Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 2: Primary Noxious Weed Seeds
Regulation Notes:
Distribution :
Répartition :
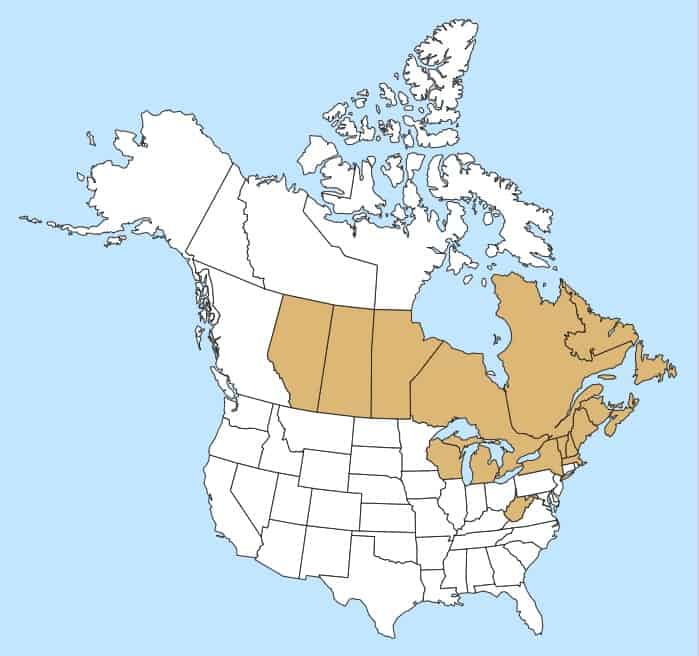
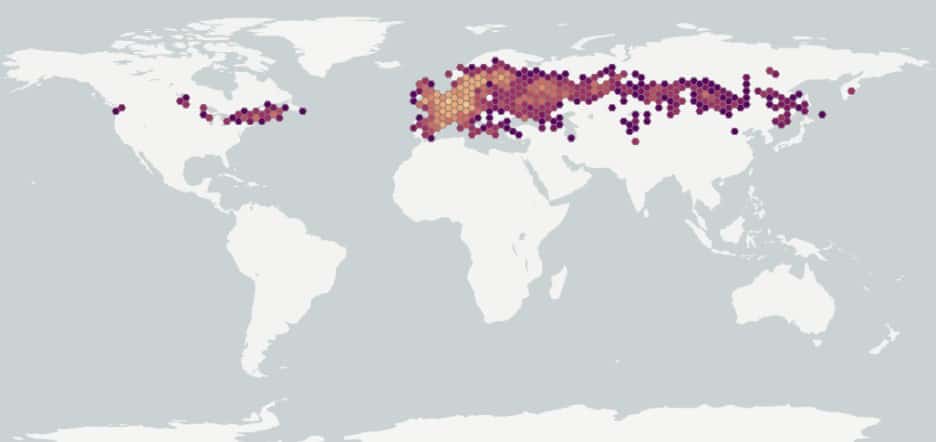
Native to Europe and temperate Asia and introduced in North America (USDA-ARS 2022). In the United States it is found in the northeast and Great Lakes regions (USDA-NRCS 2022). Occurs across Canada except for British Columbia, Nunavut, Yukon and the Northwest Territories (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Cultivated fields, old fields, pastures, hay crops, native grasslands, roadsides and railway lines (Darbyshire 2003; Alberta Invasive Species Council 2022). Does not compete well with annual crops (Alberta Invasive Species Council 2022), but can persist in pastures or hayfields, contaminating cut hay (Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Seed
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
O. verna subsp. serotinus was first introduced into Manitoba as seeds in packing crates imported from Germany in the 1950s (Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022). Plants were estimated to produce 1400 seeds (Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022) that can spread in contaminated hay, as a seed contaminant, or by sticking to clothing and equipment such as all-terrain vehicles (Alberta Invasive Species Council 2014).
O. verna subsp. serotinus is a facultative hemiparasite, producing sufficient energy, but is able to absorb water and nutrients from surrounding plants using root connections (Govier et al. 1967). This species is able to connect to a large range of species and derives different nutrients depending on the species (eg. increased nitrogen from legumes) (Govier et al. 1967).
.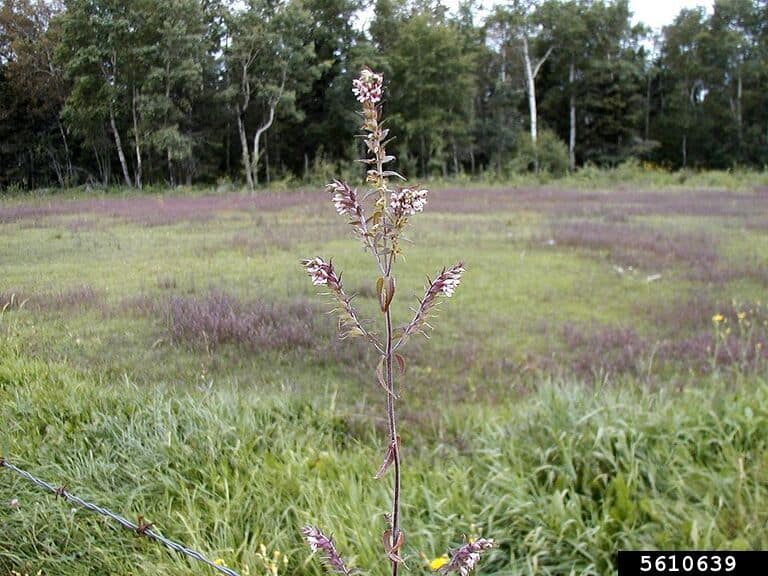
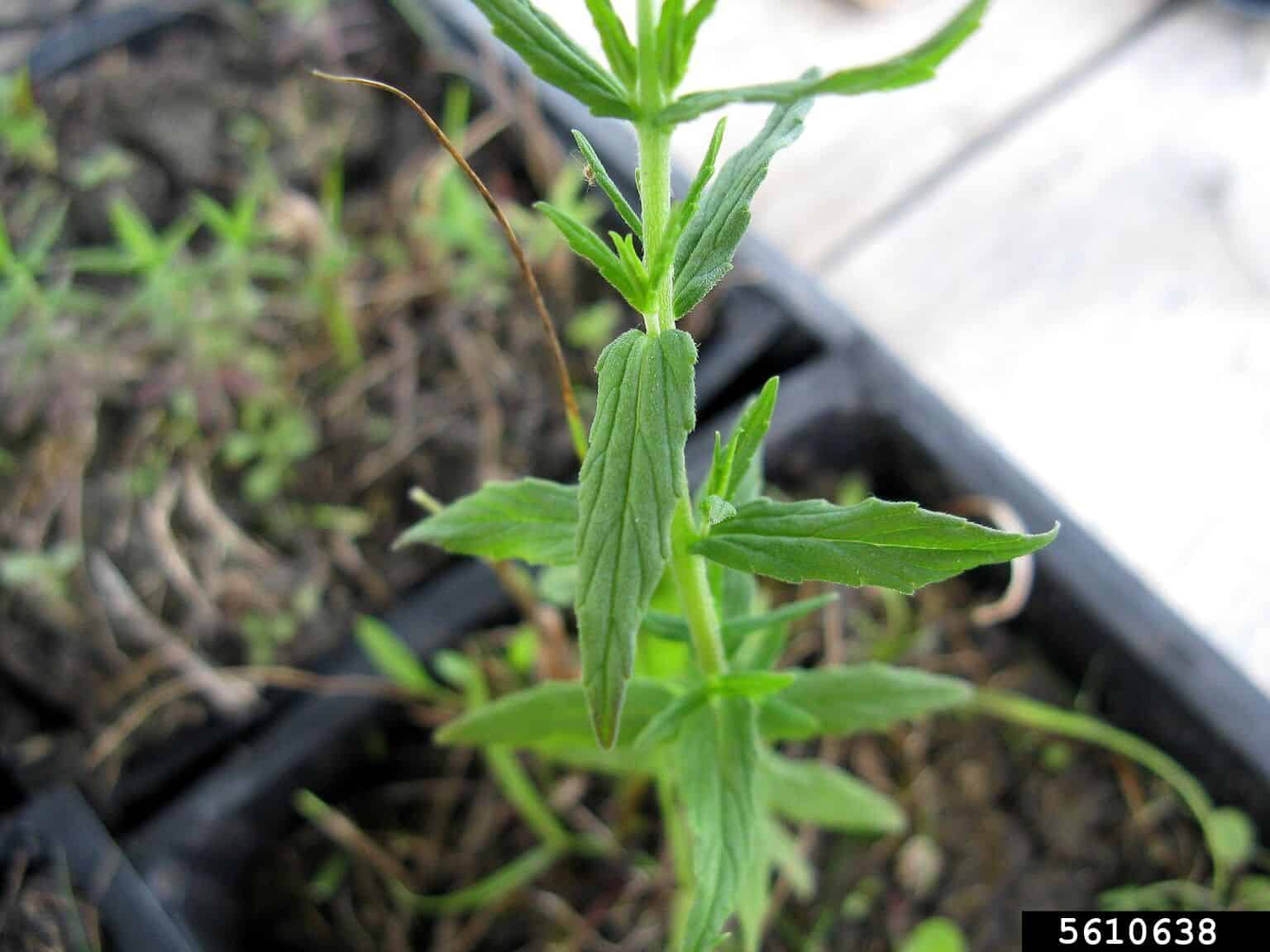
Odontites vernus flowering plant (Fred Paulson, Interlake Weed District, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
Capsule
Size
- Capsule length: 7 – 8 mm; width: 3 – 4 mm (FNA 1993+)
Shape
- Capsule shape is narrowly elongated oval (elliptic) (FNA 1993+; Minnesota Wildflowers 2006+)
Surface Texture
- Capsule surface is hairy (Minnesota Wildflowers 2006+; Alberta Invasive Species Council 2022)
Colour
- Capsule becoming dark purple when mature (Minnesota Wildflowers 2006+); old capsules are brown
Other Features
- Capsule may be same length or somewhat longer than the persistent calyx (Minnesota Wildflowers 2006+)
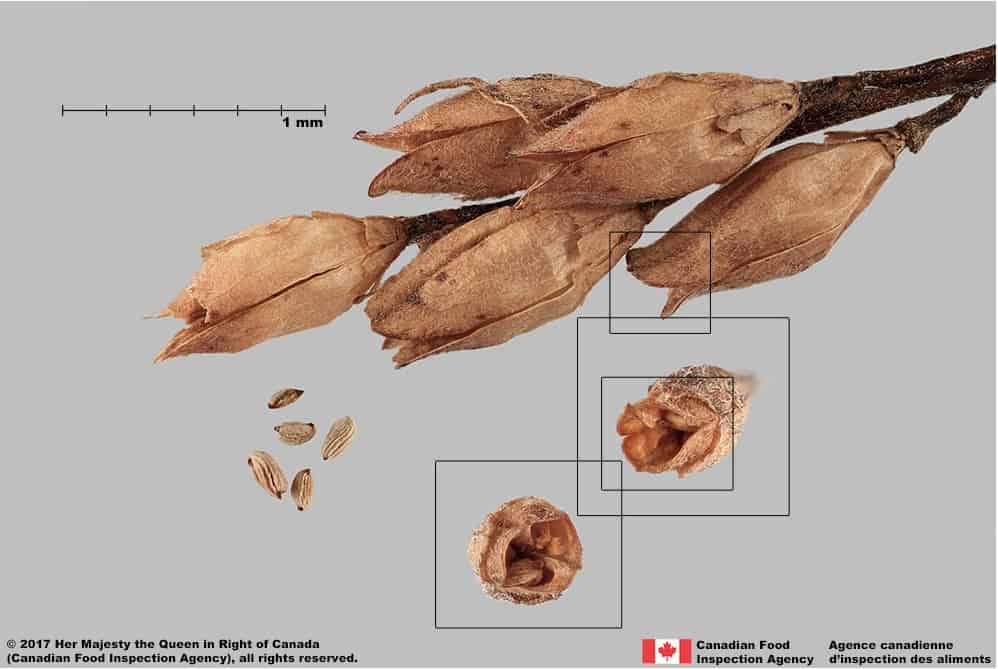
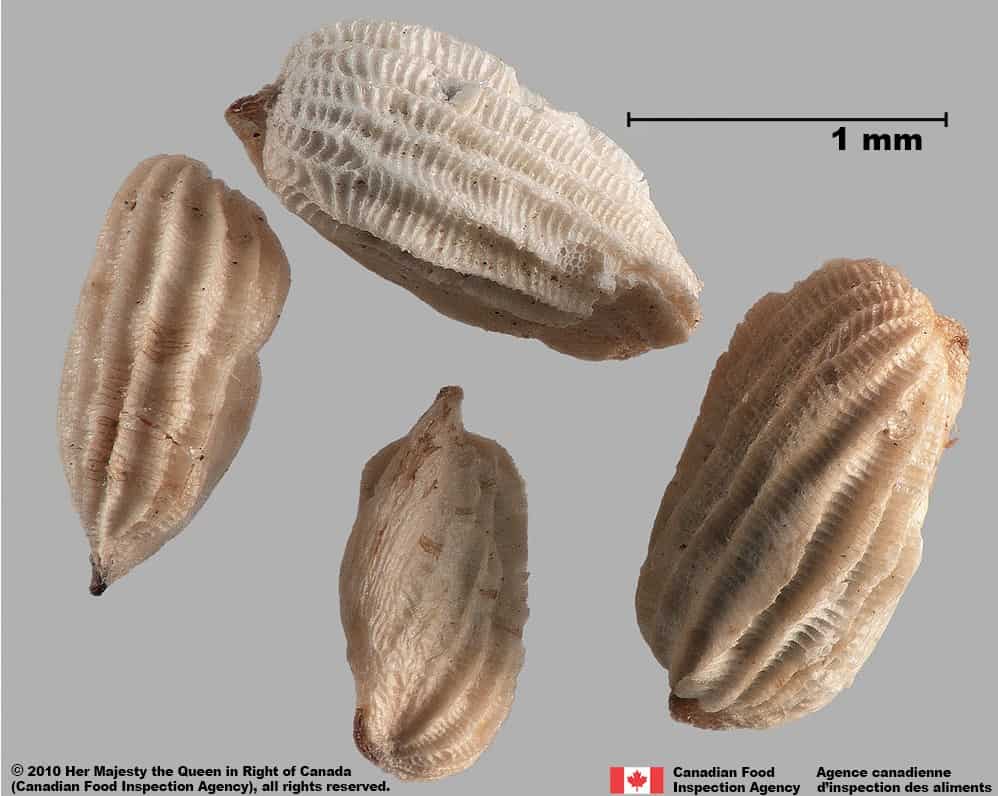
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) dried fruits and seeds

-
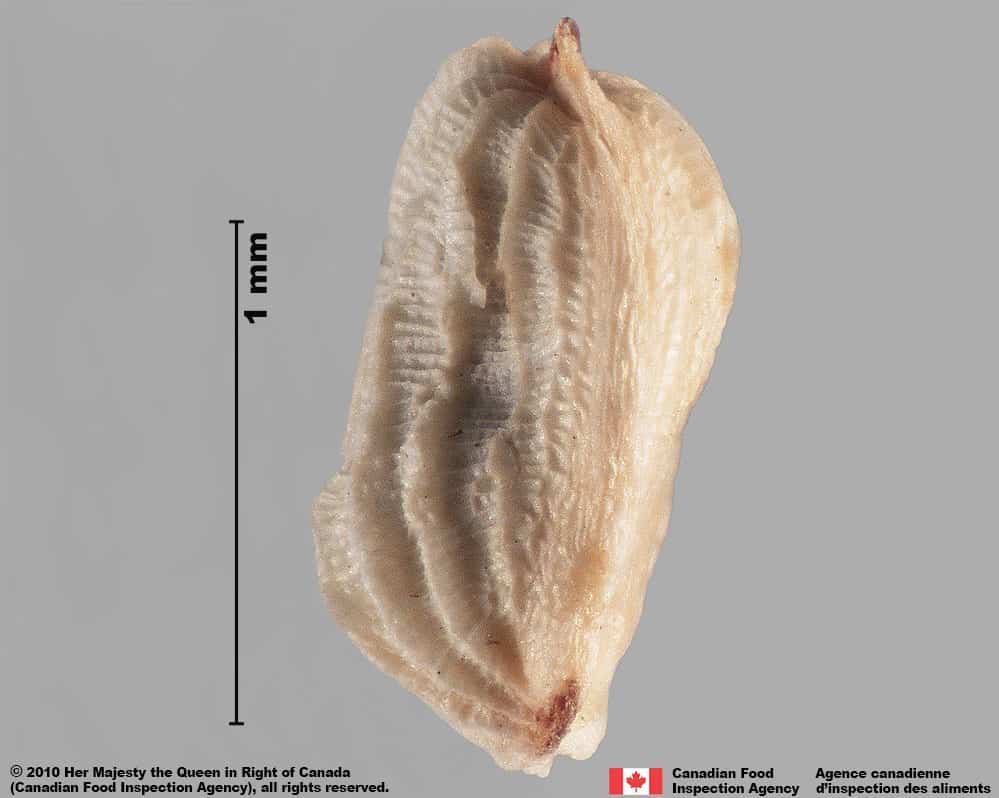
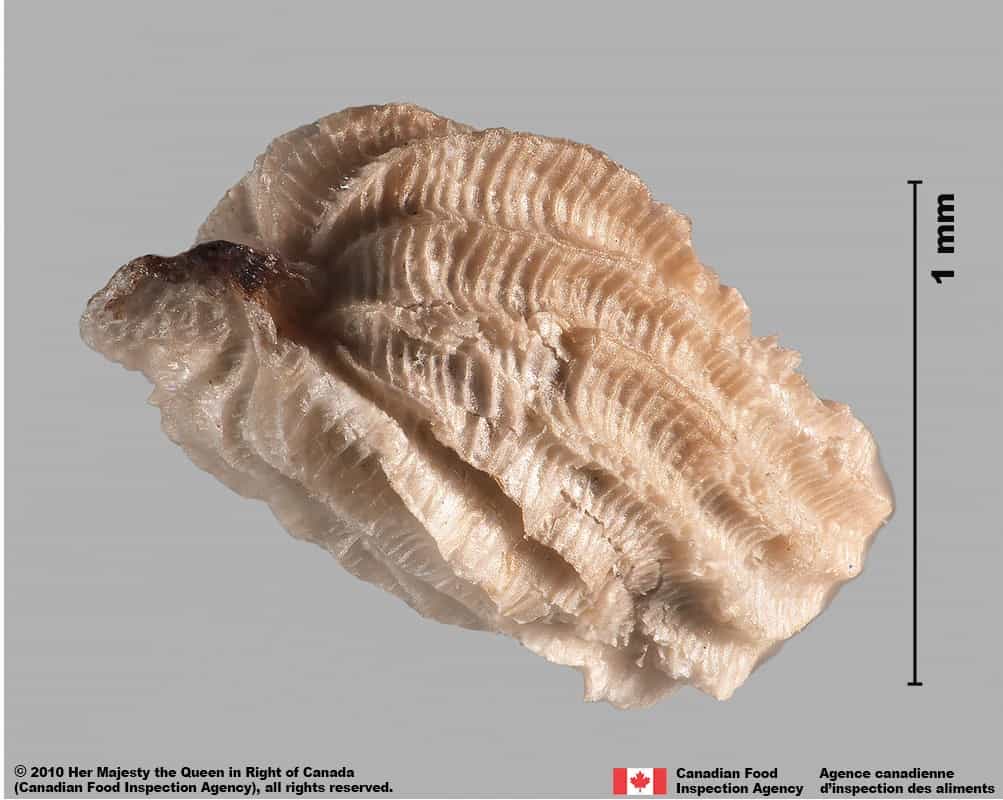
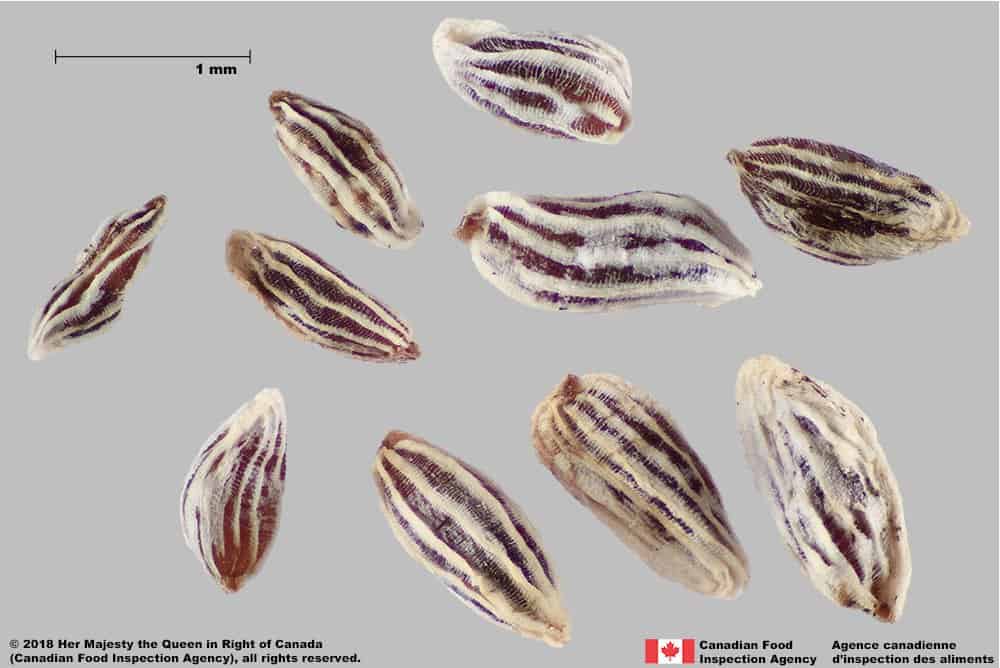
Seed
Size
- Seed length*: 1.2 – 2.0 mm; width: 0.7 – 1.0 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 seeds in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Seed elongated oval shaped, one end may be tapered, cylindrical in edge view
- Shape may appear irregular due to the persistent outer tissue layer
Surface Texture
- Seed has an outer, sculptured tissue layer with alternating grooves and ridges
- Seed surface is not visible under the opaque tissue layer
- Seed surface underneath is grooved reticulate textured
Colour
- Outer tissue coating is dull white to pale yellow with brown ends
- Seed surface underneath is shiny brown coloured
Other Features
Hilum and hilum area
- Hilum is at one end of the seed, but is generally not visible or an identification feature
Other features
- Outer tissue layer is easily removed, but generally remains intact after seed processing
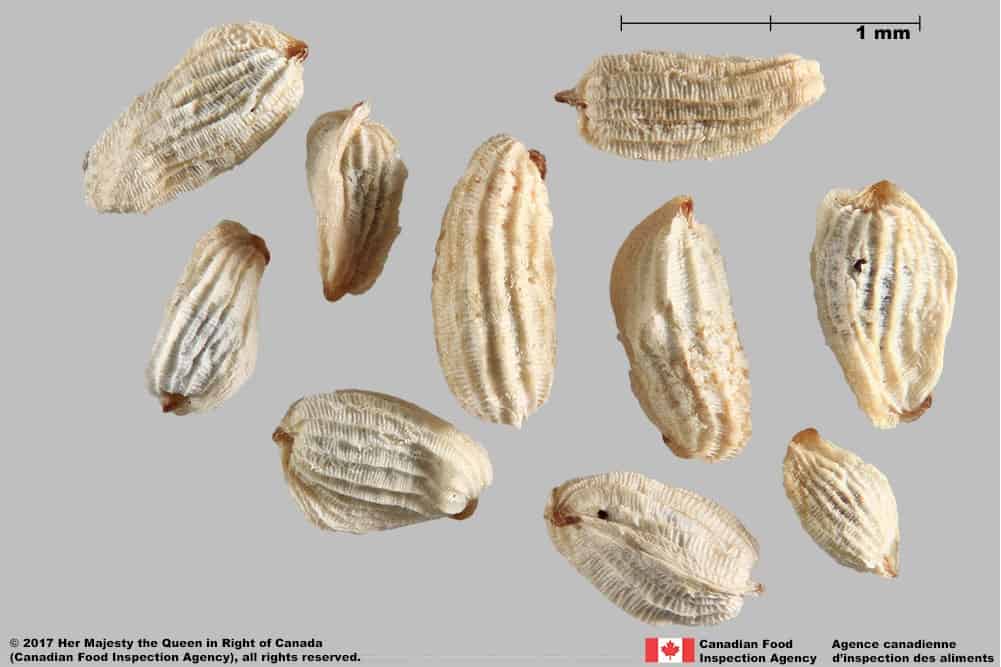

Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seeds




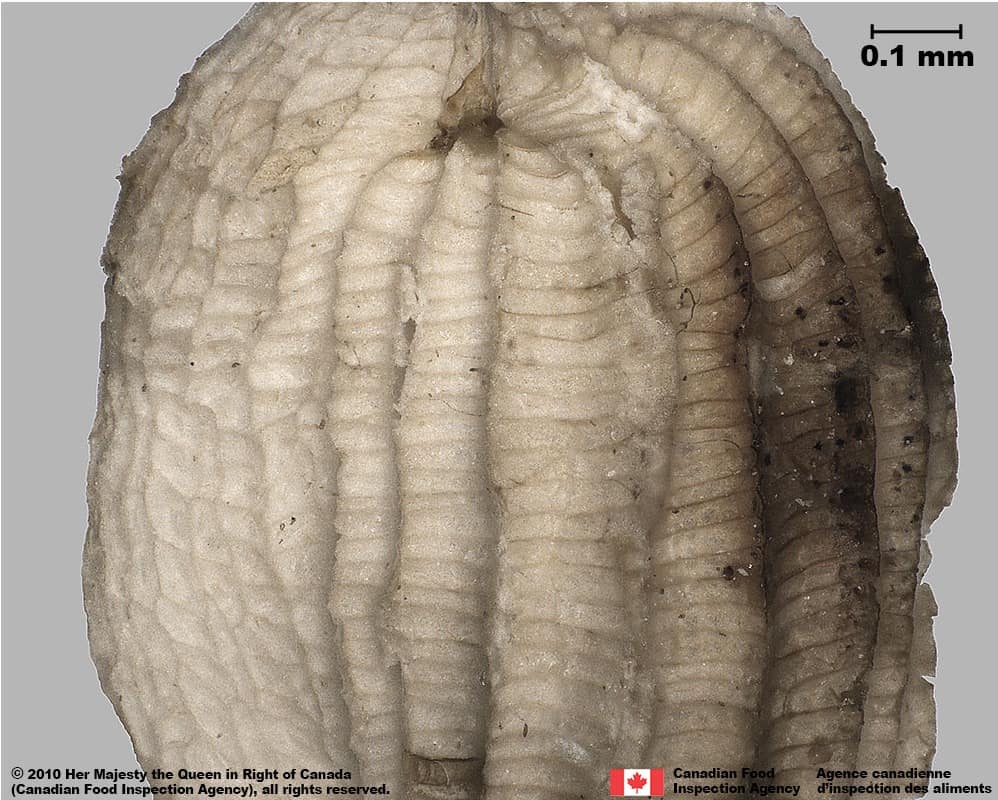
-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo is a rudimentary size
Shape
- Embryo is linear shaped, basal position
Endosperm
- Endosperm is soft- textured, oily and translucent brown coloured
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
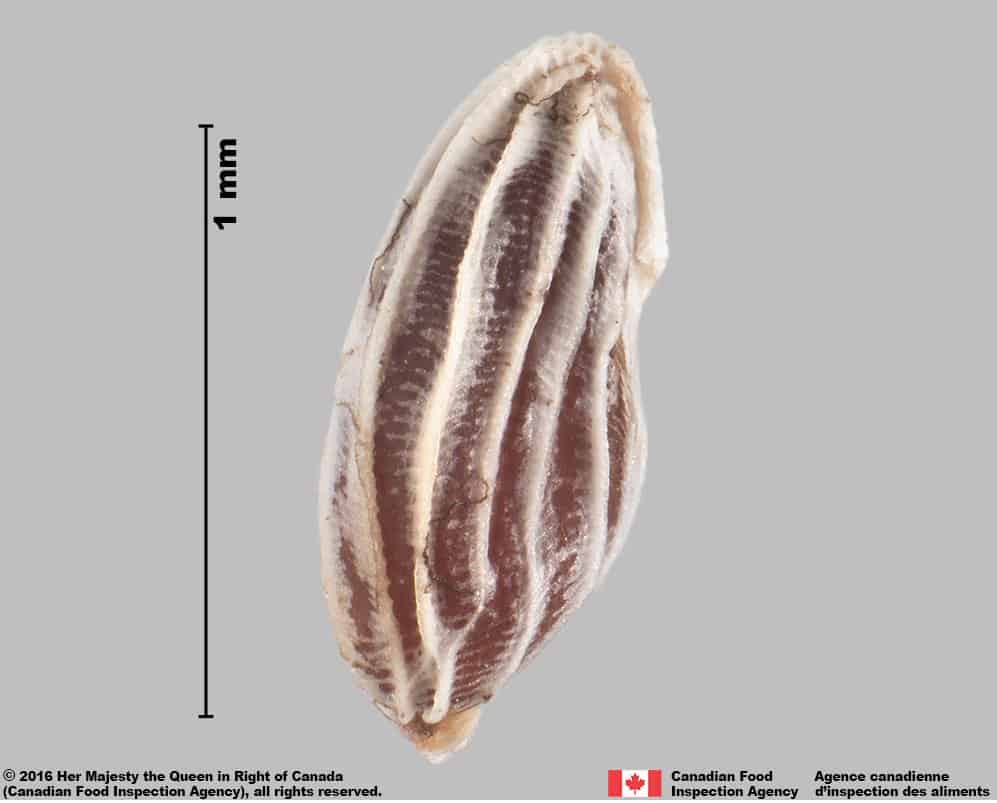
The seeds of O. verna subsp. serotinus are small and lightweight, common features in the Orobanchaceae and Scrophulariaceae families. Seeds of the species can be distinguished by the sculptured layer of whitish tissue obscuring the seed surface. Seeds of similar species in North America such as in Euphrasia have a thinner outer tissue layer on the seeds.

Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seed





Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Flowers/Inflorescence
- O. verna subsp. serotinus flowers are reddish purple coloured clustered at the top of the flowering stem
- Flowers 8 – 10 mm long (Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022)
Vegetative Features
- Plants 15 – 30 cm tall (Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022); 15 – 50 cm (FNA 1993+)
- Leaves are 1 – 4 cm long, arranged opposite each other along the stem (Alberta Invasive Species Council 2022)
- Leaves are hairy with a few teeth (Minnesota Wildflowers 2006+; Alberta Invasive Species Council 2022)

Odontites vernus flowering plant (Fred Paulson, Interlake Weed District, Bugwood.org)


Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
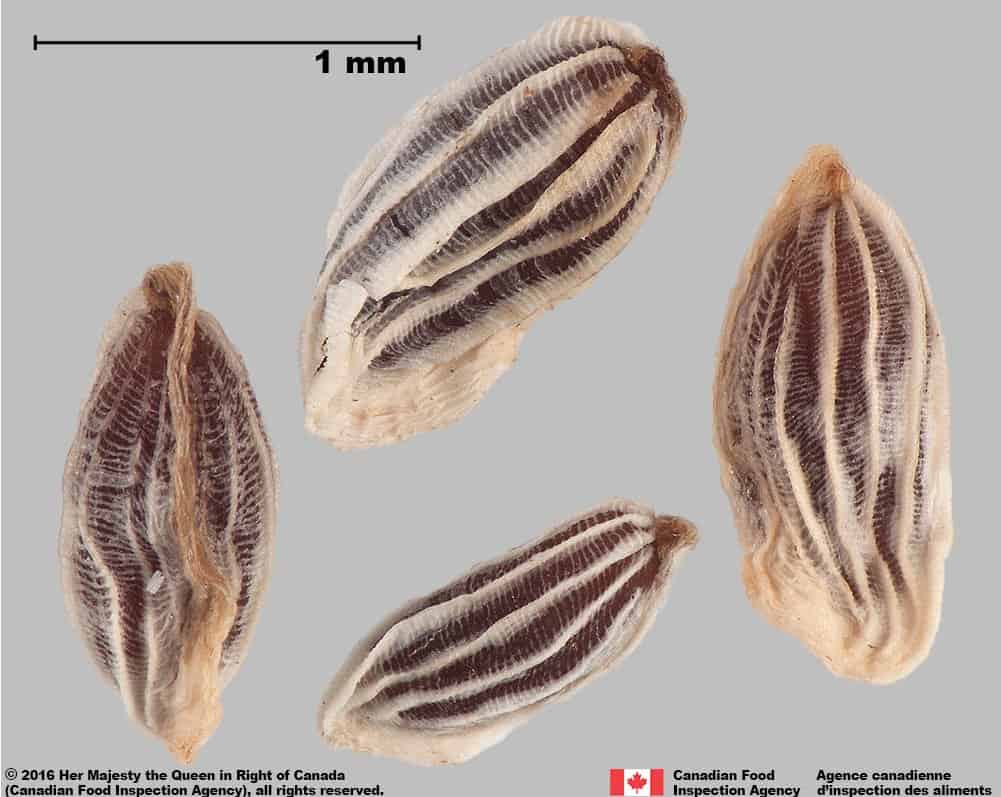
Euphrasia officinalis L. (eyebright )
E. officinalis seeds are generally smaller (length*: 1.1 – 1.7; width: 0.4 – 0.7 mm) than O. verna subsp. serotinus seeds, and the white outer coating on the seeds is thinner, allowing the reddish colour of the seed surface to show between the ridges.
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 seeds in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces

Euphrasia officinalis
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) seed, close-up of surface
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus

Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus
Orobanchaceae
Red bartsia (Odontites vernus subsp. serotinus) dried fruits and seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Euphrasia officinalis

Euphrasia officinalis
Orobanchaceae
Common eyebright (Euphrasia officinalis) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Euphrasia officinalis

Euphrasia officinalis
Orobanchaceae
Common eyebright (Euphrasia officinalis) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Euphrasia officinalis

Euphrasia officinalis
Orobanchaceae
Common eyebright (Euphrasia officinalis) seed
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Alberta Invasive Species Council. 2014. Red Bartsia Factsheet, https://www.abinvasives.ca/fact-sheets Accessed February 11, 2022.
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed September 07, 2021.
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
FNA. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico. 19+ vols. Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. New York and Oxford, http://www.fna.org/FNA/ Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/5415024 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
Govier, R.N., Nelson, M.D., and Pate, J.S. 1967. Hemiparasitic nutrition in angiosperms 1. The transfer of organic compounds from host to Odontites verna (Bell.) Dum. (Scrophulariaceae). New Phytology 66: 285-297.
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide. https://www.idseed.org/authors/details/method_for_seed_size_measurement.html
Manitoba Agriculture, Food, and Rural Initiatives 2022. How to control red bartsia (Odontites serotina), http://www.gov.mb.ca/agriculture/crops/weeds/how-to-control-red-bartsia.html Accessed February 11, 2022.
Minnesota Wildlfowers. 2006+. https://www.minnesotawildflowers.info/flower/red-bartsia Accessed April 19, 2022.
Tropicos.org. 2022. Missouri Botanical Garden. https://tropicos.org Accessed April 19, 2022.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2022. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysimple.aspx Accessed Accessed February 11, 2022.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2022. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. http://plants.usda.gov Accessed February 14, 2022.