Pentanema britannicum
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 1: Prohibited Noxious Weed Seeds
- USA Federal Noxious Weed List
Regulation Notes:
Prohibited Noxious, Class 1 in the Canadian Weed Seeds Order (2016) under the Seeds Act. All imported and domestic seed must be free of Prohibited Noxious weed seeds.
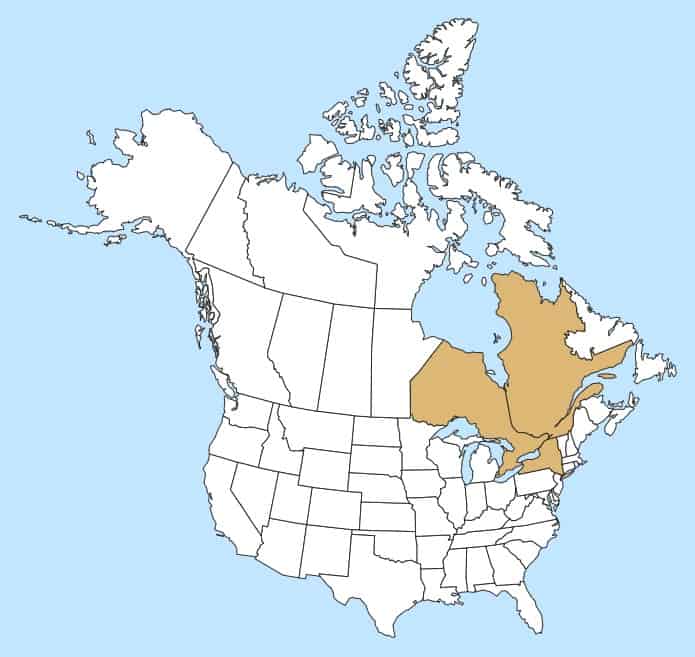
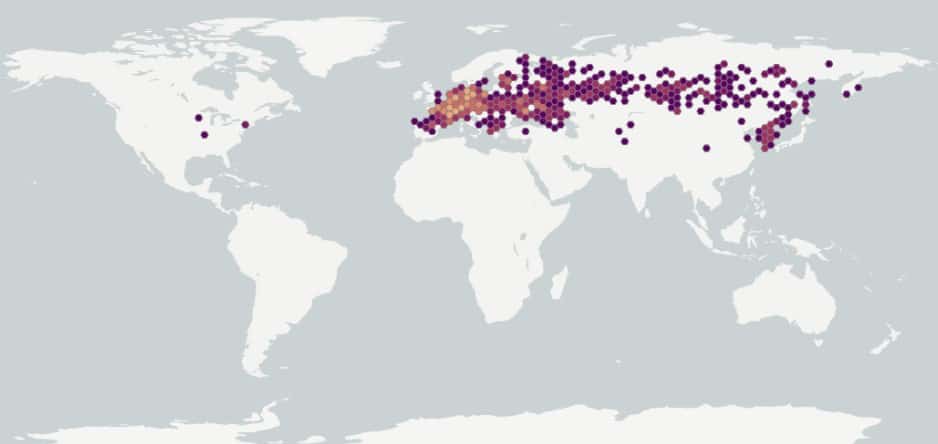
Distribution :
Répartition :
Native to Europe and temperate Asia, introduced to Canada and the United States (New York, District of Columbia) (CABI 2020). May be an occasional escape rather than truly established in North America (FNA 1993+). Occurs in Ontario and Quebec (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Wet places (e.g., streambanks, ditches, marshes, wet woods and grasslands), nurseries, roadsides and waste places (FNA 1993+; CABI 2020). Its roots and rhizomes are known to contaminate Hosta species root systems (CABI 2020).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Perennial
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Achene
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Introductions of Pentanema britannicum into Canada and the eastern United States started in approximately the 1920s and have mostly occurred through the nursery trade. Populations either did not persist or are small and contained (Lehtonen and Schall 2000).
In the Netherlands, where this species is known to be associated with Hosta species, it has been subject to aggressive control since 2000 (Lehtonen and Schall 2000).
.Identification
Identification
-
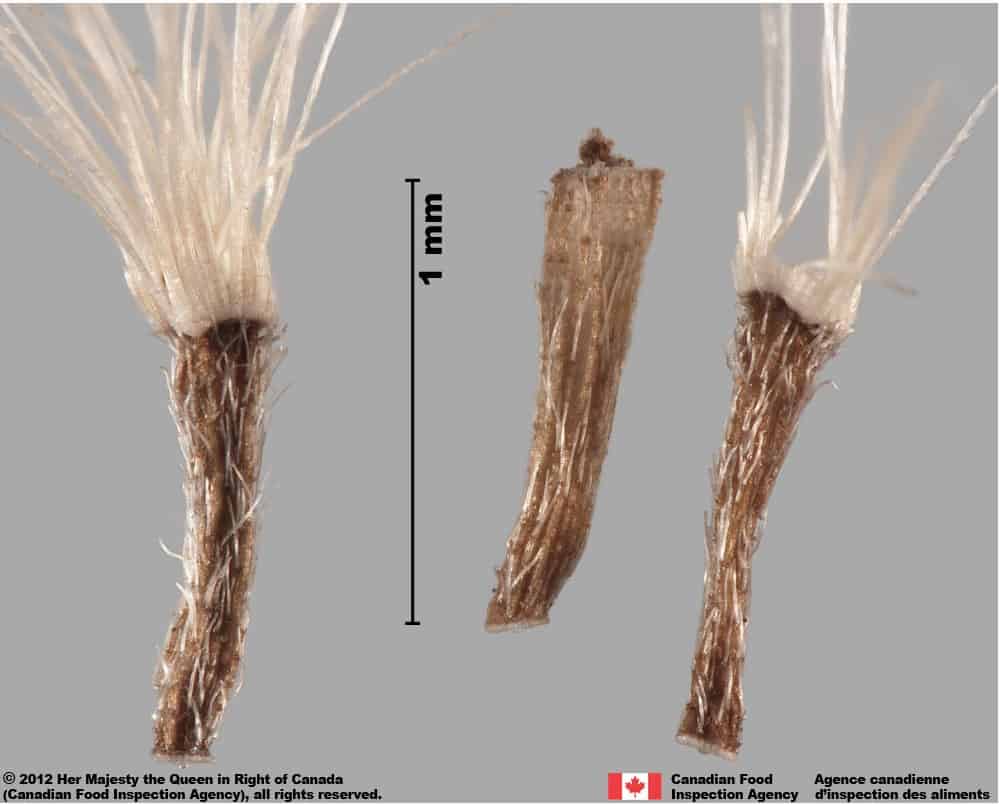
Achene
Size
- Achene length*: 1.0 – 1.5 mm; width: 0.2 – 0.5 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 5 achenes in a normal range of this species using specimen measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Achene is cylindrical with truncate ends
Surface Texture
- Surface of achene has several longitudinal ribs covered with long and thin white hairs
Colour
- Achene is dull medium brown coloured
Other Features
Pappus
- Pappus is persistent when the achene is mature (FNA 1993+)
- Pappus hairs are long (length : 4.0 – 6.0 mm, FNA 1993+) and dull white coloured
- Pappus bristles are generally attached by their bases in a ring (FNA 1993+)
Achene end with pappus
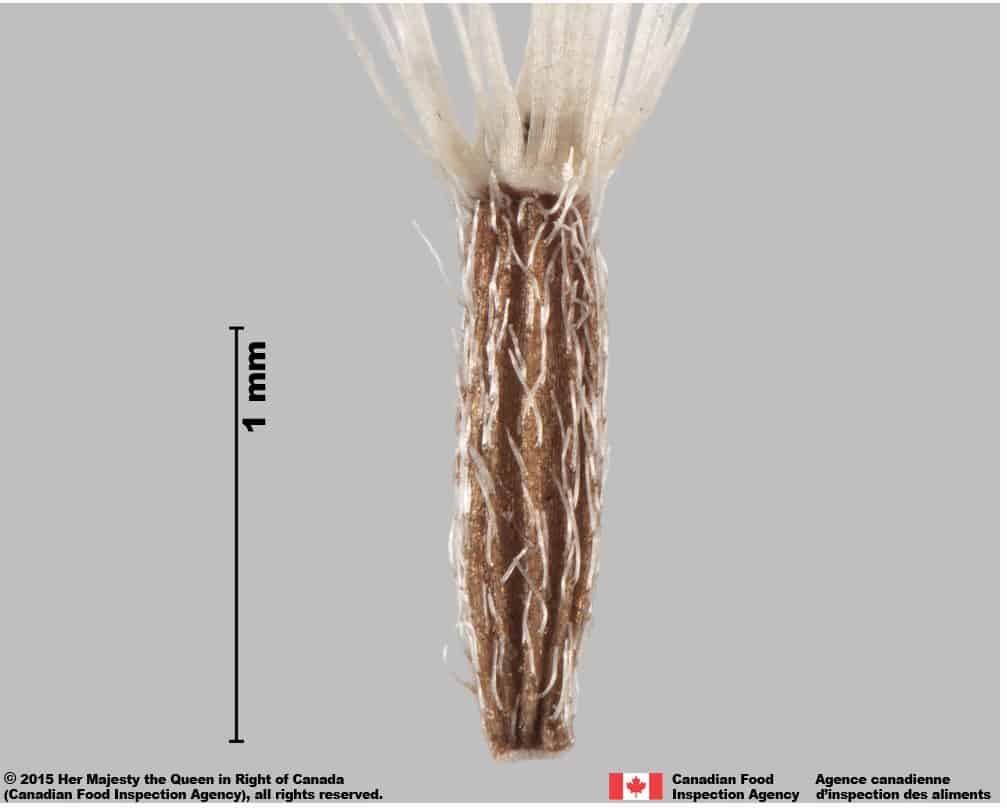
- A small, thin style remnant is in the center of truncate end surrounded by the pappus
Achene end without pappus
- Thin ring of white tissue at one end of the achene
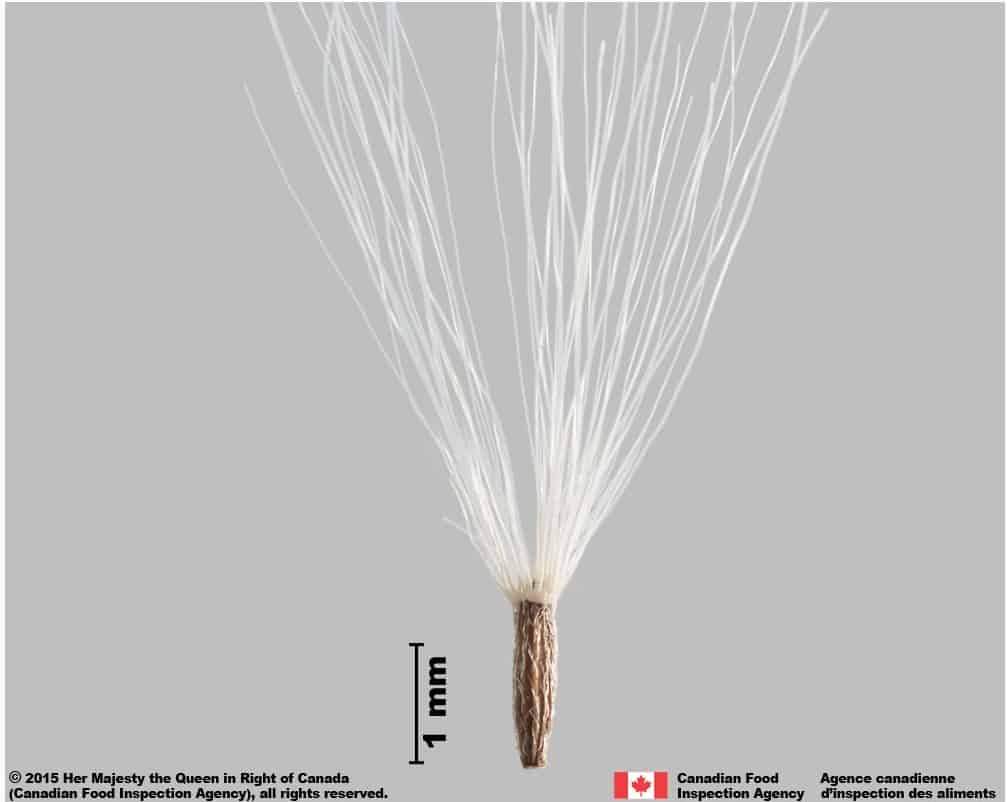

Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) achene with pappus
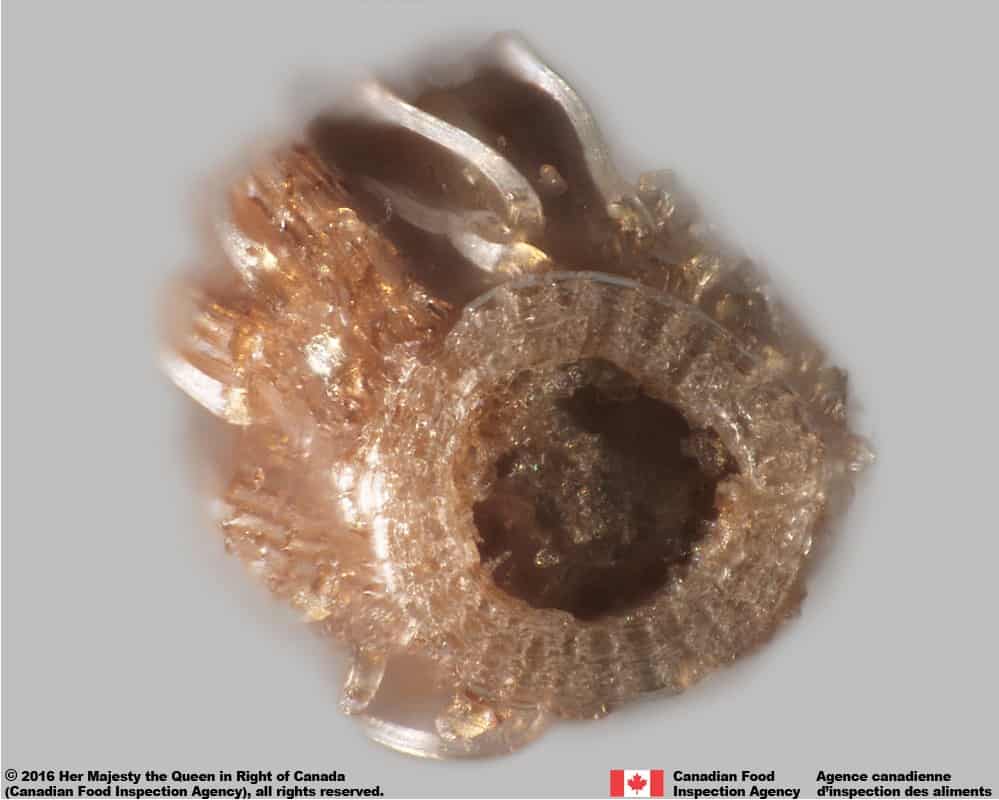




-
Seed
Size
- Seed size similar to achene size
Shape
- Seed oblong shape
Surface Texture
- Seed surface smooth
Colour
- Seed light yellow coloured
Other Features
- Seed coat thin, whitish coloured, adhering to the fruit wall
-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo fills the seed
Shape
- Embryo is spatulate, axial position
Endosperm
- Endosperm absent, nutritive tissue stored in the cotyledons
Other Features
- Embryo is soft-textured
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
The long white persistent pappus, long surface hairs and white ring of tissue on the end opposite the pappus are distinguishing features of P. britannicum achenes.

Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) achene with pappus



Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Flowers/Inflorescence
- Flowers yellow and daisy-like with both disc and ray florets (CABI 2020)
Vegetative Features
- Can reproduce vegetatively by creeping rhizomes (CABI 2020)
Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
Senecio vulgaris L. (common groundsel)
S. vulgaris achenes are larger (length*: 1.9 – 2.7 mm; width: 0.4 – 0.6 mm) they can be shades of reddish-brown, brown or grey and are narrowed at both ends. Pentanema britannicum achenes are medium brown coloured and do not narrow at the ends. S. vulgaris surface hairs are short and thick; the hairs on P. britannicum achenes are longer and thinner. S. vulgaris achenes do not have a white ring of tissue at the end of the achene opposite the pappus.
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 achenes in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces
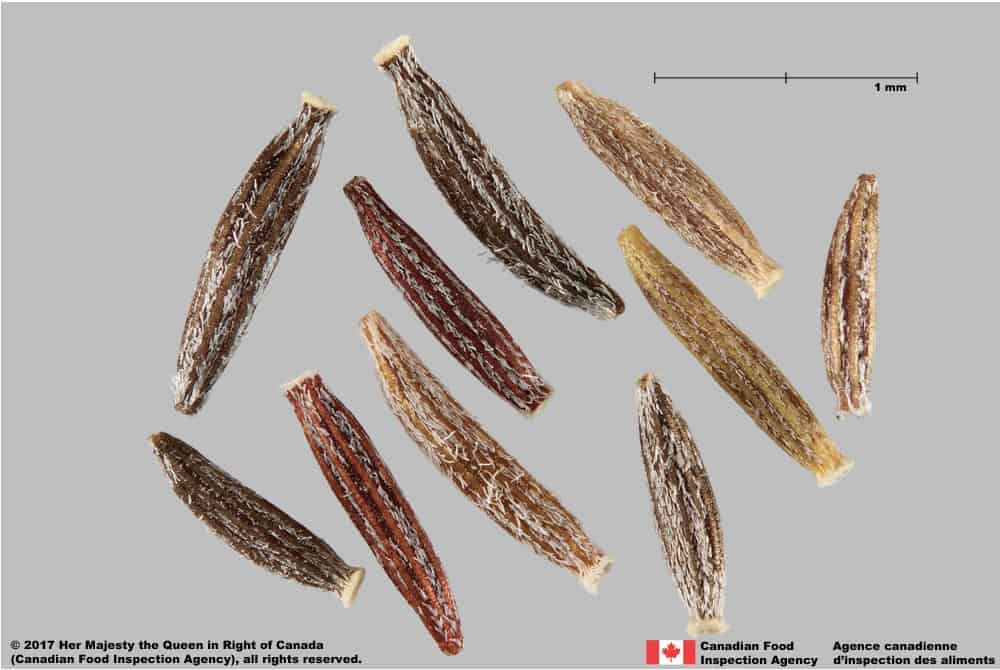

Senecio vulgaris
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Pentanema britannicum

Pentanema britannicum
Asteraceae
Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) achene with pappus
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Pentanema britannicum

Pentanema britannicum
Asteraceae
Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) achene with pappus
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Pentanema britannicum

Pentanema britannicum
Asteraceae
Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) immature achenes
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Pentanema britannicum

Pentanema britannicum
Asteraceae
Pentanema britannicum (British yellowhead) base of achene
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Senecio vulgaris

Senecio vulgaris
Asteraceae
Common groundsel (Senecio vulgaris) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Senecio vulgaris
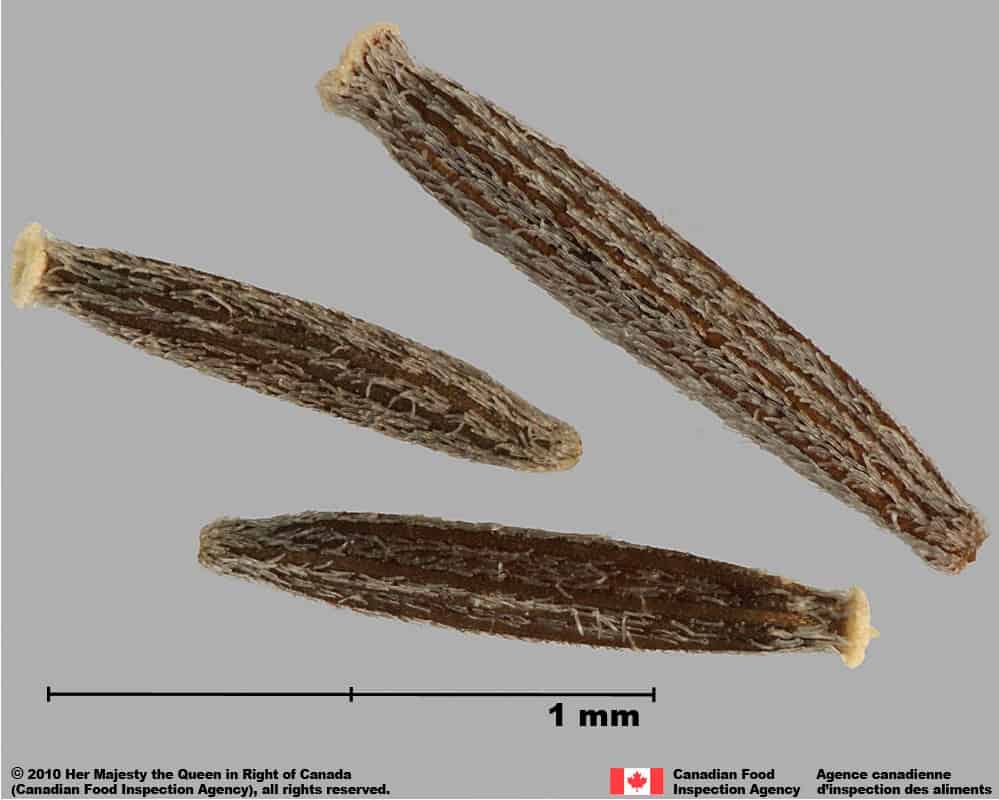

Senecio vulgaris
Asteraceae
Common groundsel (Senecio vulgaris) achenes
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Senecio vulgaris
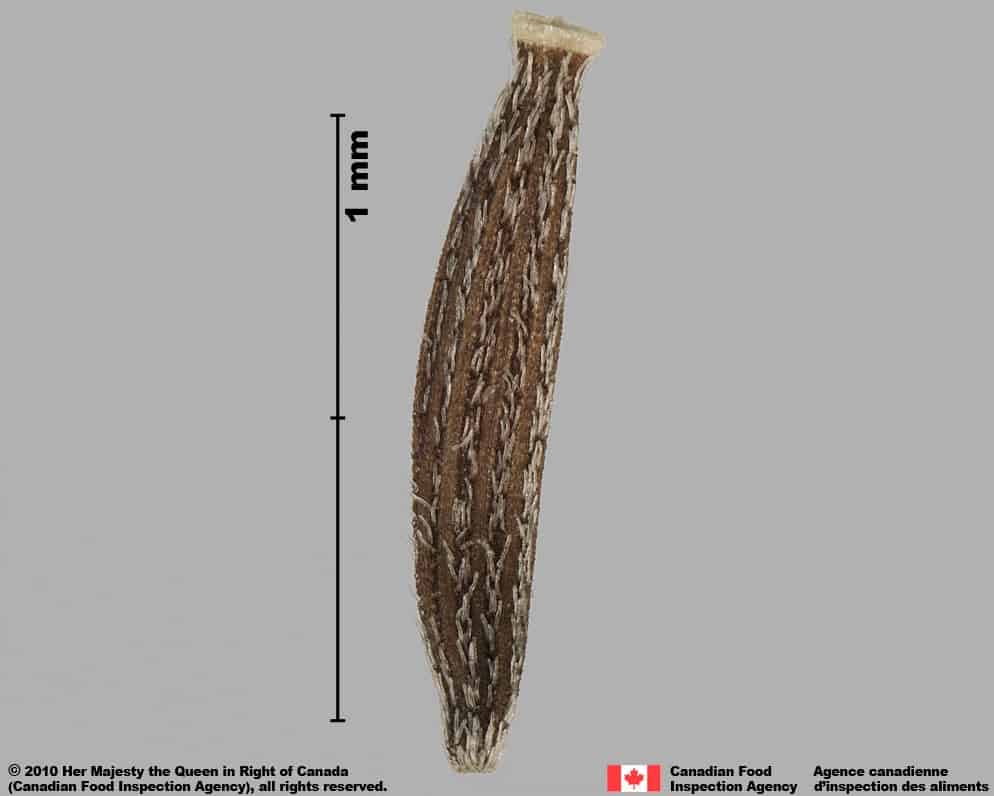

Senecio vulgaris
Asteraceae
Common groundsel (Senecio vulgaris) achene
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed October 15, 2020.
Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International (CABI). 2022. Invasive Species Compendium, CAB International, Wallingford, UK. https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/journal/cabicompendium Accessed October 13, 2020.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. Accessed December 29, 2022
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/10010617 Accessed December 29, 2022
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide.
Lehtonen, P. and Schall, R. A. 2000. Inula britannica L. (British elecampane) Weed Risk Assessment. USDA, APHIS, PPQ. 15 pp., http://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/plant_pest_info/weeds/ Accessed October 15, 2020.