Fallopia convolvulus
Explore More :
Explore plus :
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- Quarantine lists of countries e.g. Mexico *may be updated without notice
Regulation Notes:
On quarantine lists of countries e.g. Mexico*.
*Quarantine lists of countries may be updated without notice.
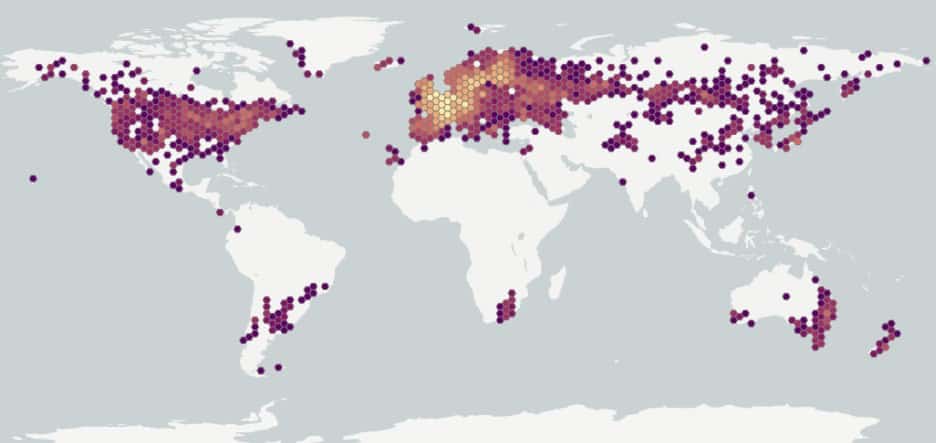
Distribution :
Répartition :
This species is native to northern Africa and Eurasia. Introduced in South Africa, Australasia, Japan, and North and South America (USDA-ARS 2017). Widespread in the United States (USDA-NRCS 2017).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Wild buckwheat grows in cultivated fields and waste places, including old fields, fencerows, shores, railway lines, roadsides, and disturbed areas (Darbyshire 2003; FNA 2017).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Achene, may be enclosed in a perianth
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
This species is an aggressive weed of crops and prolific seed producer. Vines entangle crop plants causing lodging and making harvesting and tillage operations difficult (Hume et al. 1983; FNA 2017).
.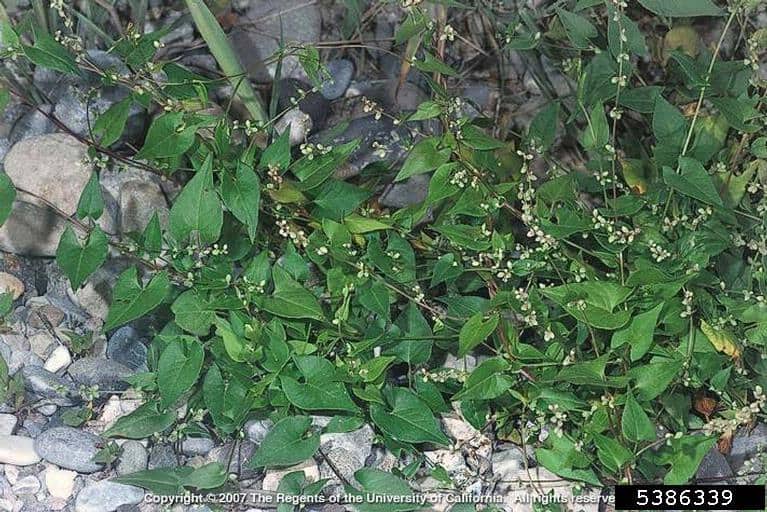
Fallopia convolvulus plant (Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
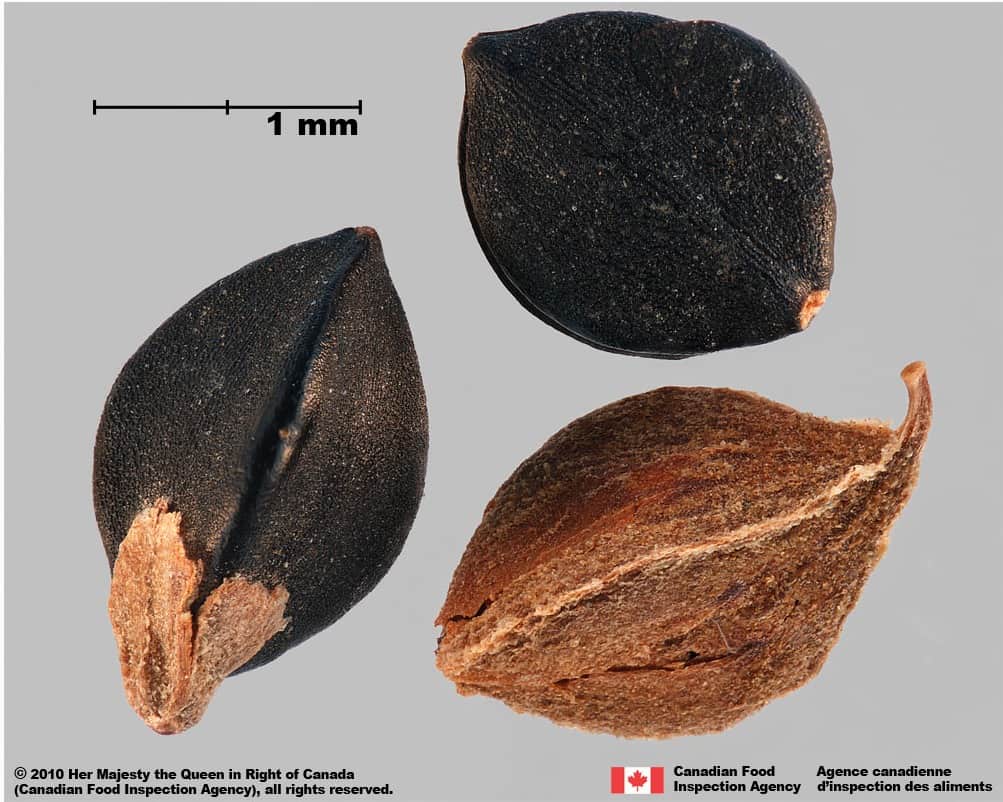
Perianth
Size
- Perianth length: 3.3 – 4.5 mm (average: 4.0 mm); width: 2.1 – 2.7 mm (average 2.4 mm)
Colour
- Perianth is reddish-brown
Other Features
- The perianth is roughened and papery; divided into lobes that overlap around the achene
- A portion of the perianth may remain at one end of the achene if it is removed
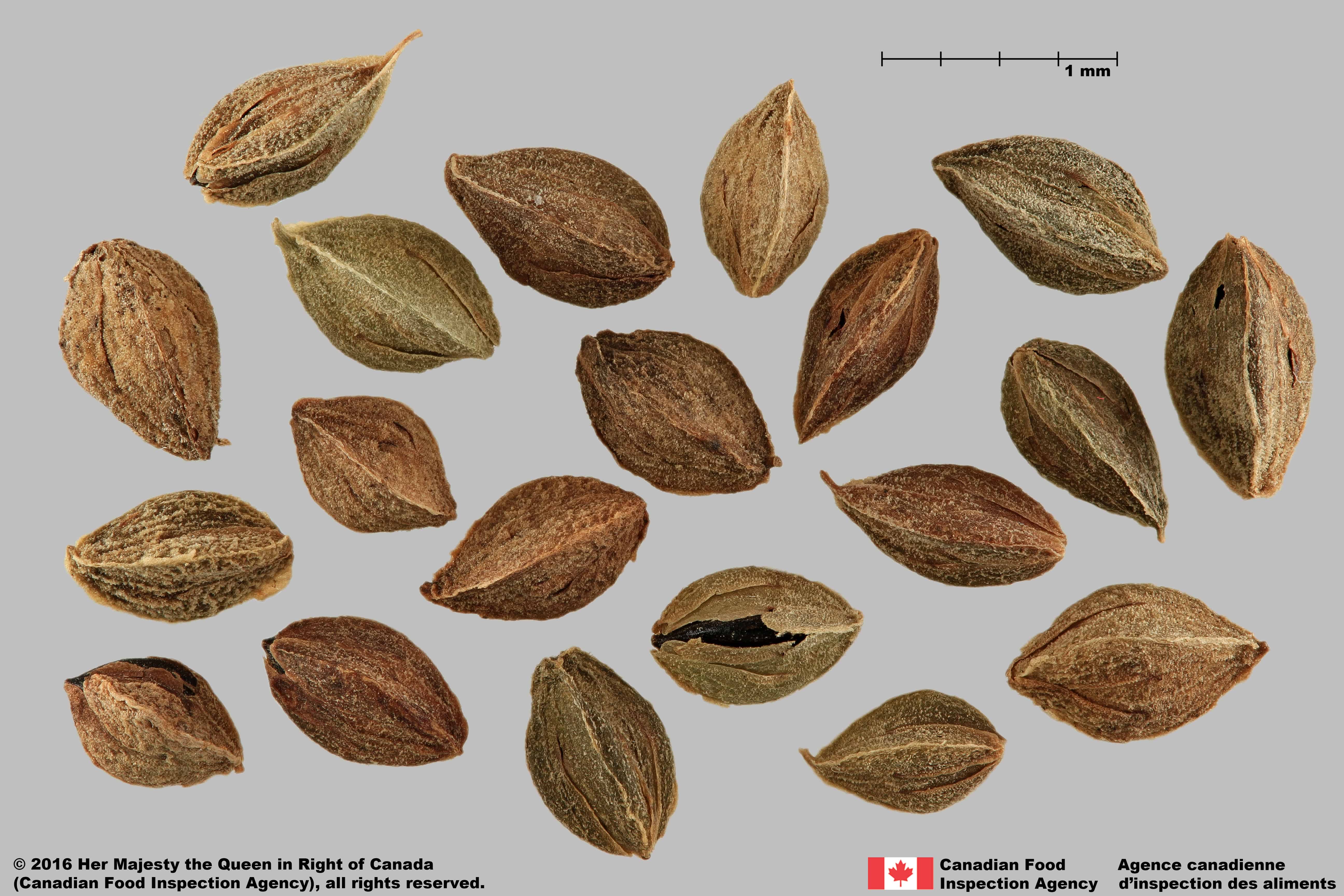

Fallopia convolvulus perianths




-
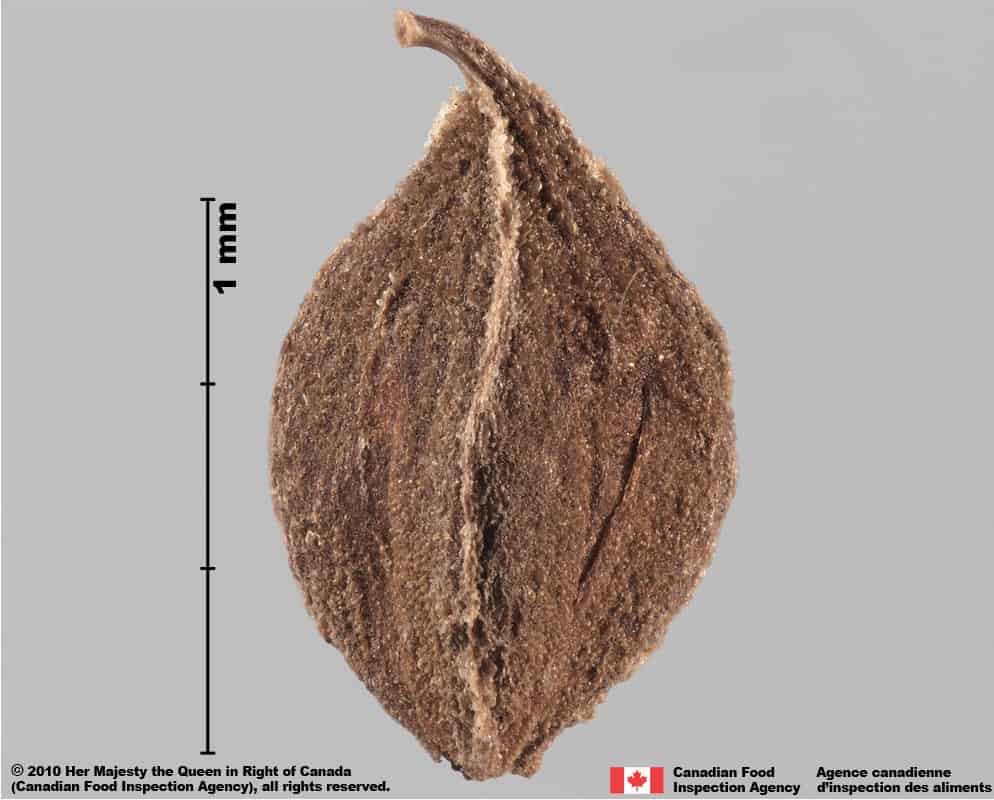
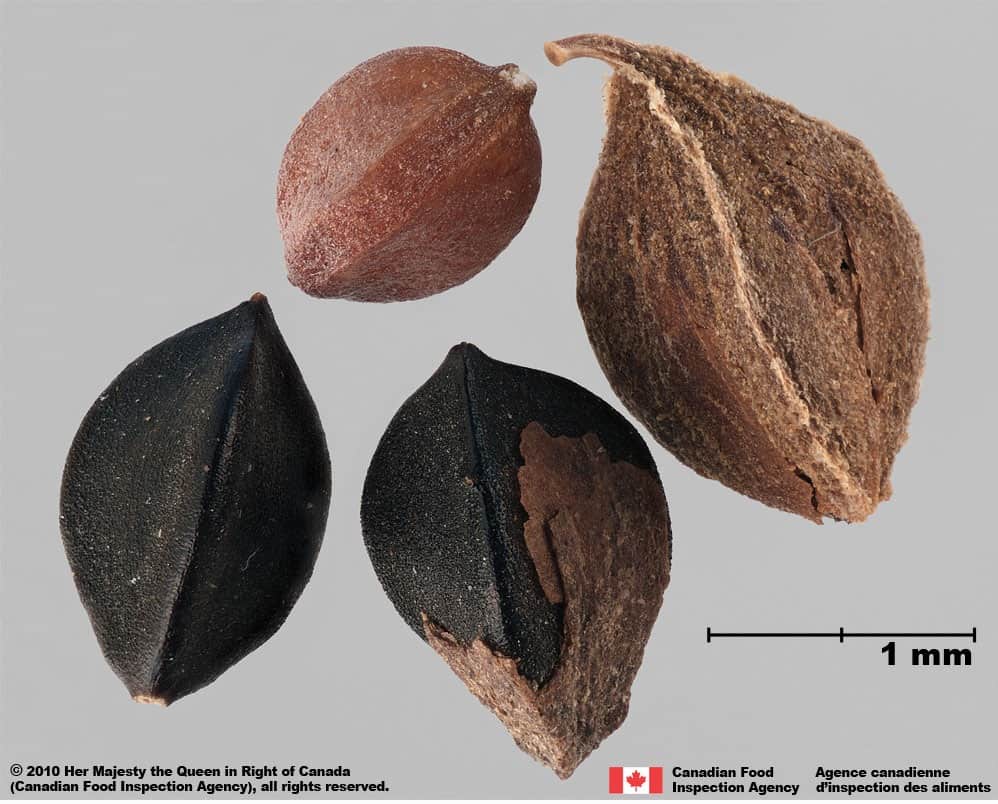
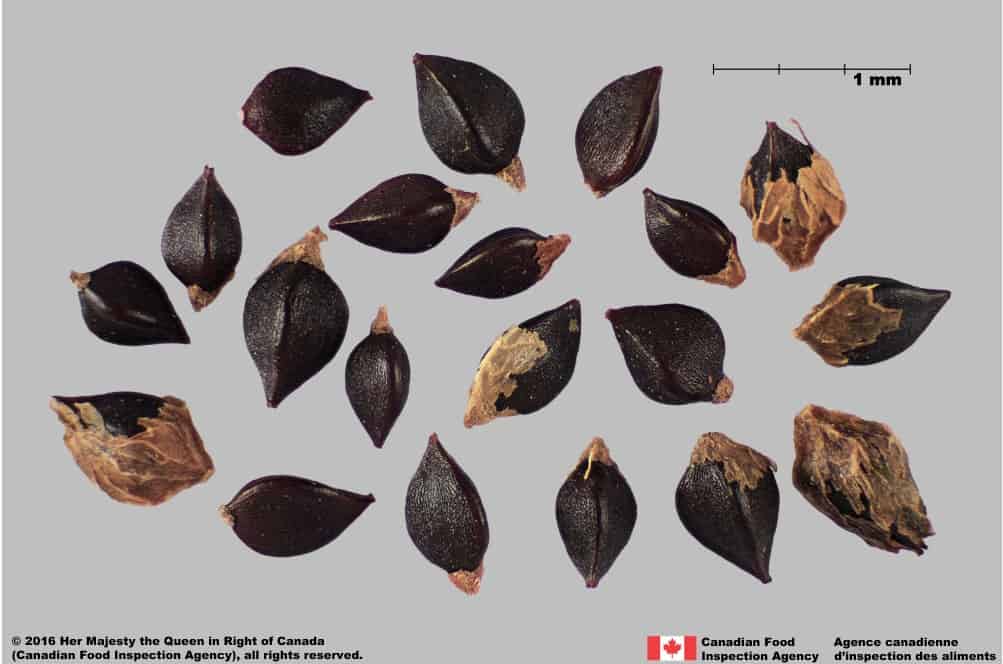
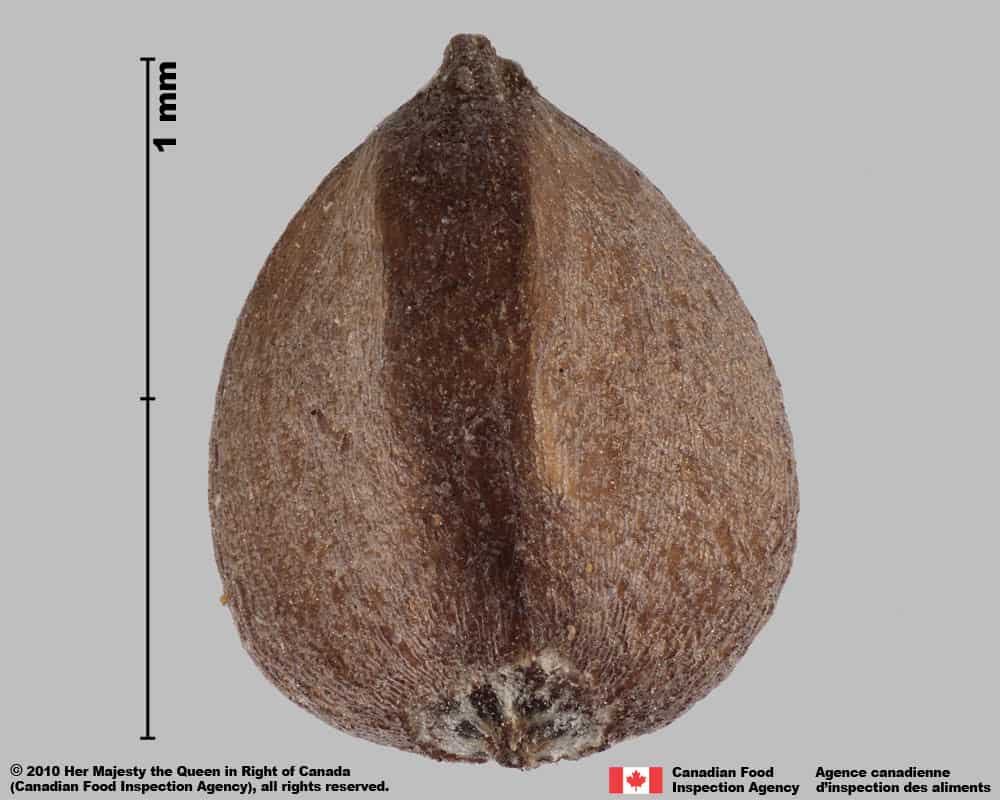
Achene
Size
- Achene length: 3.0 – 4.1 mm (average: 3.5 mm); width: 1.8 – 2.4 mm (average 2.0 mm)
Shape
- Achene is egg-shaped in two dimensional outline and is strongly trigonous with slightly concaved sides
Surface Texture
- Achene surface is roughened with wrinkles on the flat faces and smooth on the edges
Colour
- Achene is dull and solid black
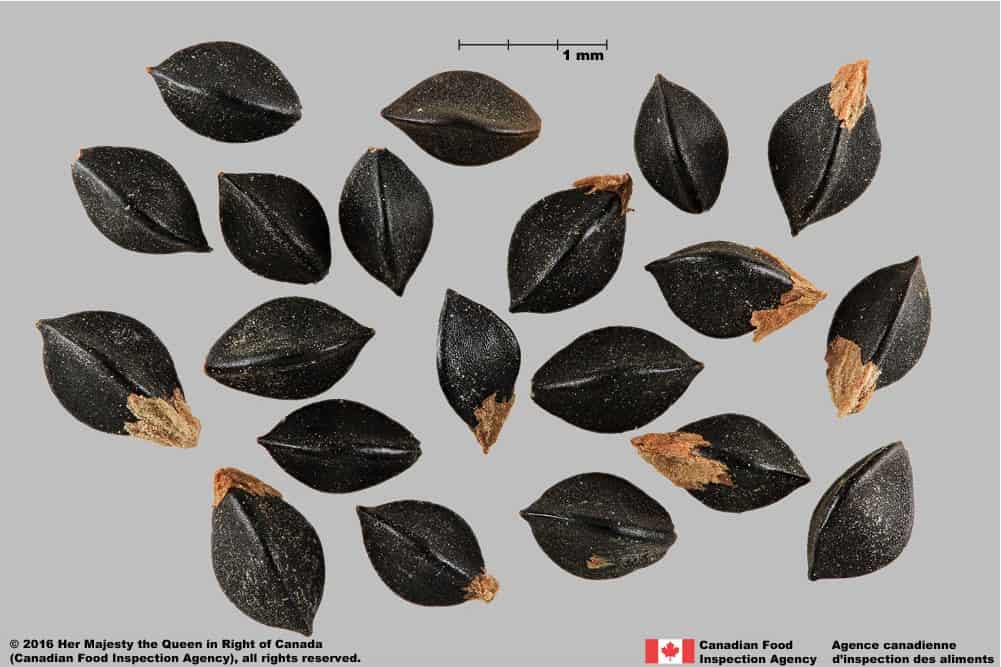

Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achenes
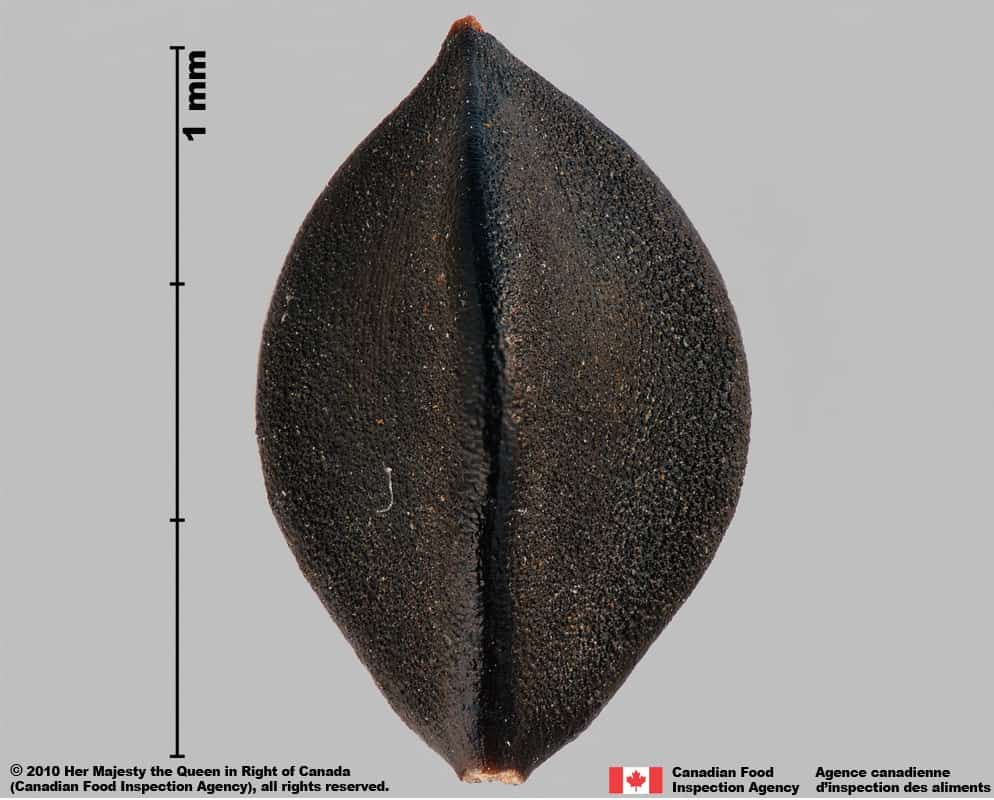




Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
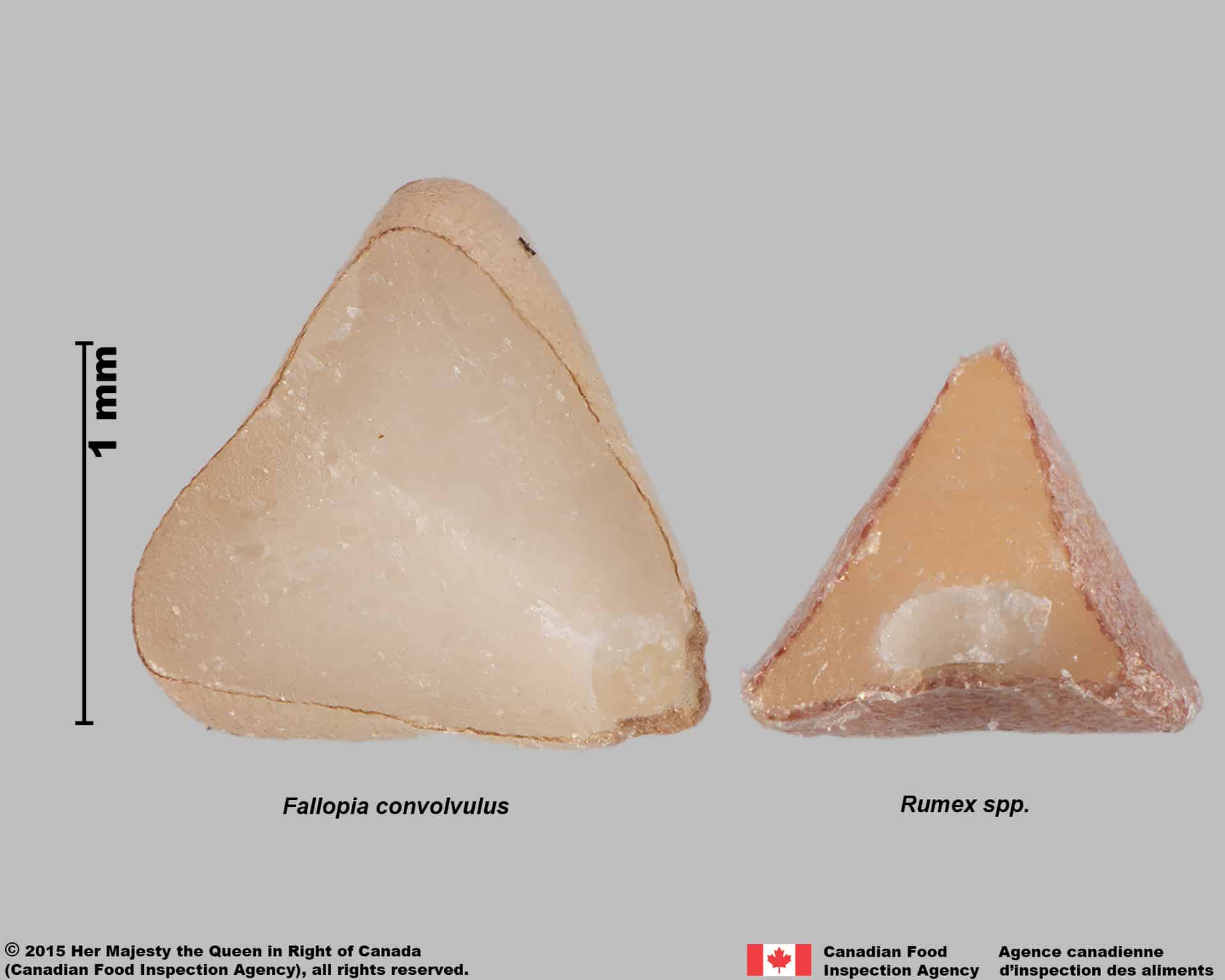
Fallopia convolvulus and Rumex spp. comparison

Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
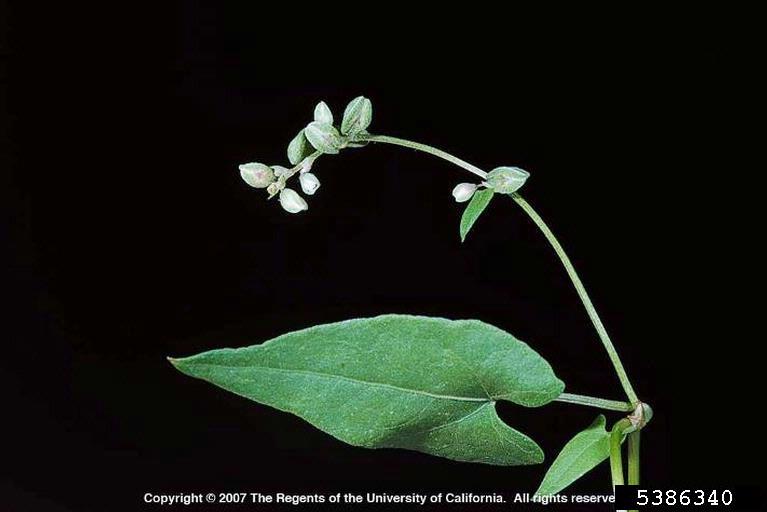

Fallopia convolvulus flower (Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org)




Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
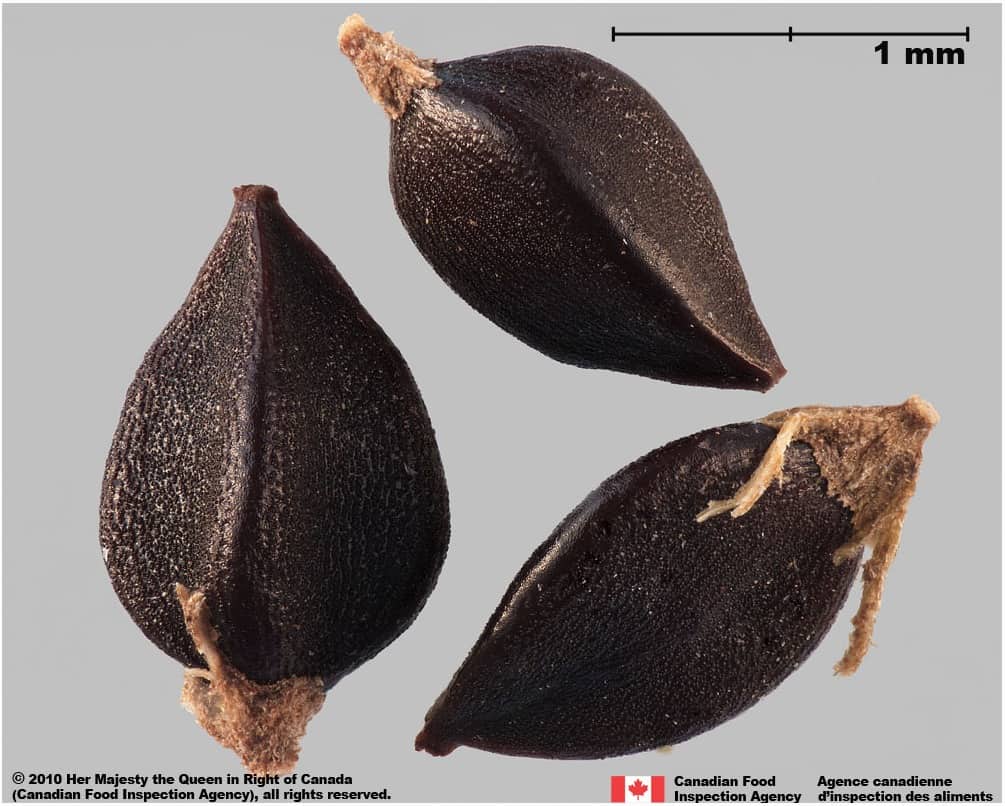
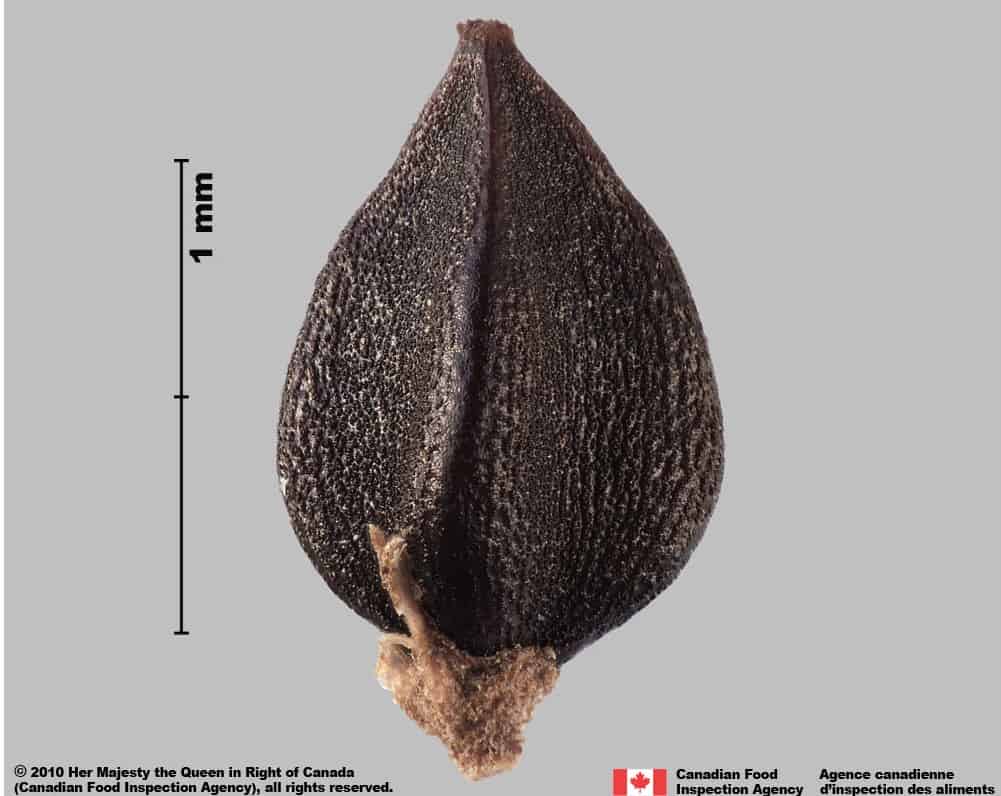
Polygonum aviculare (prostrate knotweed)
Polygonum aviculare achenes are a similar trigonous shape, rough surface texture and black colour as wild buckwheat.
Polygonum aviculare achenes are generally smaller (average length: 2.4 mm; average width: 1.3 mm), an ovate shape, and have roughened edges. Seeds are similar to wild buckwheat seeds.
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces

Polygonum aviculare
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achenes
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Fallopia convolvulus perianths
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achenes and perianth
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achenes, seed and perianth
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achene with perianth
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Wild buckwheat (Fallopia convolvulus) achene
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
Fallopia convolvulus (wild buckwheat) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Fallopia convolvulus

Fallopia convolvulus
Polygonaceae
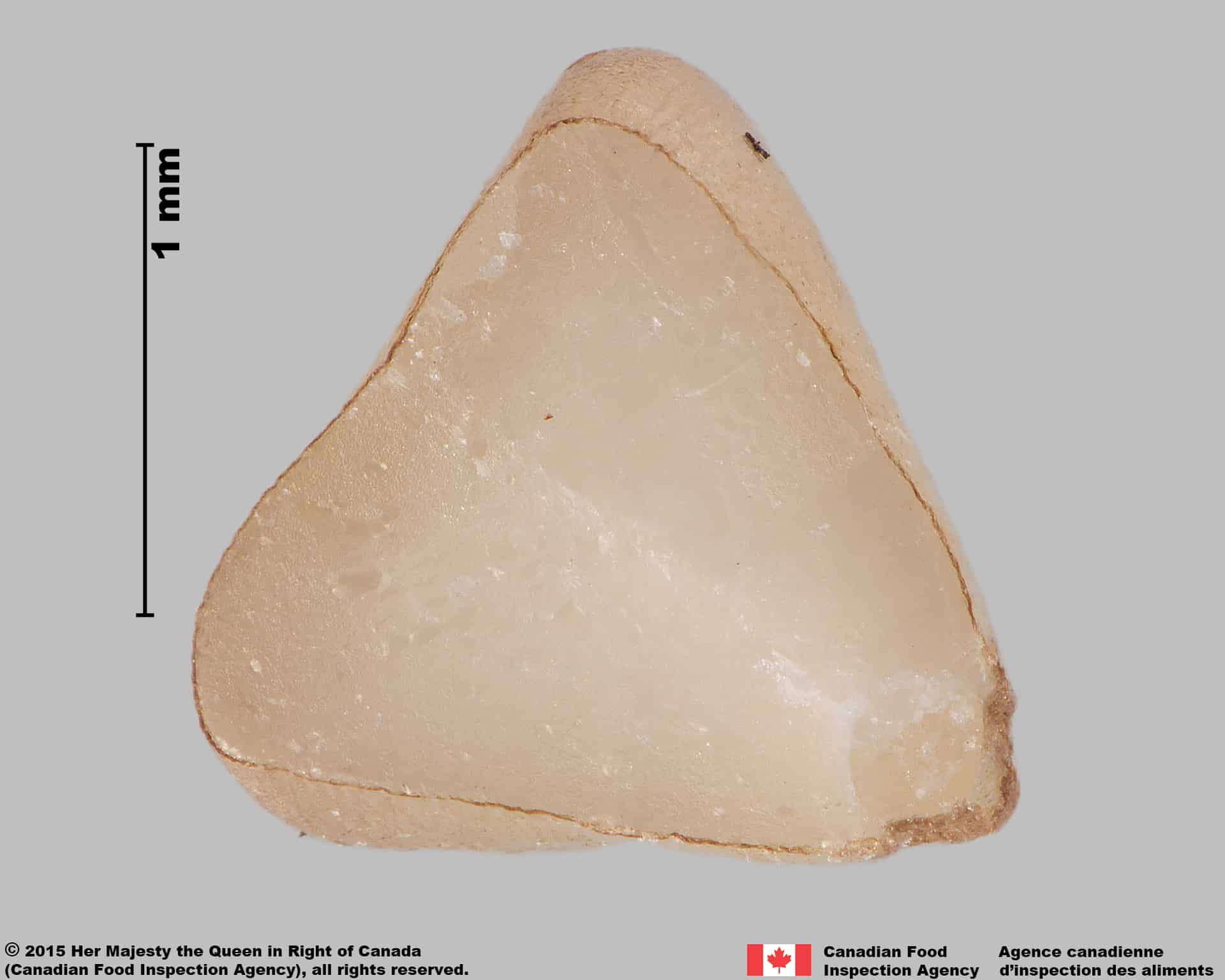
Fallopia convolvulus seed, cross section
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Polygonum aviculare

Polygonum aviculare
Polygonaceae
Prostrate knotweed (Polygonum aviculare) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Polygonum aviculare

Polygonum aviculare
Polygonaceae
Prostrate knotweed (Polygonum aviculare) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Polygonum aviculare

Polygonum aviculare
Polygonaceae
Prostrate knotweed (Polygonum aviculare) achene
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. http://beta.floranorthamerica.org. Accessed April 25, 2017.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/6391461 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Hume, L., Martinez, J. and Best, K. 1983. The biology of Canadian weeds. 60. Polygonum convolvulus L. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 63: 959-971.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2017. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysearch Accessed April 25, 2017.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2017. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. https://plants.usda.gov/home Accessed April 25, 2017.