Proboscidea louisianica
Explore More :
Explore plus :
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- Quarantine lists of countries e.g. India *may be updated without notice
Regulation Notes:
On quarantine lists of countries e.g. India*.
*Quarantine lists of countries may be updated without notice.
Distribution :
Répartition :
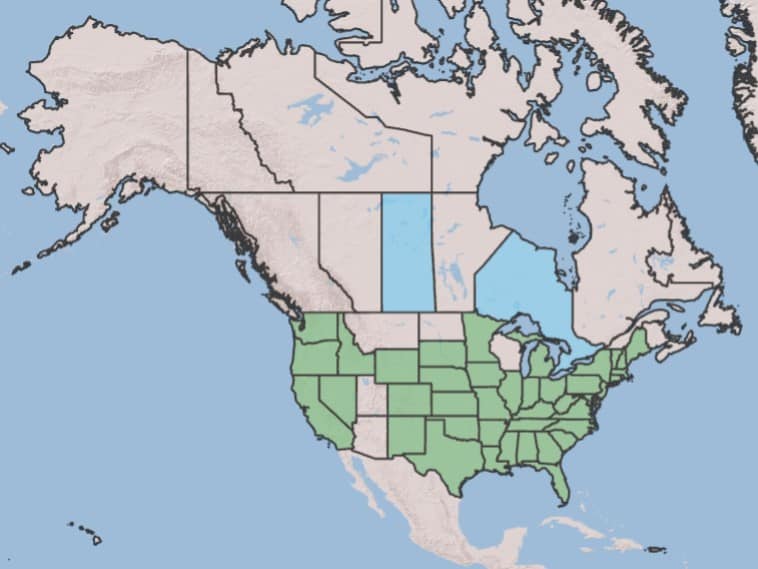
Devil’s claw is native to south-central North America (USDA-ARS 2017). Introduced to some parts of Africa, Australia and Europe (USDA-ARS 2017). It is widespread in the US, in every state except Arizona, Montana, North Dakota and Utah (USDA-NRCS 2017).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Devil’s claw occurs in cultivated fields, cultivated fallows, annual pastures, river flats, gardens, disturbed areas (Prostko and Chandler 1998; Parsons and Cuthbertson 2001; DiTomaso and Healy 2007; Thompson et al. 2009).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Seed
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Devil’s claw plants are covered in glandular hairs that secrete a putrid, sticky resin. The dried fruit has two long, sharp recurved claws which enable attachment and dispersal on livestock, people and machinery (Parsons and Cuthbertson 2001; DiTomaso and Healy 2007; Small 2013).
.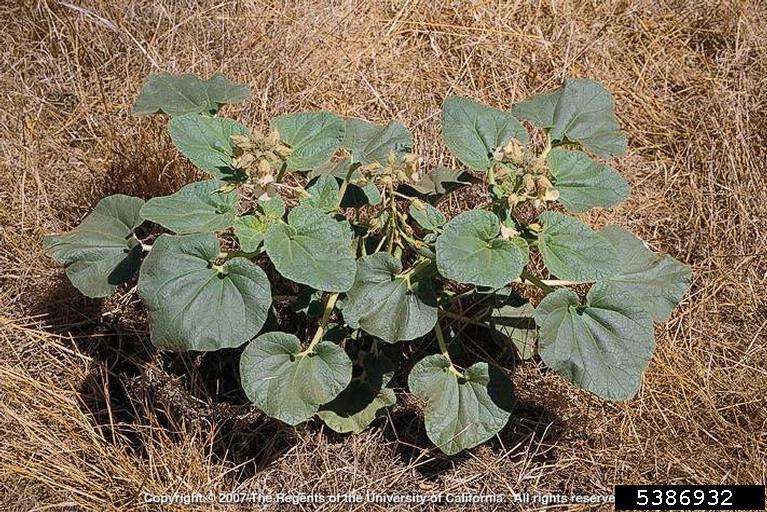
Proboscidea louisianica plant (Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
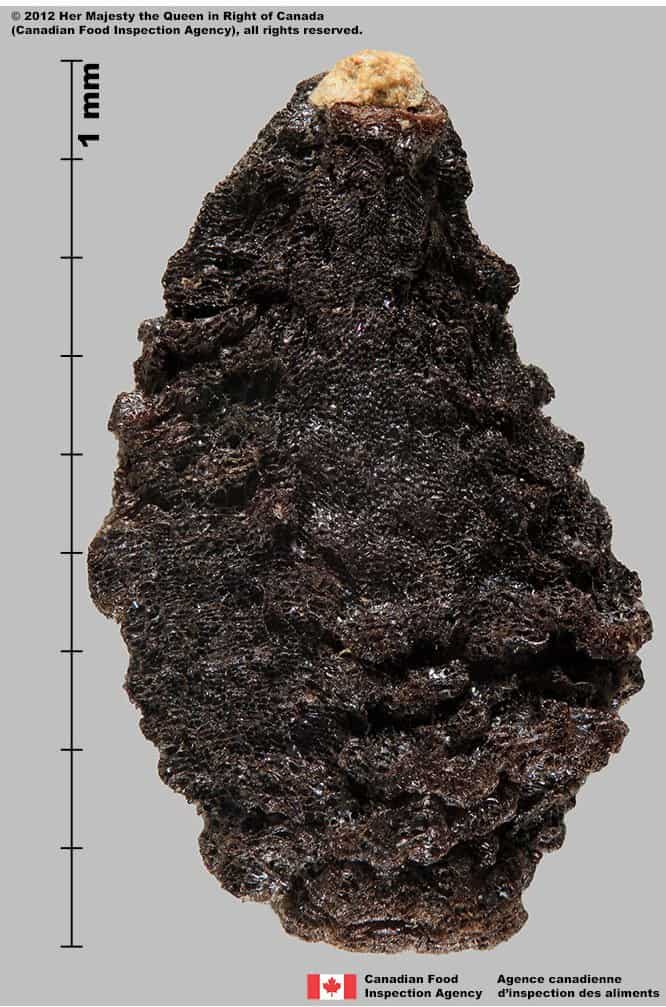
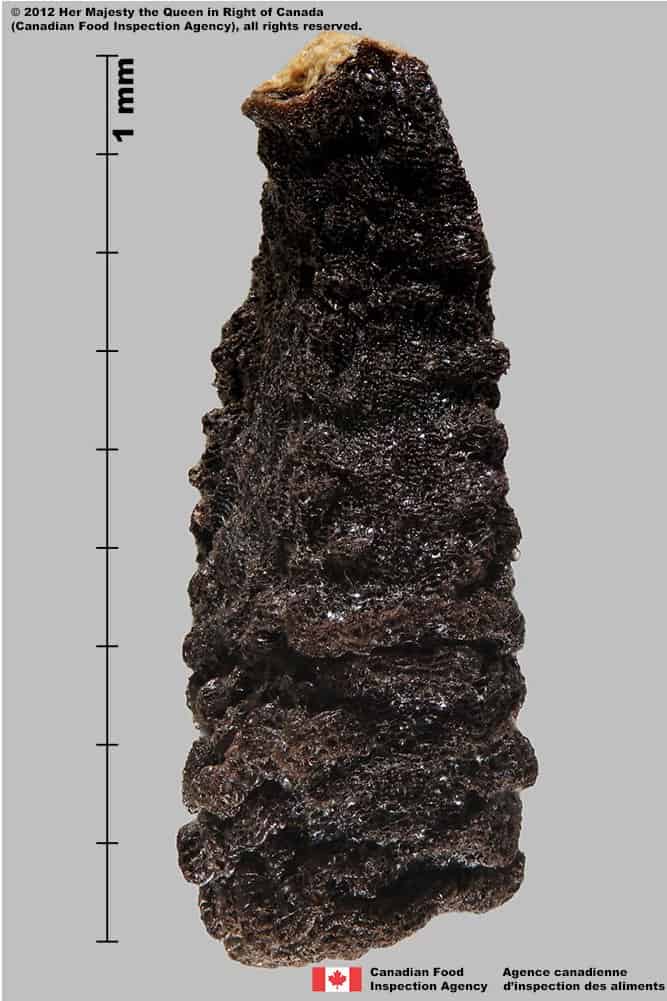
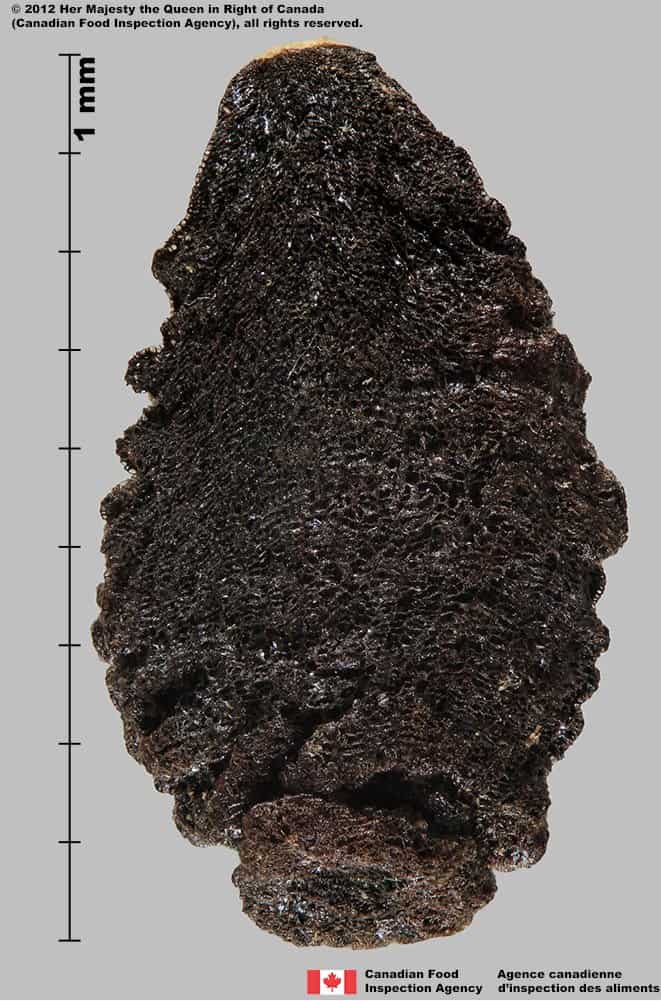
Seed
Size
- Seed length: 8.4 – 10.5 mm (average: 9.2 mm) ; width: 4.3 – 5.5 mm (average: 4.8 mm)
Shape
- Seeds are angularly egg-shaped with scalloped margins
- Seeds can be 2 to 5 sided
Surface Texture
- Seed has a bumpy, rough surface with tubercles
- Tubercles and seed surface are deeply pitted and porous
Colour
- Seed is dull and dark brown to black in colour
- When viewed under a magnification, parts of some seeds are covered with a thin, glittery crust
Other Features
- Hilum is at the narrow end of seed
- Inner part beneath the thick seed coat is white
- When pressed with forceps the inner tissue of seed is oily
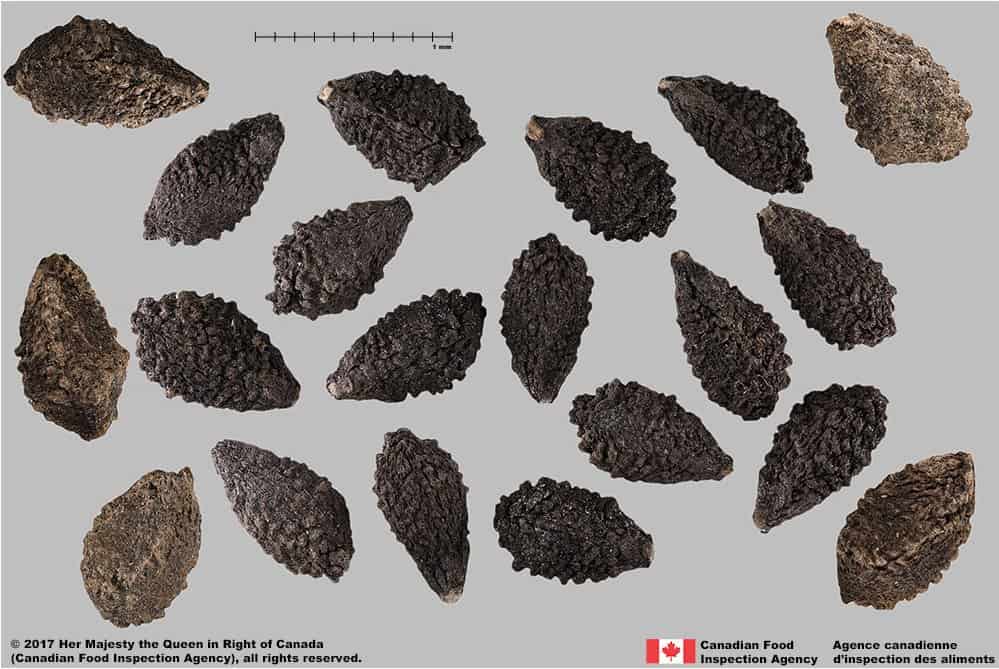

Devil’s claw (Proboscidea louisianica) seeds




Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
Ibicella lutea (yellow unicorn plant)
Ibicella lutea plant seeds are a similar shape, length (average length: 9.5 mm), and dark brown colour with white inner tissue as devil’s claw.
Ibicella lutea plant seeds can be wider (average width: 6.2 mm) than those of devil’s claw, with surfaces that are less bumpy and pitted. Under magnification the seed surface may have stratified layers that are brown or mixed white with brown. The hilum is at the end of an obvious bump on one side of the seed and is further away from the narrow end than on devil’s claw seed.
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces
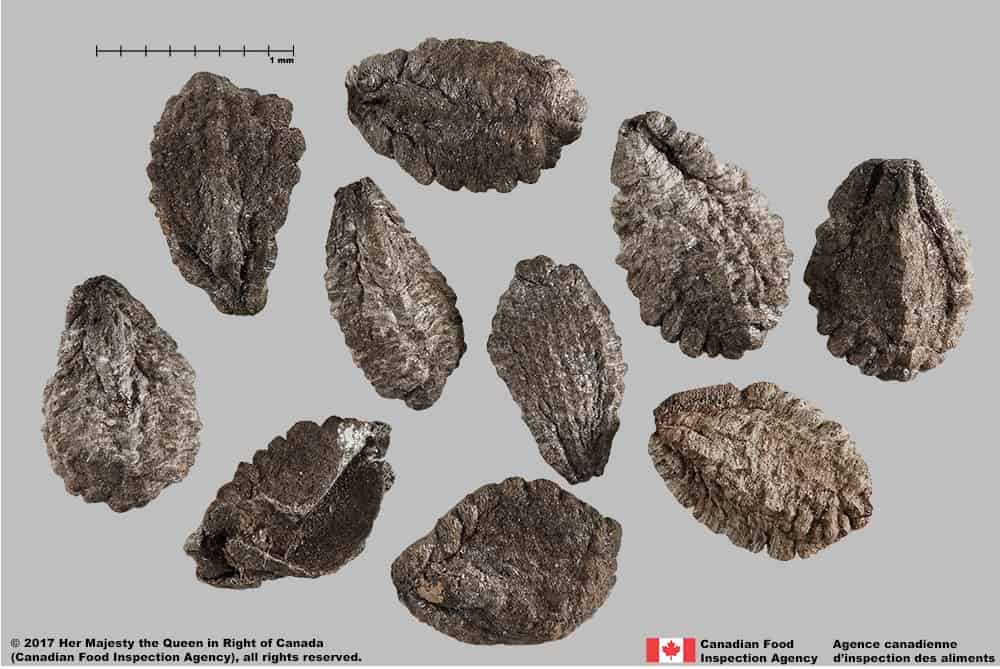

Ibicella lutea
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Proboscidea louisianica

Proboscidea louisianica
Martyniaceae
Devil’s claw (Proboscidea louisianica) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Proboscidea louisianica

Proboscidea louisianica
Martyniaceae
Devil’s claw (Proboscidea louisianica) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Proboscidea louisianica

Proboscidea louisianica
Martyniaceae
Devil’s claw (Proboscidea louisianica) seed; side view
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Proboscidea louisianica

Proboscidea louisianica
Martyniaceae
Devil’s claw (Proboscidea louisianica) seed
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Ibicella lutea

Ibicella lutea
Martyniaceae
Yellow unicorn plant (Ibicella lutea) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Ibicella lutea
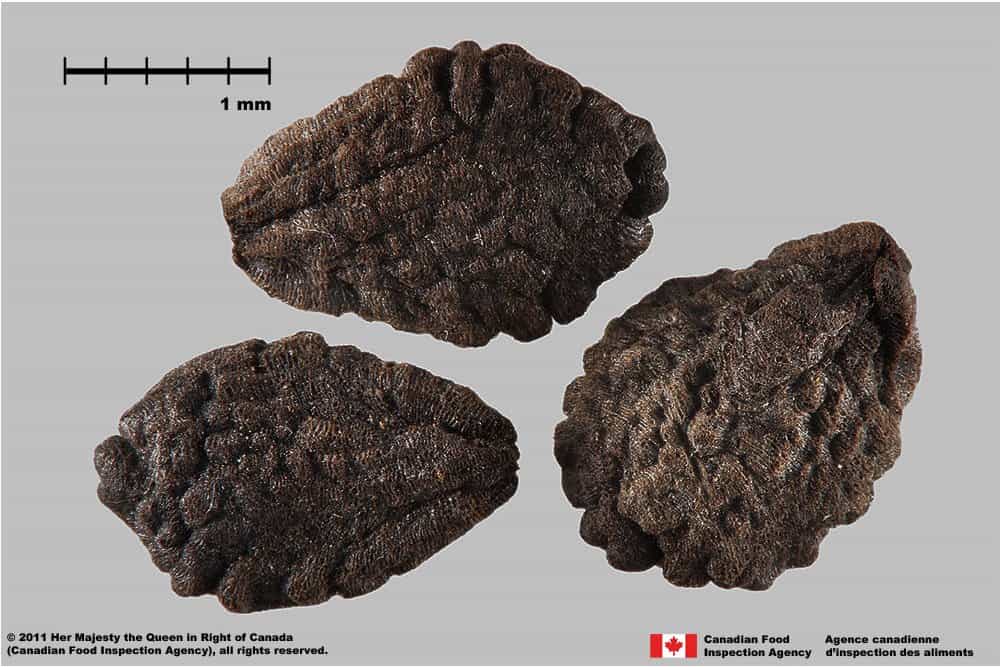

Ibicella lutea
Martyniaceae
Yellow unicorn plant (Ibicella lutea) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Ibicella lutea
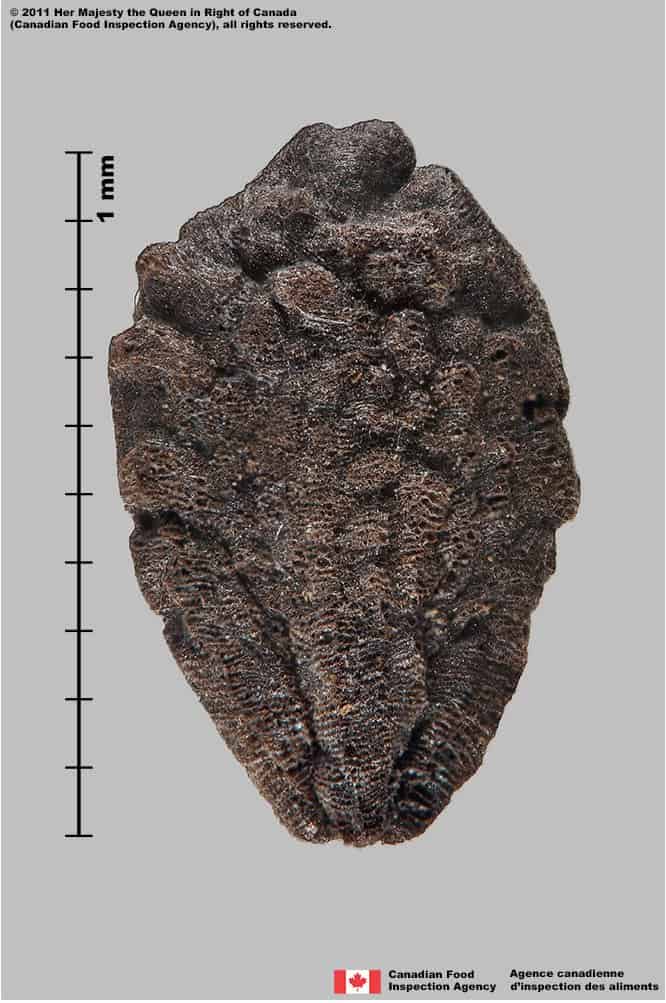

Ibicella lutea
Martyniaceae
Yellow unicorn plant (Ibicella lutea) seed
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Ibicella lutea
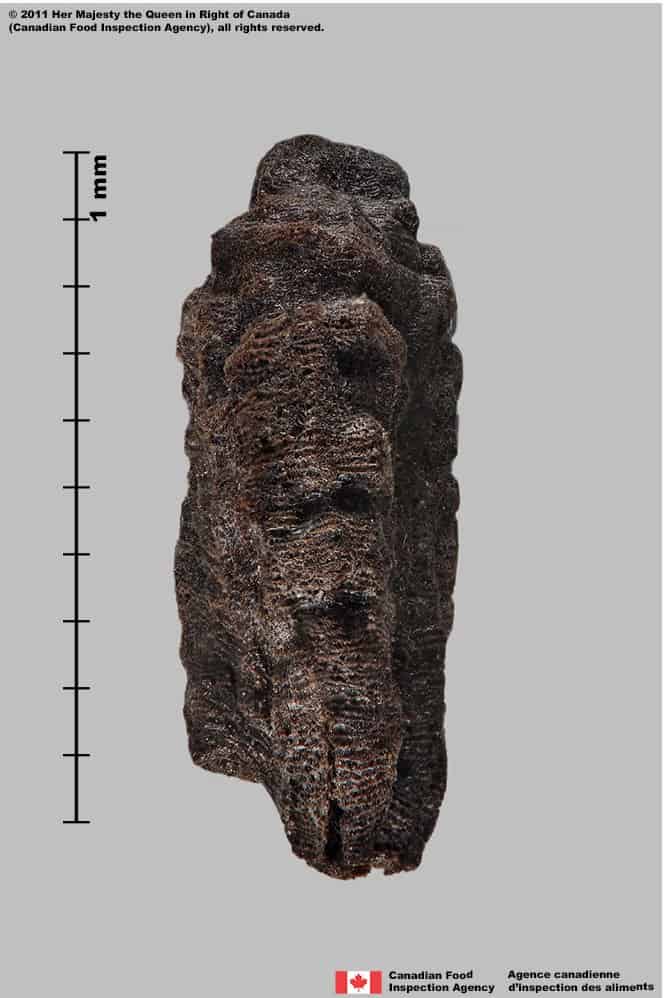

Ibicella lutea
Martyniaceae
Yellow unicorn plant (Ibicella lutea) seed; side view
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
DiTomaso, J.M. and Healy, E.A. 2007. Weeds of California and other Western States. University of California, Oakland, California.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/2703746 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Parsons, W.T. and Cuthbertson, E.G. 2001. Noxious weeds of Australia, second edition. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, Victoria, Australia.
Prostko, E.P. and Chandler, J.M. 1998. Devil’s-claw (Proboscidea louisianica) and smellmelon (Cucumis melo var. dudaim) control in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) with pyrithiobac. Weed Technology 12:19-22.
Small, E. 2013. North American cornucopia: top 100 indigenous food plants. CRC Press Boca Raton, Florida. 793 pp.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2017. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysearch Accessed April 25, 2017.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2017. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. https://plants.usda.gov/home Accessed April 25, 2017.