Galium verrucosum
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 3: Secondary Noxious Weed Seeds
Regulation Notes:
Distribution :
Répartition :
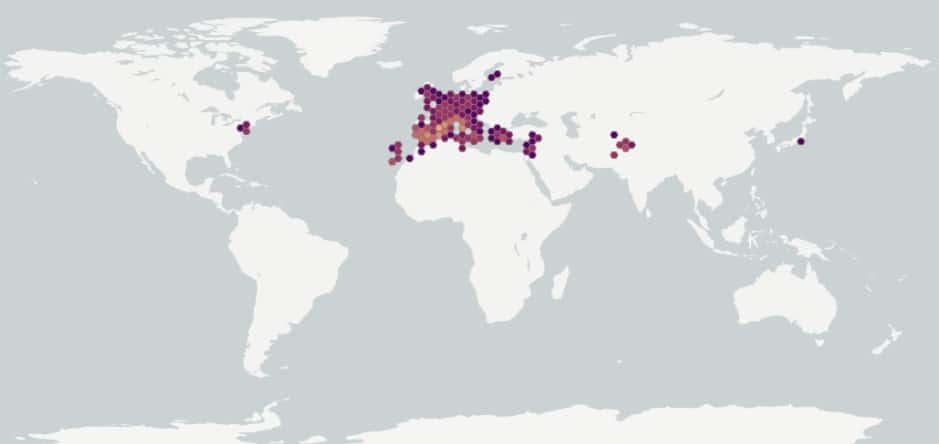
Native to southern Europe and the Mediterranean (Tutin et al. 1976; Hanf 1983). Naturalized in central Europe (Tutin et al. 1976). In the United States it has been introduced in Michigan (USDA-NRCS 2022). The species is not present in Canada (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
This species grows in cultivated fields, in scrub and degraded grassland (Hanf 1983).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Schizocarp, divided into 2 mericarps
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Galium verrucosum seed has been introduced into Great Britain as a contaminant in imported bird food (Hanson and Mason 1985). Historically, it was recorded in Zea mays L. subsp. mays (corn) fields in Great Britain (Lindley 1835).
.Identification
Identification
-
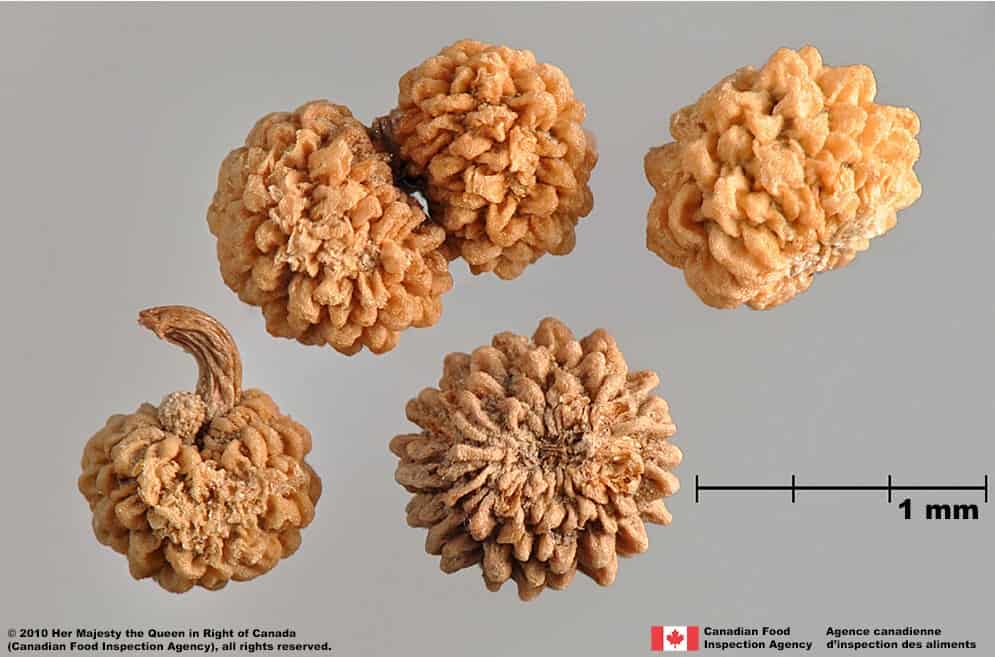
Mericarp
Size
- Mericarp length*: 2.7 – 4.6 mm; width: 2.4 – 3.7 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 mericarps in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Mericarp is round, compressed at the attachment scar and looks D-shaped in 3D
Surface Texture
- Mericarp surface is covered with warty tubercles
- Tubercles have pointed tips and an irregular base
Colour
- Mericarp is dull, straw yellow or brown coloured
- Immature fruit is green (Danin and Fragman 2016+)
Other Features
Hilum
- Hilum is located under the attachment scar on one side of the fruit
Other than hilum
- The fruit layer has a spongy consistency and can be scraped away
- Two one-seeded mericarps are joined at the hilum side and form the schizocarp
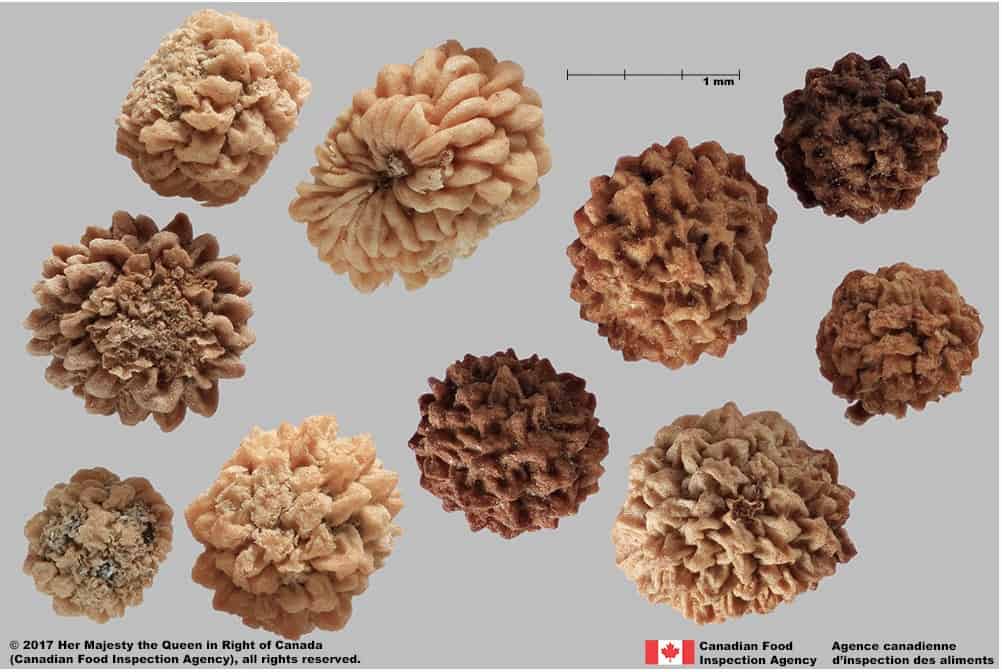

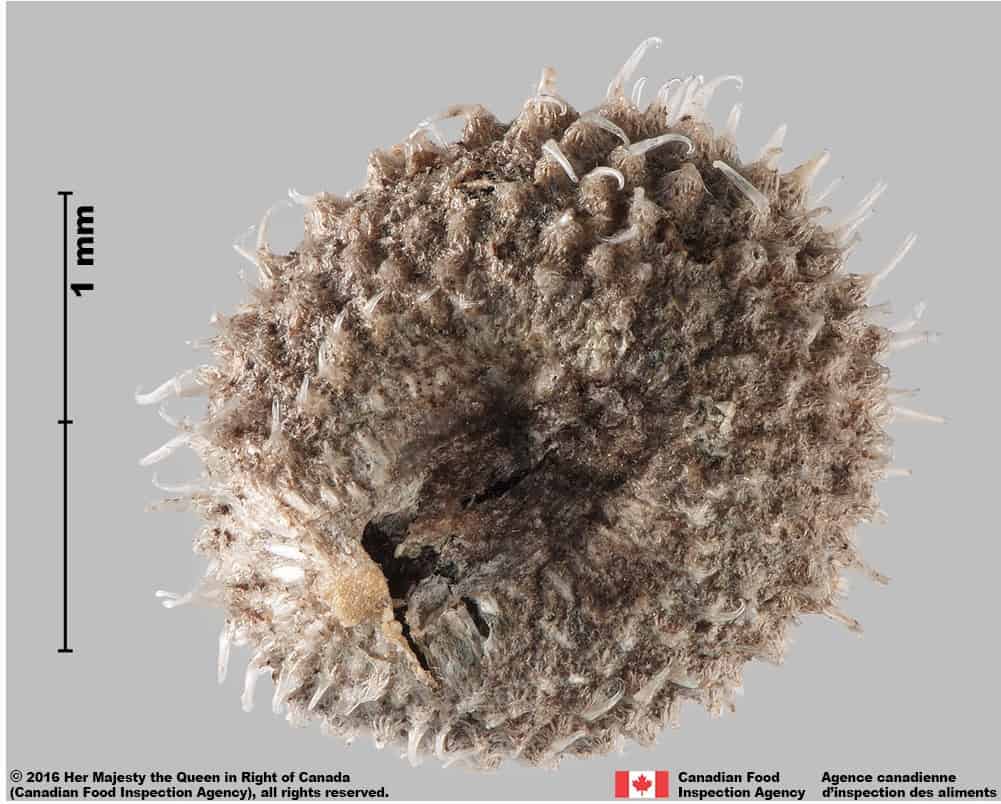
Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) fruits
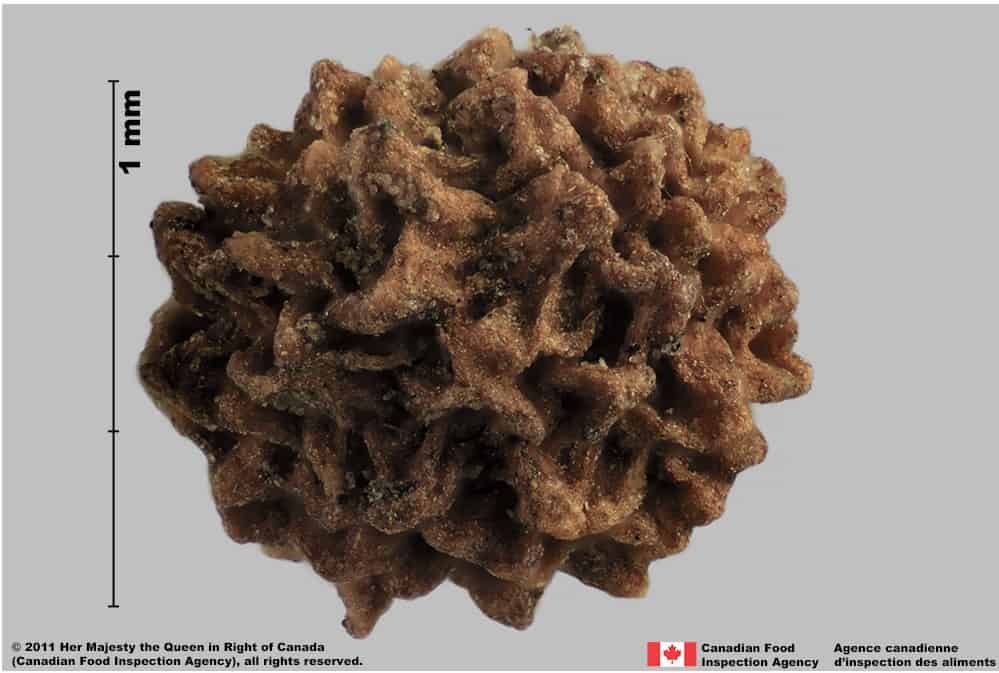




-
Seed
Size
- Seed is smaller than the mericarp
Shape
- Seed is globose
Surface Texture
- Seed surface is wrinkled
Colour
- Seed is dark reddish brown
Other Features
Hilum and Hilum area
- Hilum is in a transverse oval shaped hole underneath the attachment scar on the fruit
Other Features
- Short, linear white streaks from raphides (crystals) on the seed surface
-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo size is rudimentary
Shape
- Embryo is spatulate shaped (Martin 1946)
Endosperm
- Endosperm is hard and colourless
Other Features
- Embryo is in a peripheral position
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
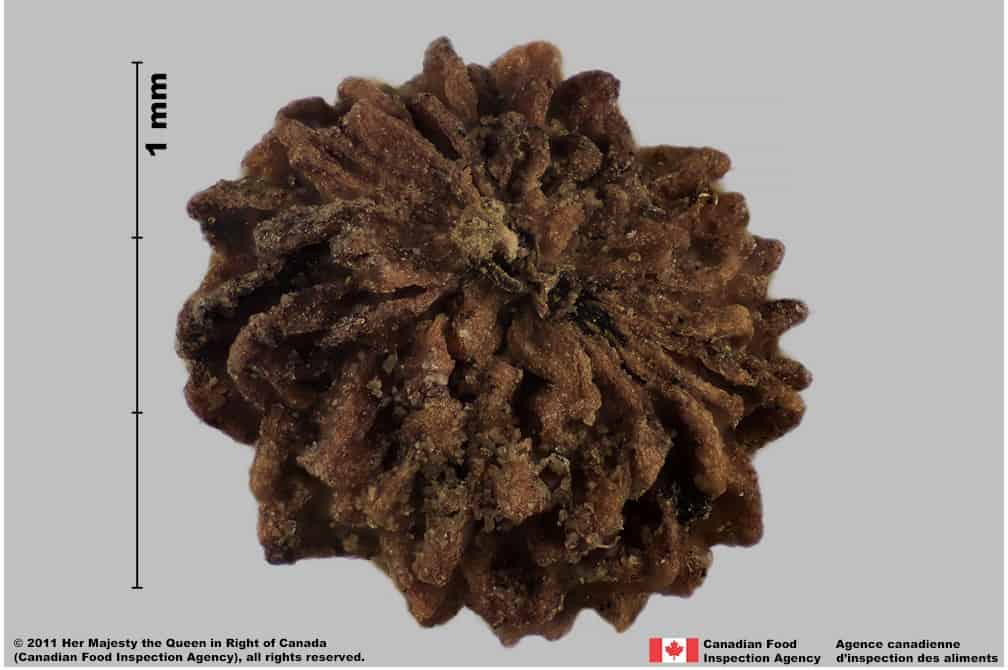
Galium verrucosum fruits are medium-sized with a distinctive warty tuberculate surface that covers the hilum. The pointed tubercles of the fruit surface make it an identifiable species without closer study.

Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) fruits




Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Flowers/Inflorescence
- Flowers are white (Danin and Fragman 2016+)
Vegetative Features
- Leaves with smooth margins are arranged in whorls of three or more (Danin and Fragman 2016+)
Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
G. aparine mericarps are generally smaller (diameter*: 1.6 – 3.2 mm) have translucent white tubercles associated with bristles and a large hole at the hilum compared to yellowish tubercles without bristles and tissue covering the hilum of G. verrucosum mericarps.
*Note: minimum and maximum of 20 mericarps in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces
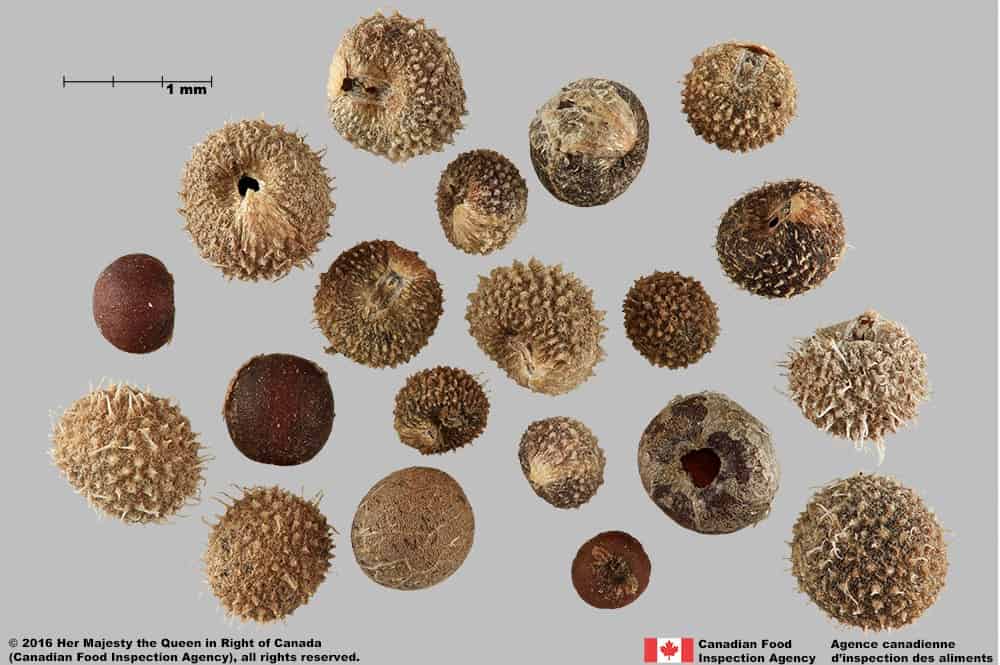

Galium aparine
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Galium verrucosum

Galium verrucosum
Rubiaceae
Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) fruits
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Galium verrucosum

Galium verrucosum
Rubiaceae
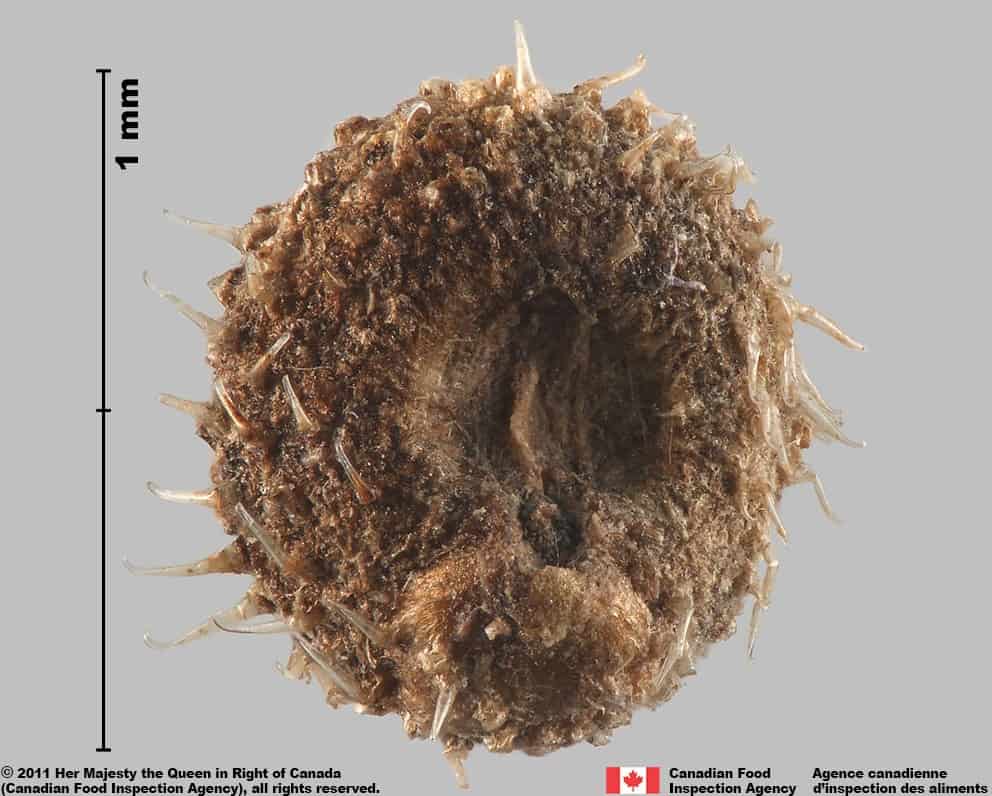
Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) schizocarp and fruits
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Galium verrucosum

Galium verrucosum
Rubiaceae
Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) fruit, inner side
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Galium verrucosum

Galium verrucosum
Rubiaceae
Warty bedstraw (Galium verrucosum) fruit, outer side
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine

Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruits
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine
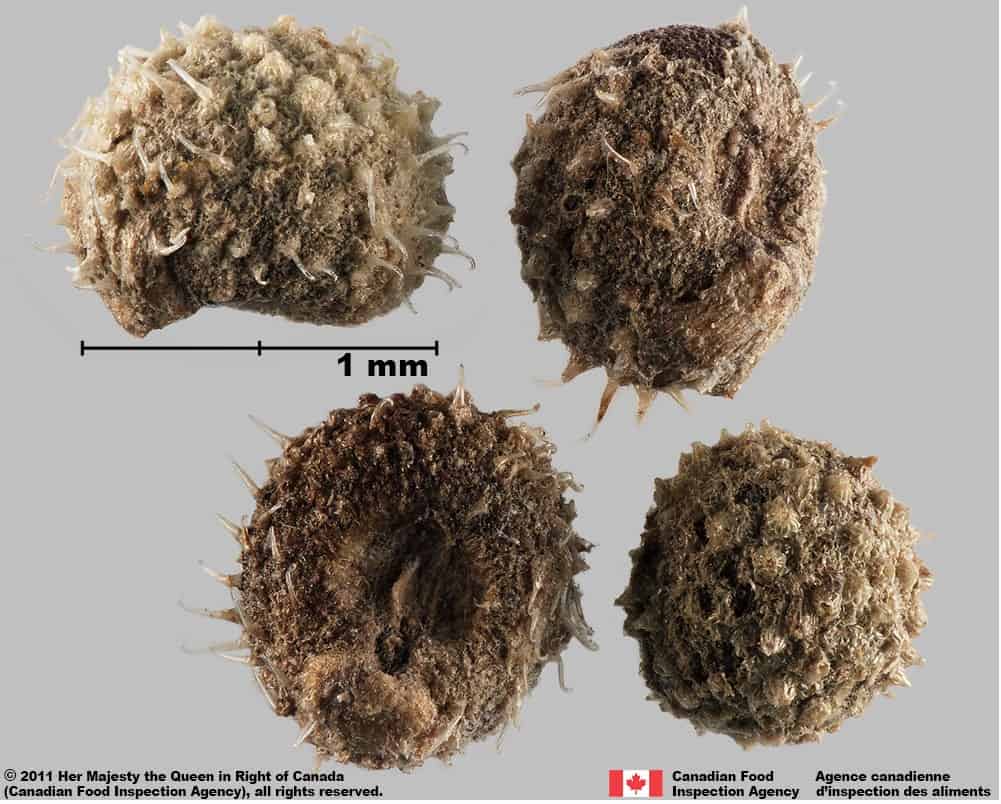

Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruits
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine
Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruit
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine
Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruit
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine

Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruit and tubercles
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Galium aparine
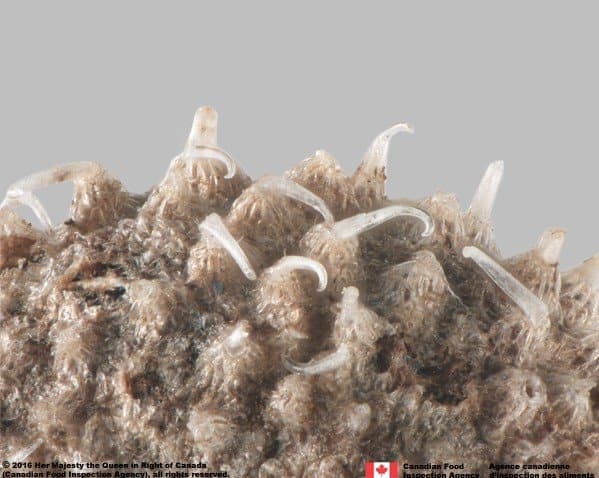

Galium aparine
Rubiaceae
Cleavers (Galium aparine) fruit, close-up of surface
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed March 28, 2022.
Danin, A. & O. Fragman- Sapir. 2016+ Flora of Israel Online. https://flora.org.il/en/plants/ Accessed March 09, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/2914754 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
Hanf, M. 1983. The Arable Weeds of Europe. BASF Aktiengessellschaft, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
Hanson, C. G. and Mason, J. L. 1985. Bird seed aliens in Britain. Walsonia 15: 237-252.
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide. https://www.idseed.org/authors/details/method_for_seed_size_measurement.html
Lindley, J. 1835. A Synopsis of the British Flora: Arranged According to the Natural Orders, 2nd Edition Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown, Green, and Longman, London, UK.
Martin, A.C. 1946. The comparative internal morphology of seeds. The American Midland Naturalist 36: 513-660.
Plants of the World Online (POWO). 2022. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet; http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ Accessed March 09, 2022.
Tropicos. 2022. Missouri Botanical Garden. https://tropicos.org Accessed March 09, 2022.
Tutin, T. G., Heywood, V. H., Burges, N. A., Moore, D. M., Valentine, D. H., Walters, S. M. and Webb, D. A. (eds.) 1976. Flora Europaea. Volume 4: Plantaginaceae to Compositae (and Rubiaceae). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2022. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. http://plants.usda.gov Accessed December 29, 2022.