Panicum
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 4: Secondary Noxious Weed Seeds
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 5: Noxious Weed Seeds
Regulation Notes:
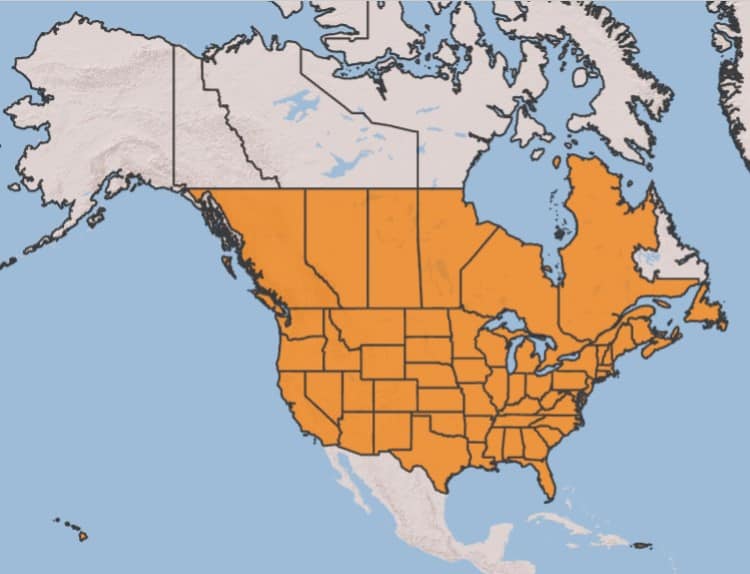
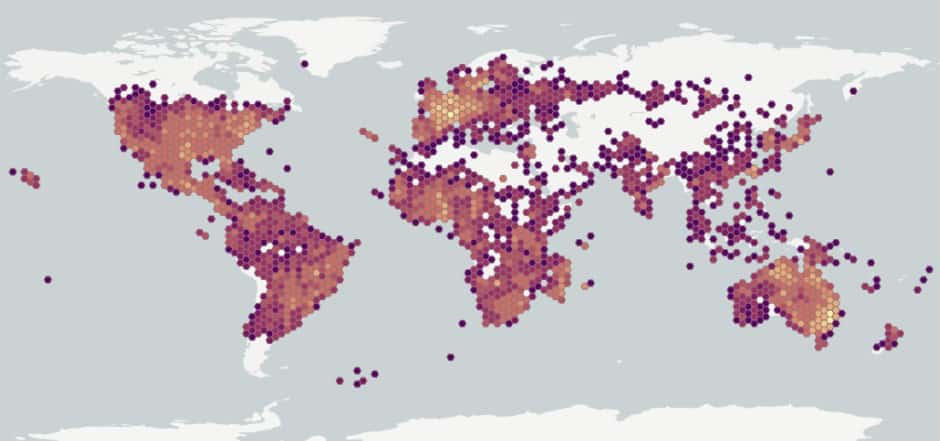
Distribution :
Répartition :
Panicum is a large genus of 300 to 600 species originating from tropical and warm temperate parts of the world (Barkworth et al. 2003; Mabberley 2008). Panicum includes a number of weedy species as well as species cultivated as fodder, grain and ornamentals (Mabberley 2008). The genus includes 34 total species in North America and 6 species distributed across Canada with the exception of Newfoundland, Nunavut and Yukon Territory (Brouillet et al. 2010+; Barkworth et al. 2003).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Cultivated fields, old fields, pastures, prairies, shores, floodplains, marshes, swamps, ditches, shallow water, dunes, forest edges, forest clearings, open forests, orchards, vineyards, roadsides, railway lines and disturbed areas (Barkworth et al. 2003; Darbyshire 2003; DiTomaso and Healy 2007). The common weedy species Panicum capillare commonly infests Zea mays (corn), Glycine max (soybeans), Triticum aestivum subsp. aestivum (common wheat) and Sorghum bicolor (sorghum), and can also infest grasslands (Clements et al. 2004).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual or perennial
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Spikelet or floret
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Of the six species occurring in Canada, four are native and two are introduced (Brouillet et al. 2010+). Most species occur as weeds of agricultural habitats (Darbyshire 2003; Clements et al. 2004). Panicum capillare, a weedy native species, is the most commonly found in cultivated fields and gardens (Frankton and Mulligan 1993).
Panicum virgatum and Panicum miliaceum subsp. miliaceum are cultivated for seed and forage, and P. miliaceum subsp. ruderale is a weedy form that is common and competitive in corn fields in Canada (Royer and Dickinson 1999; Darbyshire 2003).
.Identification
Identification
-
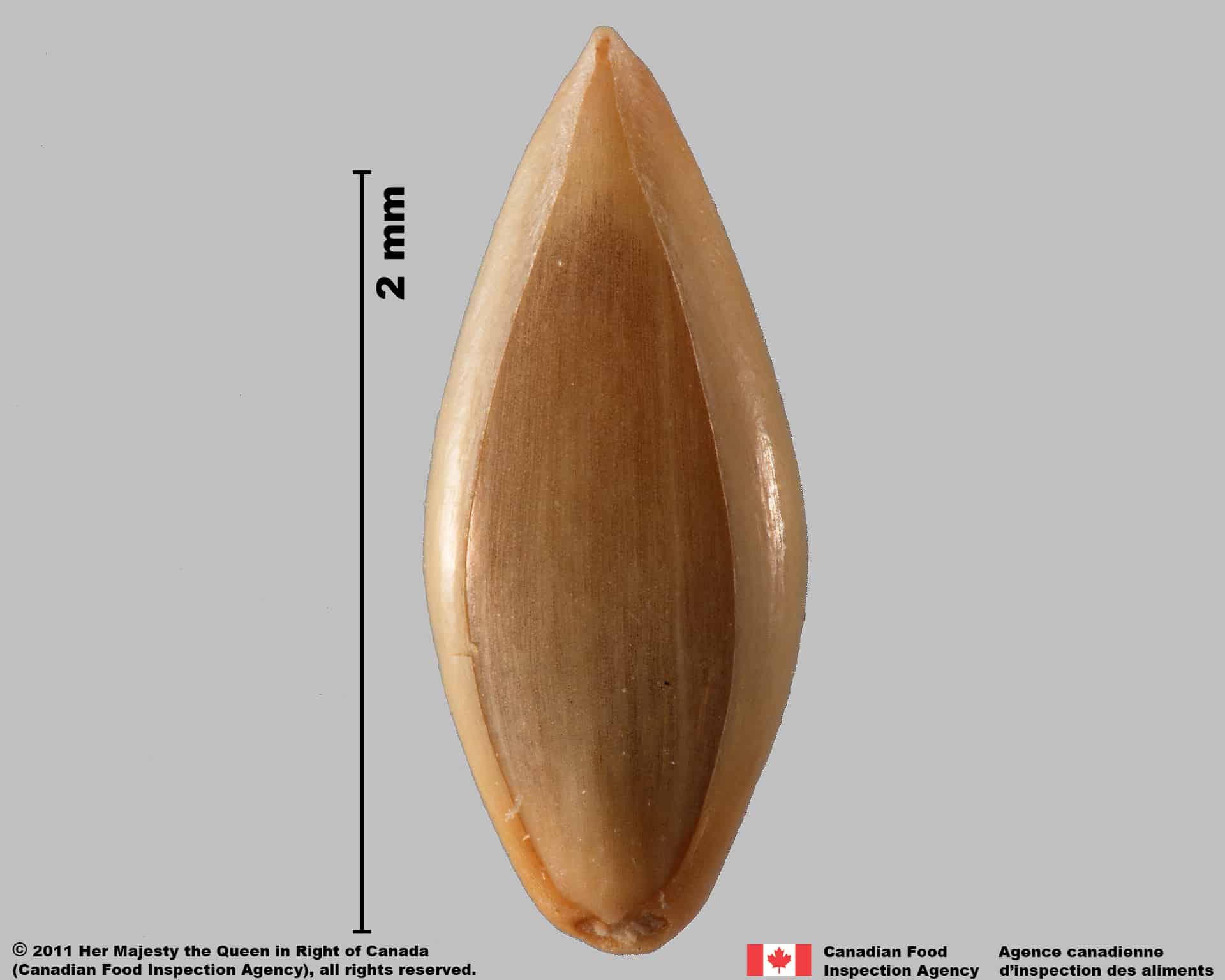
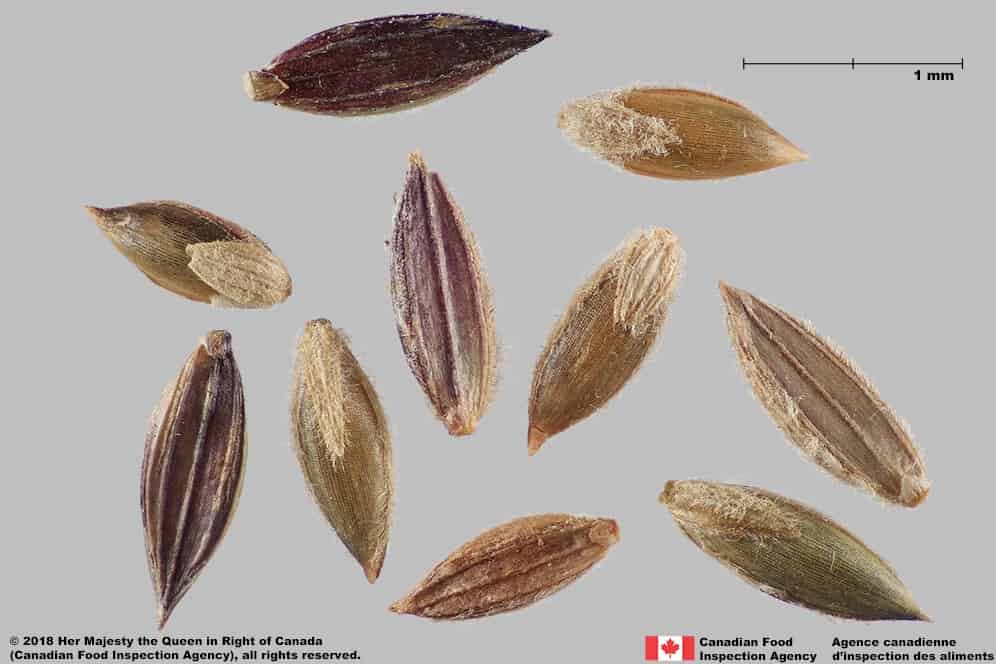
Spikelet
Size
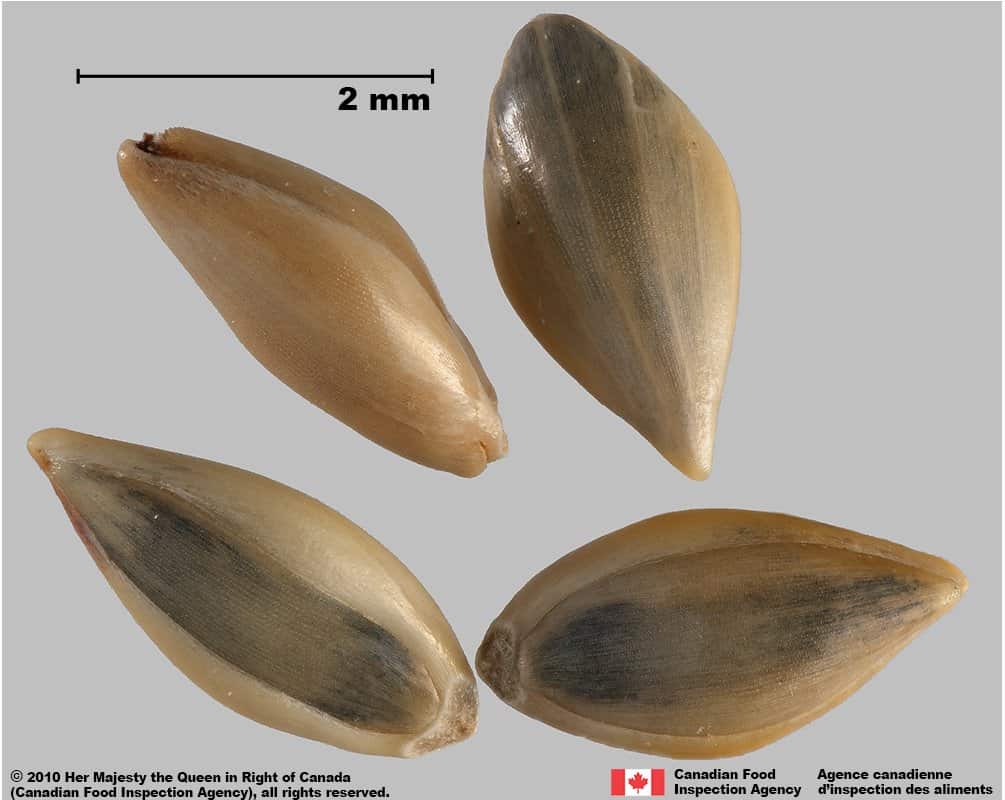
- Spikelets of weedy species Panicum capillare length*: 1.9 – 4.0 mm
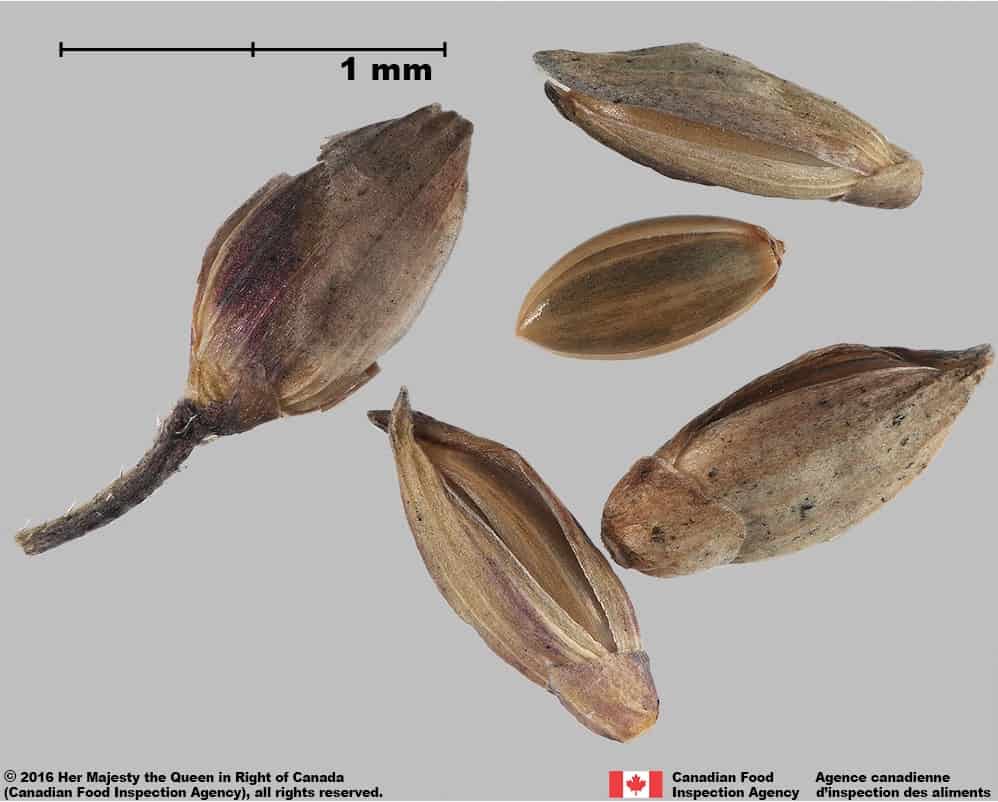
- Spikelets of weedy species Panicum dichotomiflorum length*: 1.8 – 3.8 mm; width: 0.7 – 1.2 mm
- Spikelets of crop species Panicum miliaceum subsp. miliaceum length*: 4.0 – 6.0 mm
* from Barkworth et al. 2003
Shape
- Spikelets are oval or teardrop-shaped, one end gradually narrows into a short or long point
Surface Texture
- Spikelets are smooth textured with several longitudinal nerves
Colour
- Spikelets are dull straw-yellow, brown or reddish brown
Other Features
- Spikelets have a papery consistency and may be removed by processing
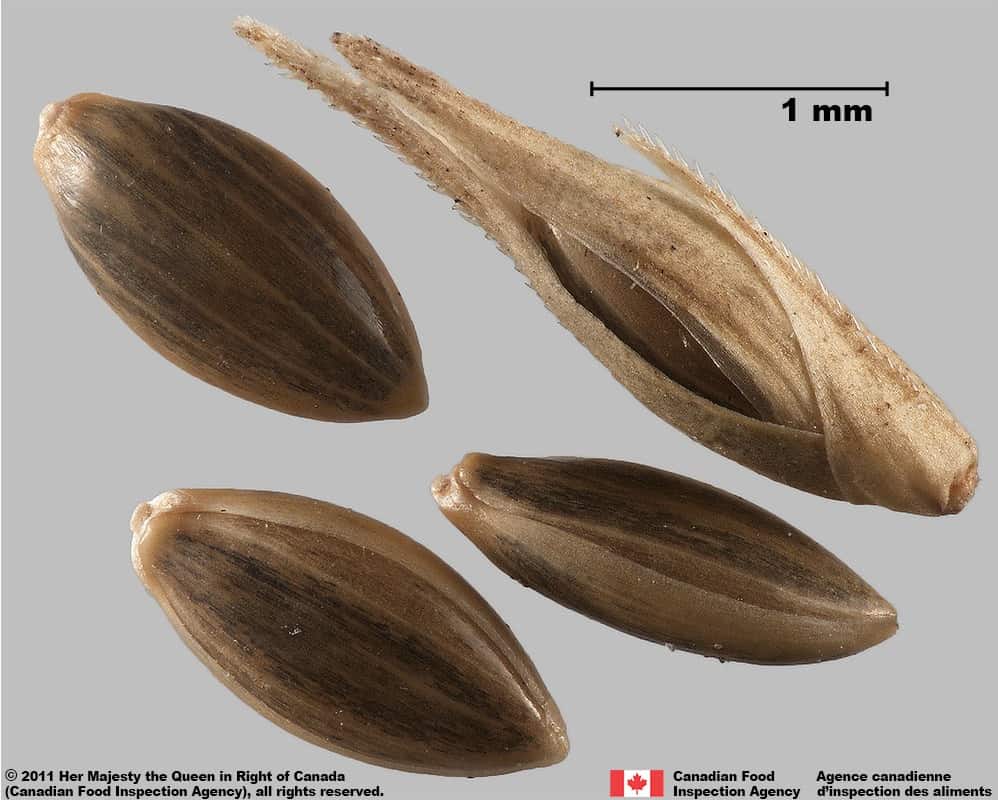

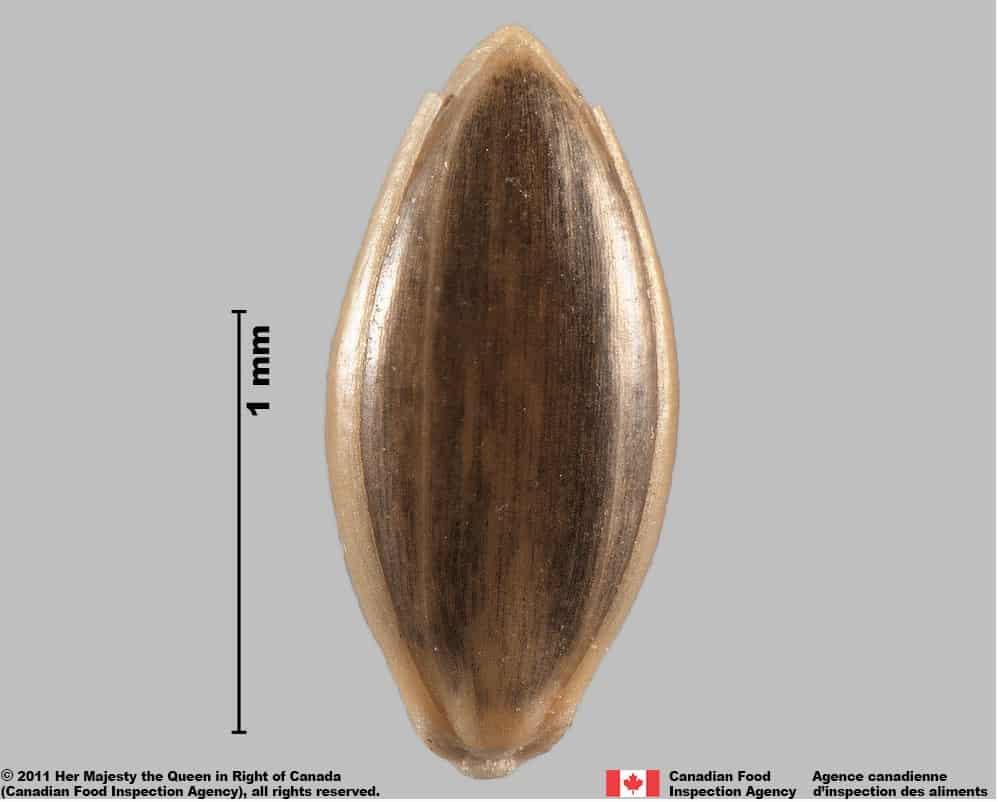
Witch grass (Panicum capillare) florets and spikelet
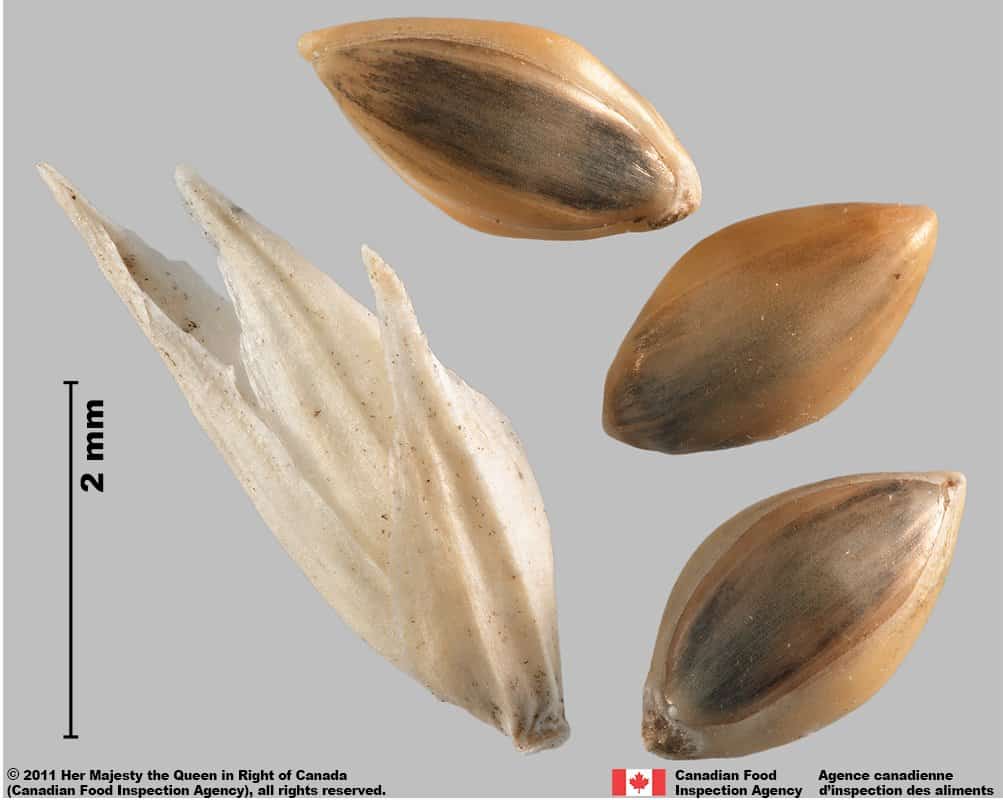




-
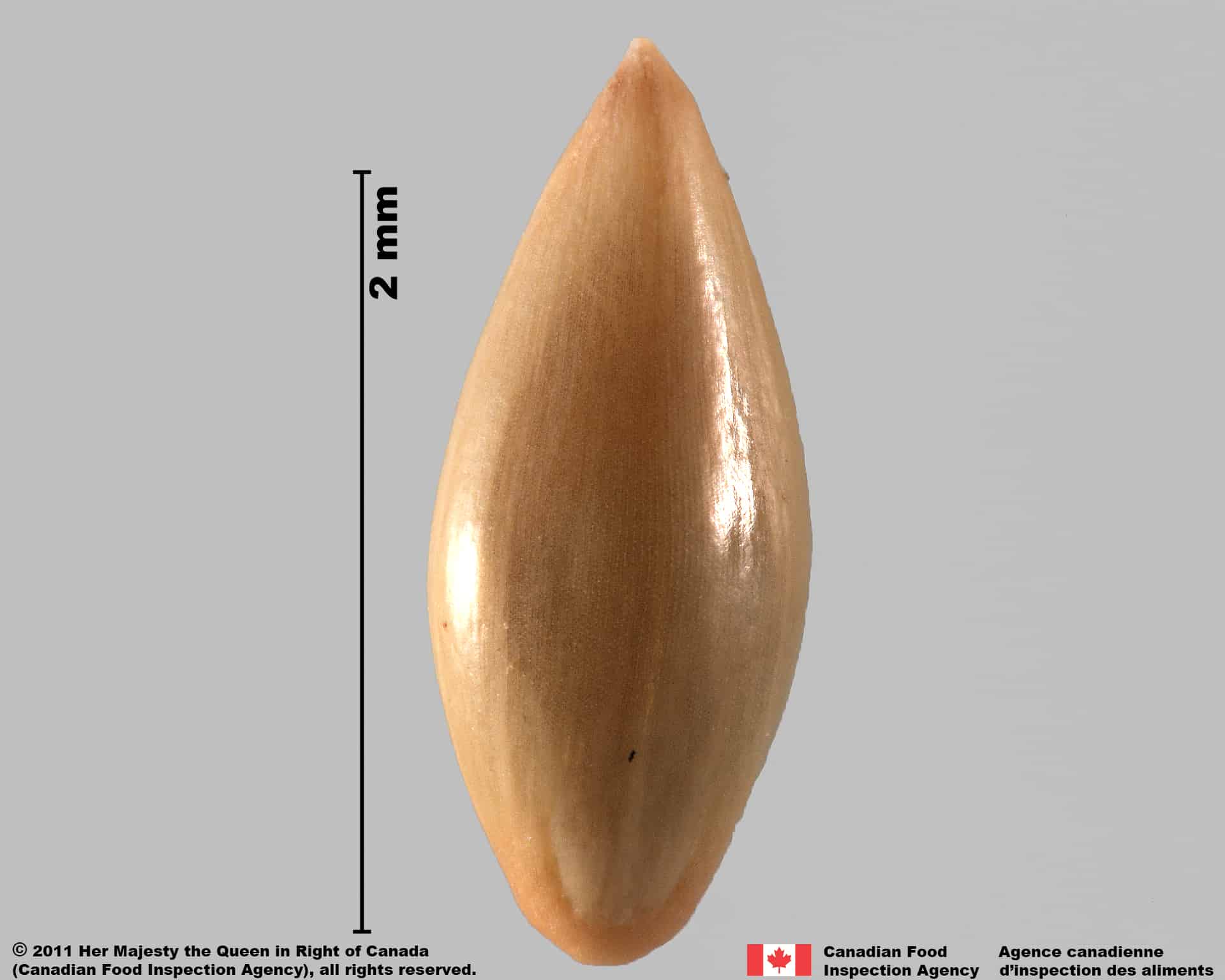
Floret
Size
- Florets of weedy species. Panicum capillare length*: 1.3 – 1.7 mm; width 0.7 – 0.8 mm
- Florets of weedy species Panicum dichotomiflorum length +: 1.4 – 2.5 mm; width: 0.7 – 1.1 mm
- Florets of crop species Panicum miliaceum subsp. miliaceum length +: 3.0 – 3.8 mm; width: 2.0 – 2.5 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 florets in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
+ from Barkworth et al. 2003
Shape
- Florets of Panicum species are oval or egg-shaped, plano-convex in edge view
Surface Texture
- Florets of Panicum species have a smooth surface
Colour
- Florets of weedy Panicum species are shiny or glossy brown or greenish-brown with straw yellow ends and longitudinal stripes
- Florets of crop Panicum species are glossy straw yellow or orange coloured
Other Features
Callus and Rachilla
- Callus at wide end of floret is kidney shaped and dull straw yellow, brown or black
Other Features
- Palea teeth not visible
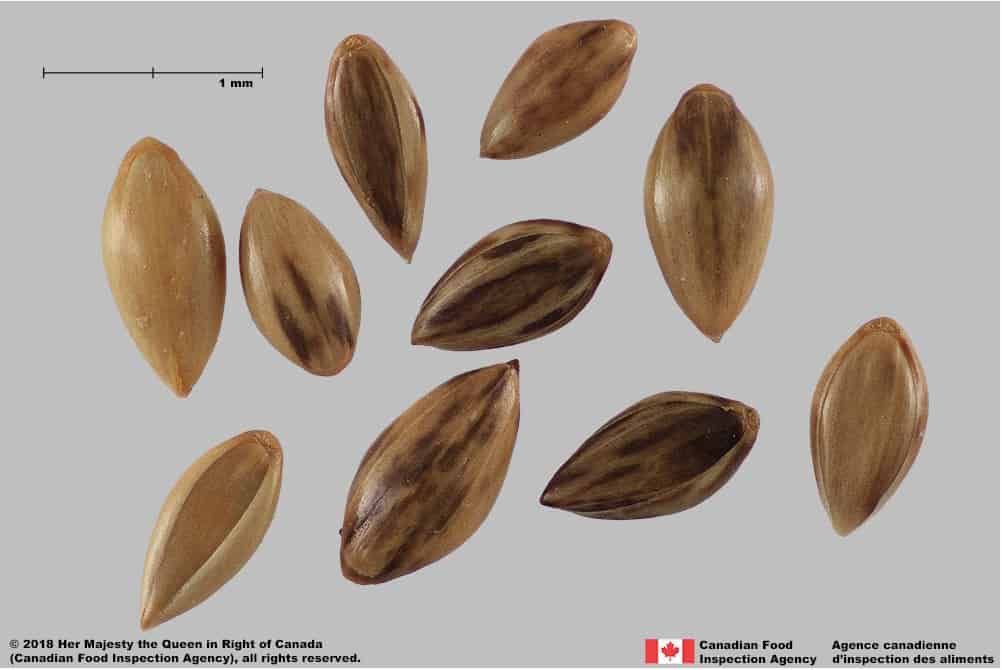

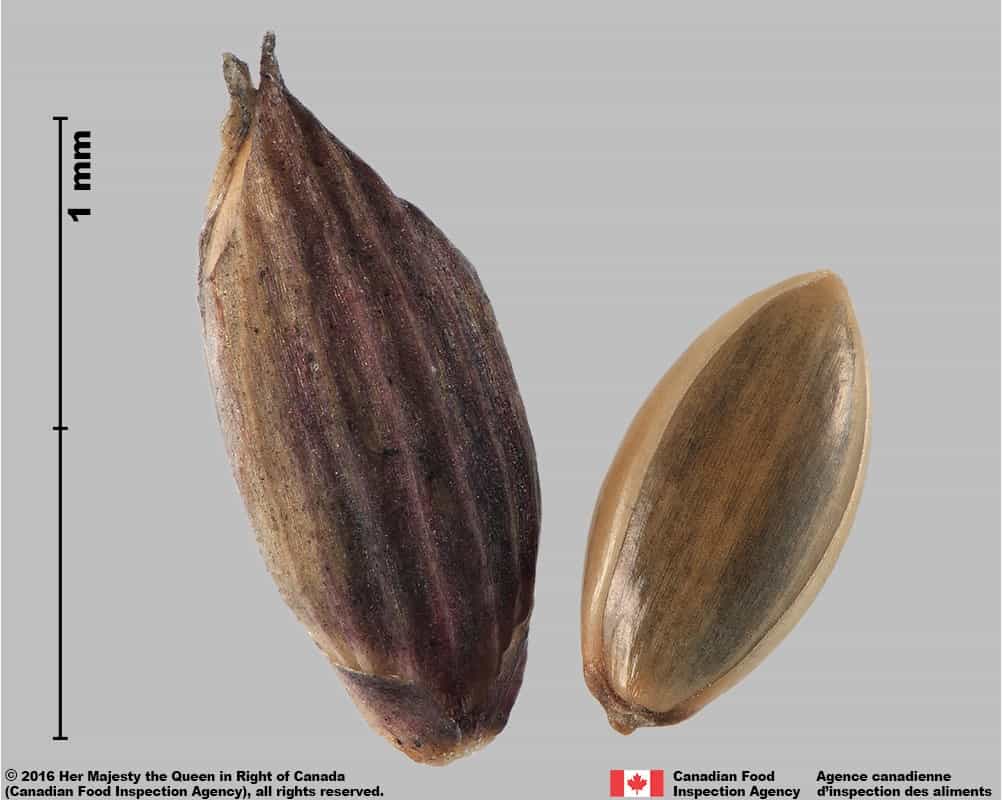
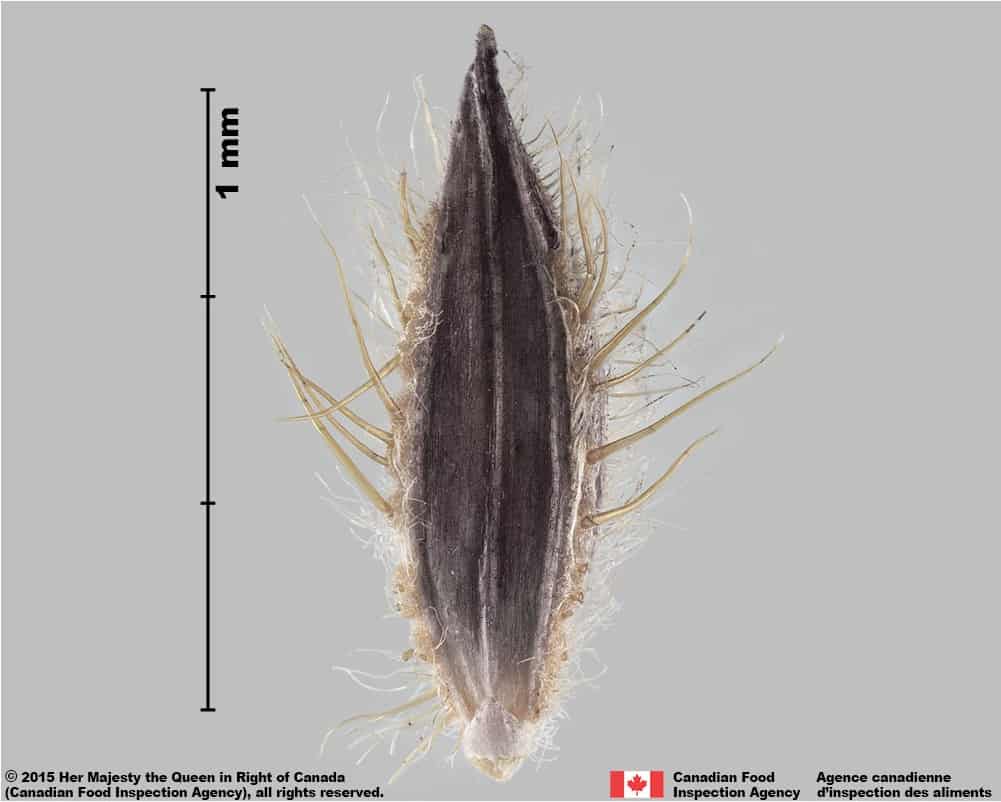
Blue panic grass (Panicum antidotale) florets
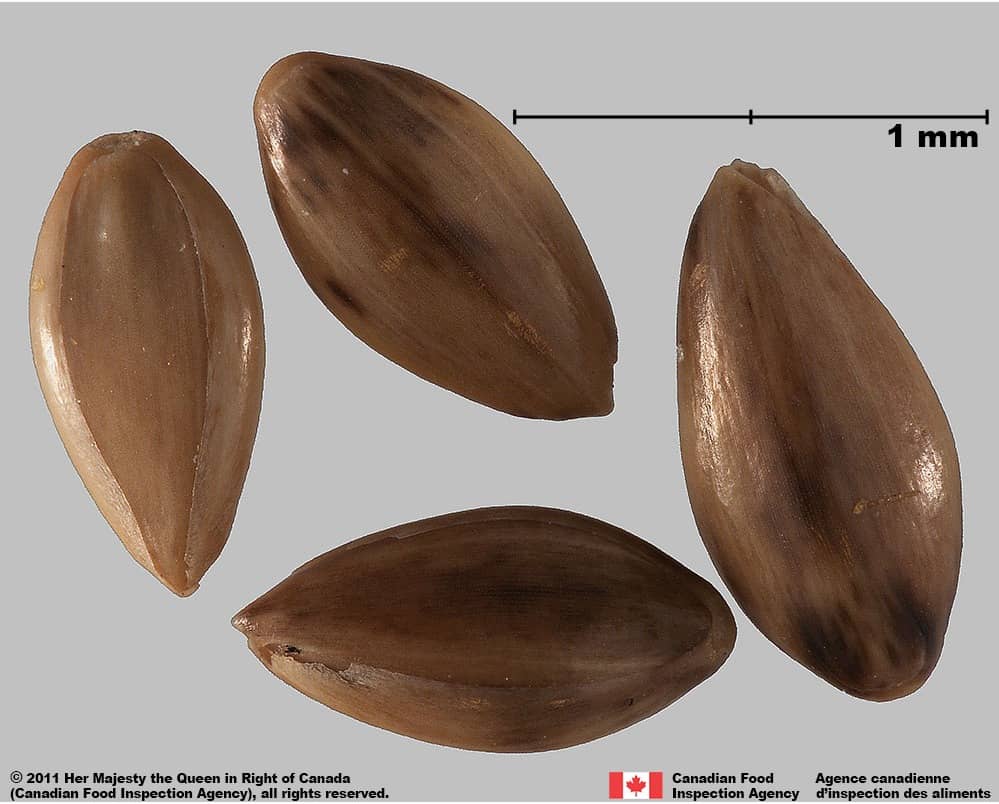
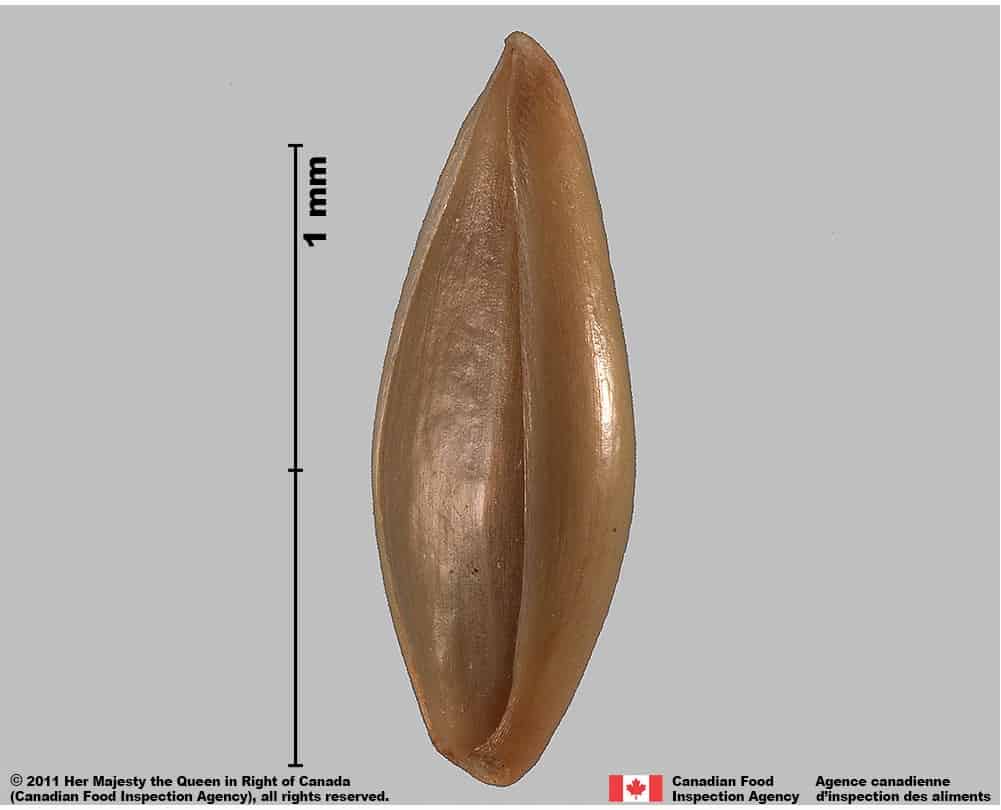












-
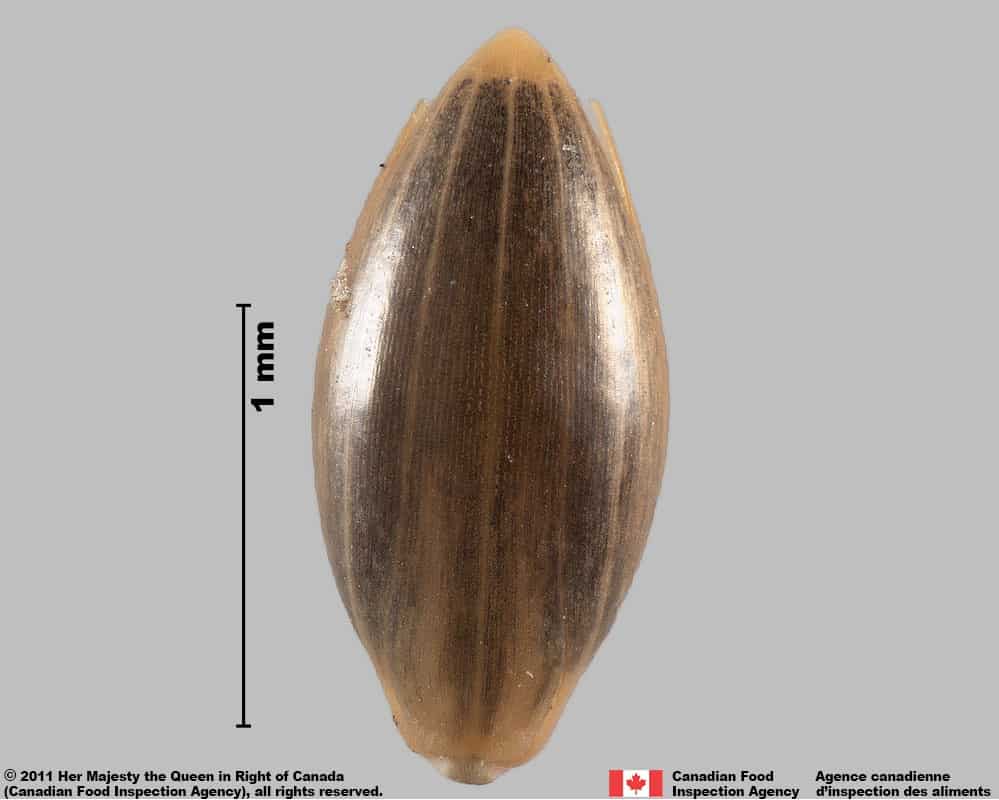
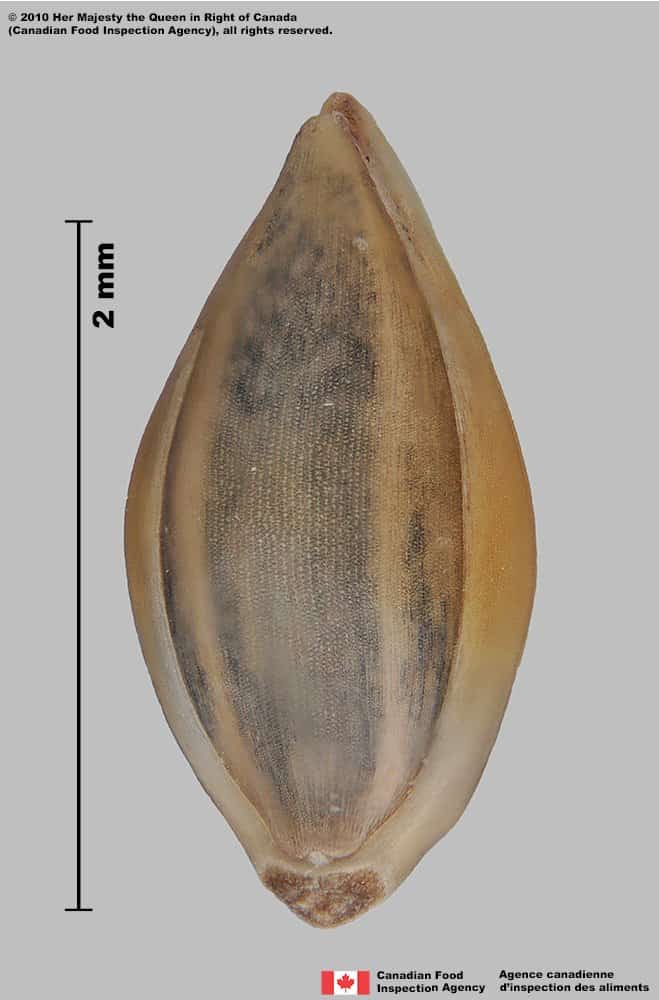
Caryopsis
Size
- Caryopsis size similar to floret size
Shape
- Caryopsis is oval shaped, compressed in edge view
Surface Texture
- The caryopsis surface is smooth
Colour
- Caryopsis is translucent straw yellow coloured
Other Features
- Caryopsis has a dark brown round or oval hilum near the end of the caryopsis, opposite the embryo side
-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo is a rudimentary size compared to the caryopsis
Shape
- Oval shaped, lateral position at one end of the caryopsis on one side
Endosperm
- Endosperm is hard and a translucent whitish colour
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
Genera from the same tribe as Panicum species, Paniceae, have features that distinguish them from other grass tribes such as:
• Shed as a spikelet
• Spikelets have papery, unequal glumes, a papery sterile lemma and a hard, or leathery fertile floret
• Florets lack a rachilla or pedicels
• Inconspicuous palea teeth
• Florets tend to be short oval rather than elongate
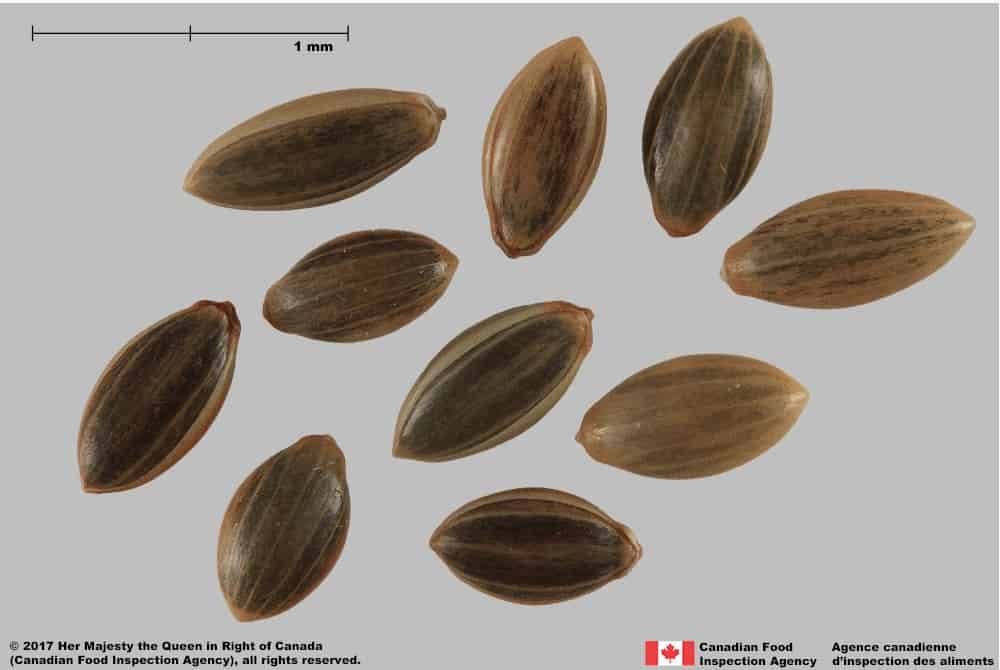
Within the Paniceae tribe, Panicum species can be distinguished by:
• Smooth, floret surface
• Glossy colour
• Kidney shaped callus
• Several light brown longitudinal stripes on the lemma of weedy Panicum species
• Florets have a hard, shell-like consistency, not leathery or papery as in other Poaceae genera

Blue panic grass (Panicum antidotale) floret













Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
Digitaria spp. L. (crabgrasses)
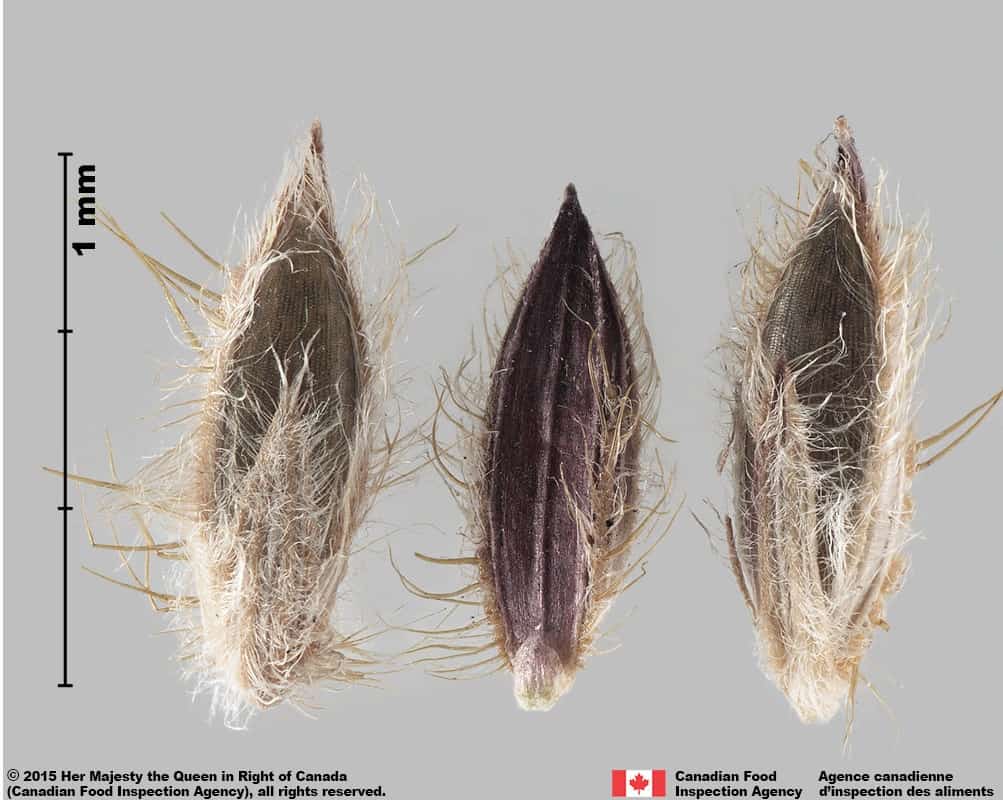
Digitaria species are compressed in edge view, spikelets are hairy, glumes are shorter than the floret, floret surface is pitted and does not have a striped colour pattern.
In comparison, Panicum species spikelets are generally inflated in edge view, glumes are smooth and cover the floret, florets are smooth and a glossy colour with a striped colour pattern.
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces

Digitaria ciliaris

Digitaria ischaemum

Digitaria sanguinalis
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Blue panic grass (Panicum antidotale) florets
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Blue panic grass (Panicum antidotale) florets
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Panicum antidotale floret
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Panicum antidotale floret
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Blue panic grass (Panicum antidotale) floret
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
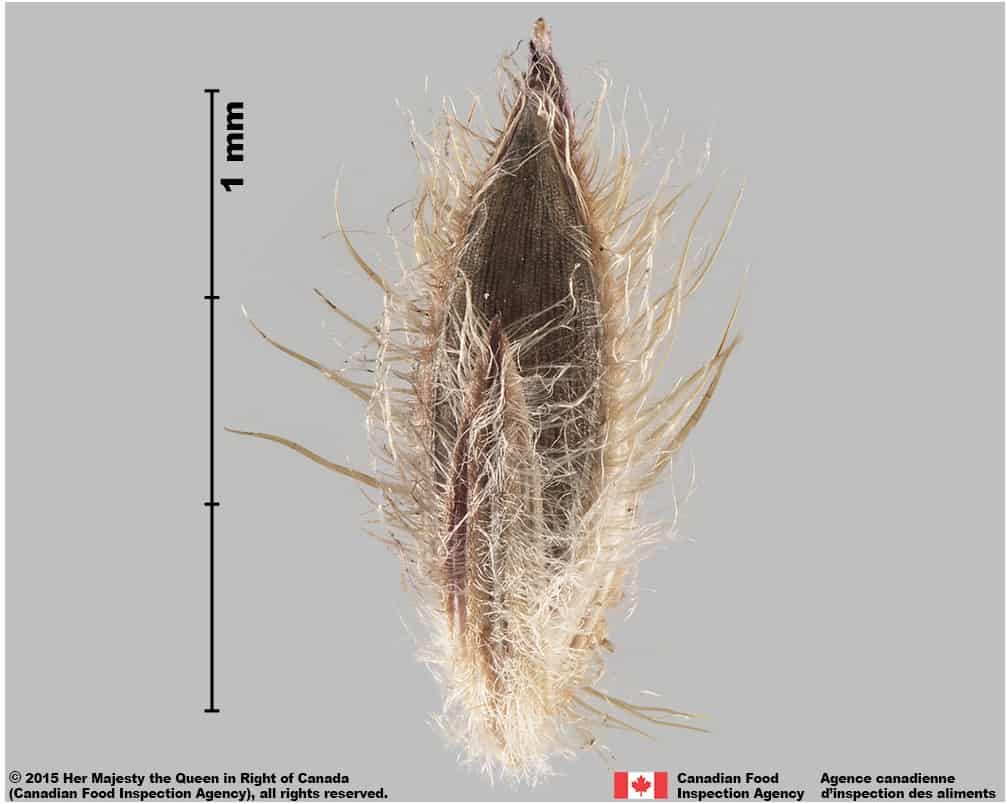
Witch grass (Panicum capillare) florets
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
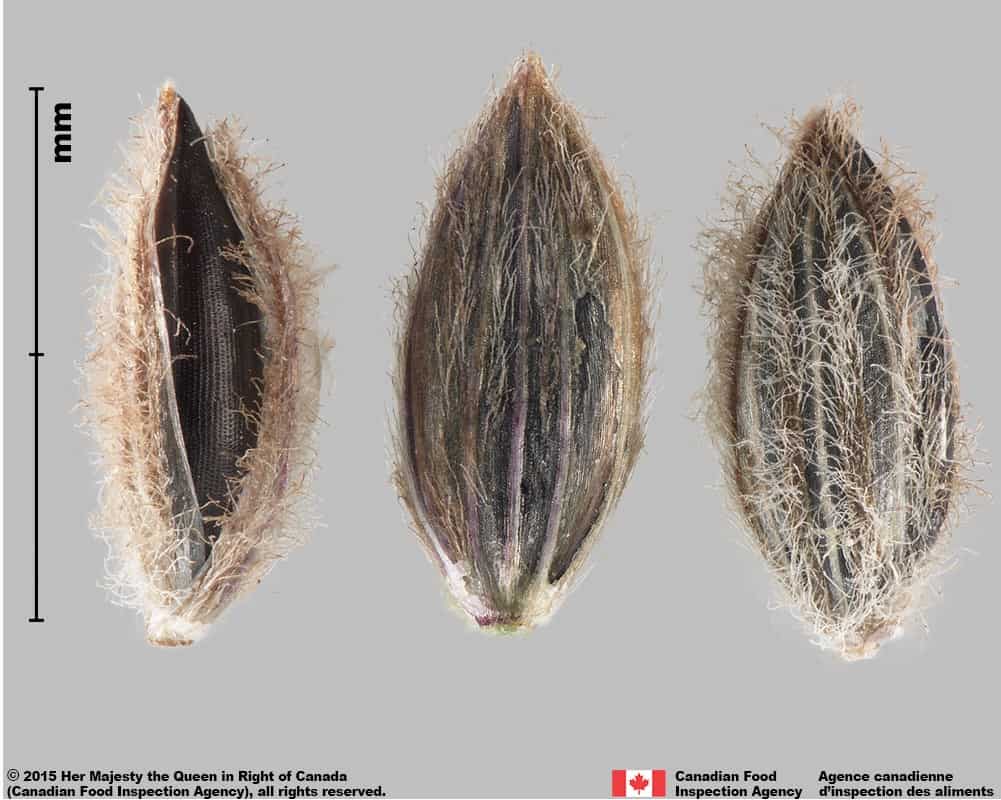
Witch grass (Panicum capillare) florets and spikelet
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Witch grass (Panicum capillare) floret, lemma view
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Witch grass (Panicum capillare) floret, palea view
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Fall panic grass (Panicum dichotomiflorum) spikelet (L) and floret (R)
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Fall panic grass (Panicum dichotomiflorum) spikelets and floret
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Panicum virgatum (switchgrass) florets
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Panicum virgatum (switchgrass) florets and spikelet
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Panicum

Panicum
Poaceae
Panicum virgatum (switchgrass) floret
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Digitaria ciliaris

Digitaria ciliaris
Poaceae
Southern crabgrass (Digitaria ciliaris) spikelets
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Digitaria ciliaris

Digitaria ciliaris
Poaceae
Southern crabgrass (Digitaria ciliaris) spikelet
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Digitaria ciliaris

Digitaria ciliaris
Poaceae
Southern crabgrass (Digitaria ciliaris) spikelet
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Barkworth, M. E., Capels, K. M., Long, S., Anderton, L. K. and Piep, M. B., (eds.) 2003. Volume 25. Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Poaceae, part 2. Oxford University Press, New York, New York.
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed April 1, 2021.
Clements, D. R., DiTommaso, A., Darbyshire, S. J., Cavers, P. B. and Sartonov, A. D. 2004. The biology of Canadian weeds. 127. Panicum capillare L. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 84: 327–341.
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
DiTomaso, J. M. and Healy, E. A. 2007. Weeds of California and Other Western States. Vol. 1. 834 pp. University of California, CA.
Frankton, C. and Mulligan, G. A. 1993. Weeds of Canada. Agriculture Canada, Publication 948.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/2705064 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide.
Mabberley, D. J. 2008. Mabberley’s plant-book: A portable dictionary of plants, their classification and uses (3rd eds). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 1021 pp.
Royer, F. and Dickinson, R. 1999. Weeds of Canada and the Northern United States. The University of Alberta Press/Lone Pine Publishing, Edmonton, Alberta.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2022. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. http://plants.usda.gov Accessed December 29, 2022.