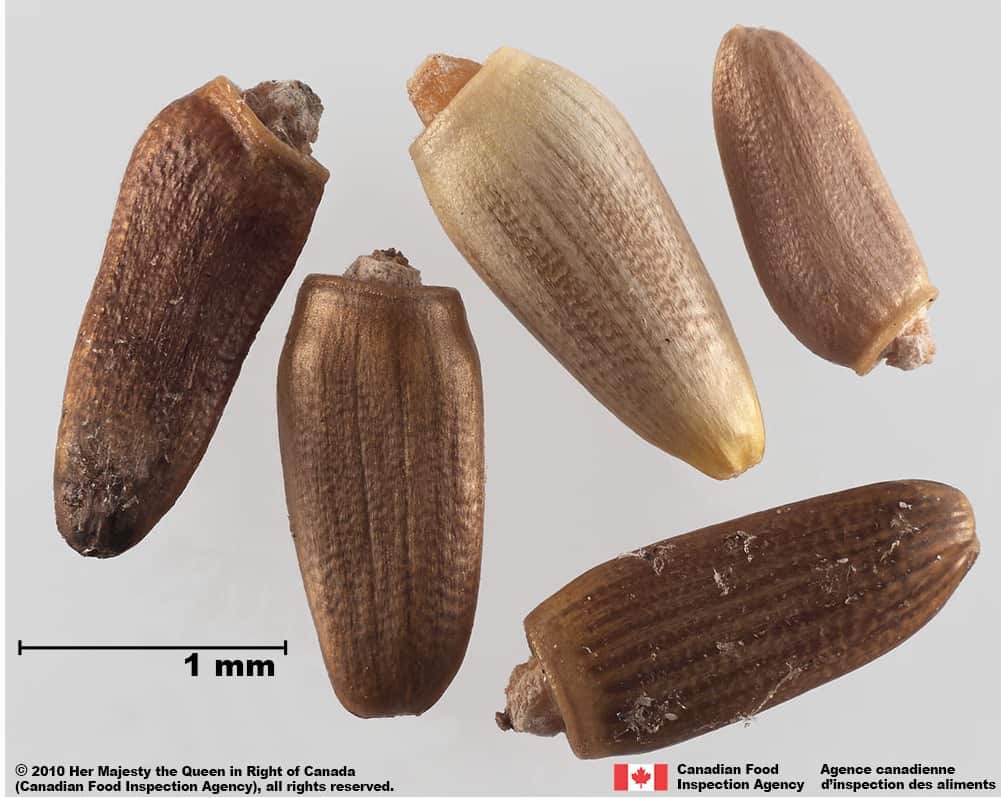

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans
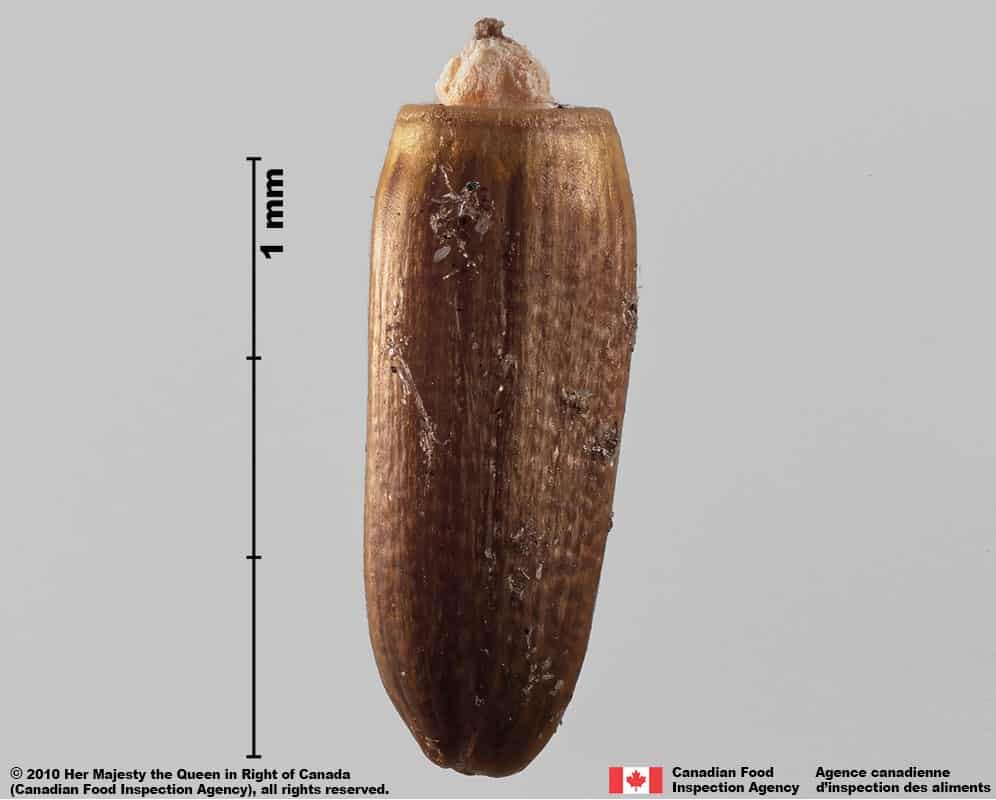

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) achene
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans
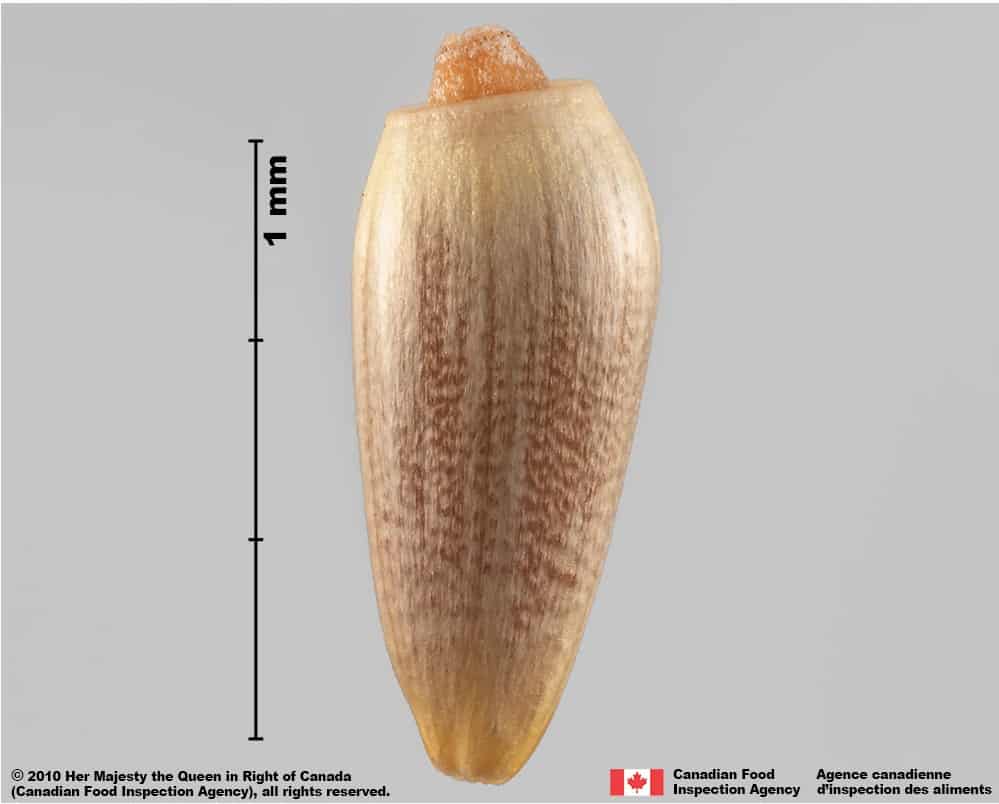

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) achene
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
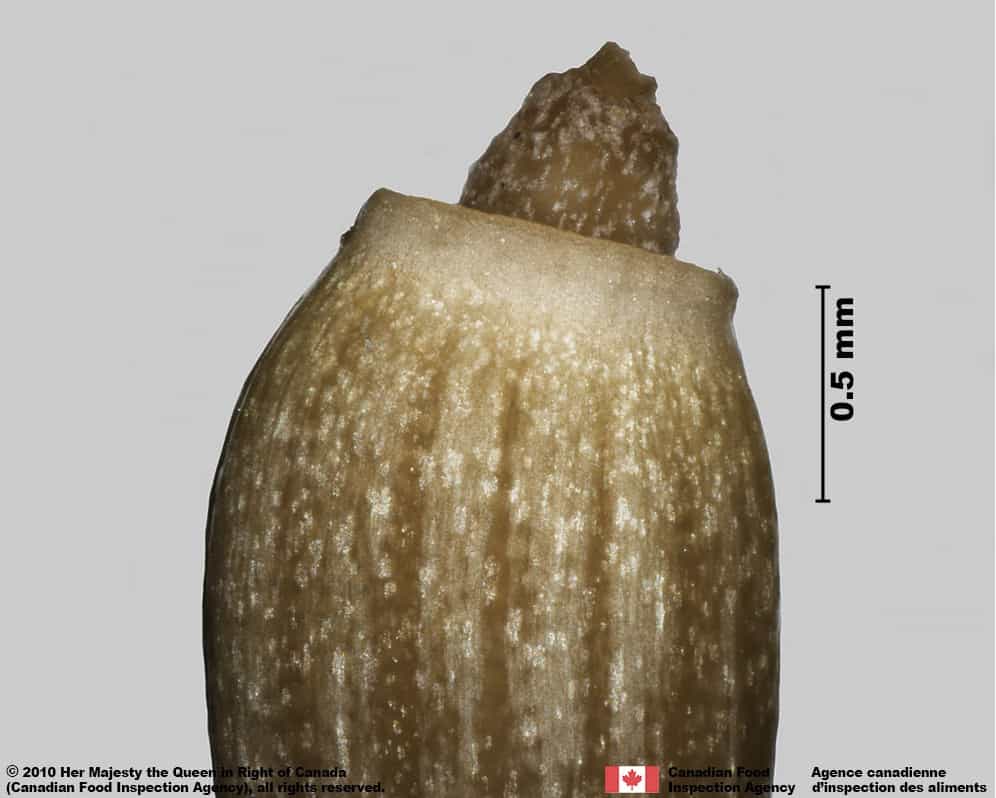
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) top of achene
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Carduus nutans

Carduus nutans
Asteraceae
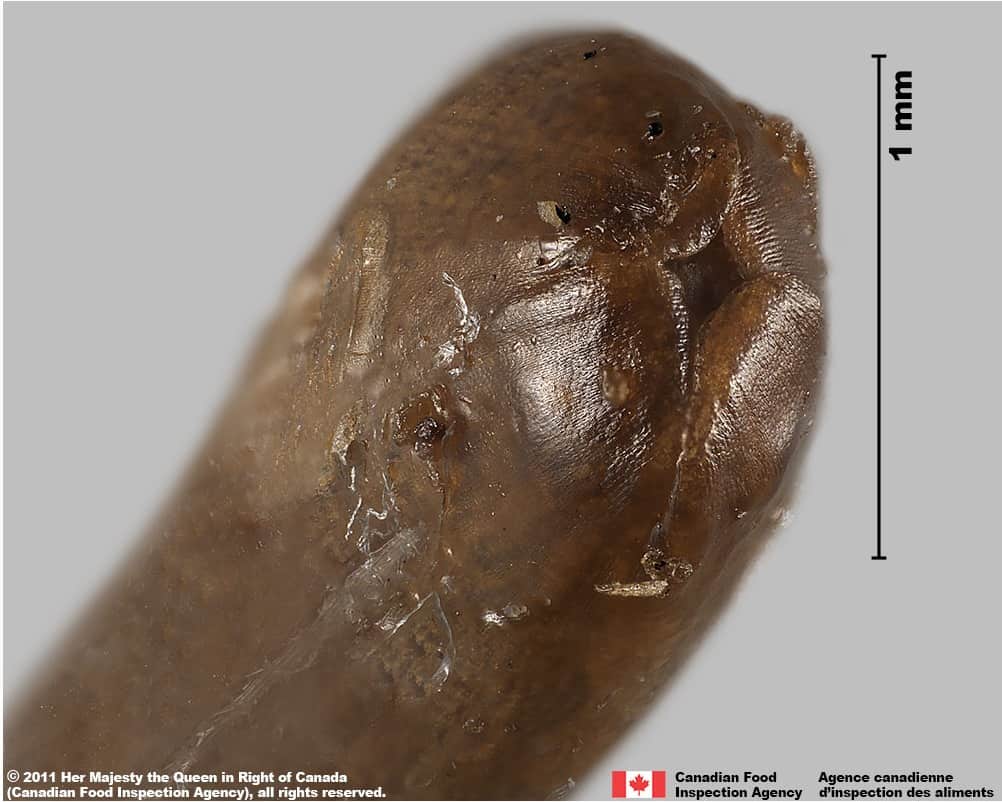
Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) bottom of achene
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA). 2019. AOSA Rules For Testing Seeds. Volume 3: Uniform Classification of Weed and Crop Seeds. AOSA, Washington, DC.
British Columbia Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Fisheries (BC MAFF). 2002. Guide to weeds in British Columbia. Open Learning Agency, Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada. 195 pp.
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed October 15, 2020..
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
Desrochers, A. M., Bain, J. F. and Warwick, S. I. 1988. The Biology of Canadian weeds. 89. Carduus nutans L. and Carduus acanthoides L. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 68: 1053-1068.
eFloras. 2020. Electronic Floras. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louise, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA., http://www.efloras.org Accessed August 19, 2020.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. http://beta.floranorthamerica.org. Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/3114643 Accessed December 29, 2022
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide. https://www.idseed.org/authors/details/method_for_seed_size_measurement.html
Kartesz, J.T. 2015. The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). North American Plant Atlas. Chapel Hill, N.C. http://www.bonap.net/napa Accessed October 13, 2020.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2022. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysimple.aspx Accessed October 13, 2020.