Solanum emulans
Explore More :
Explore plus :
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
Regulation Notes:
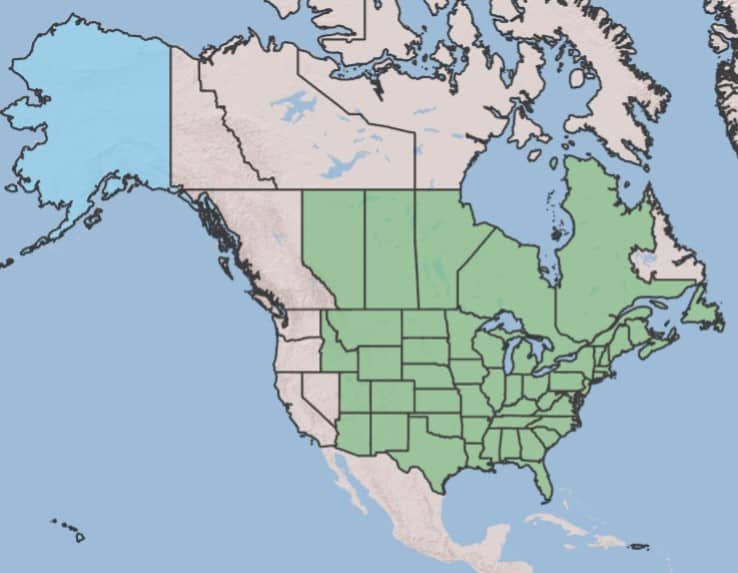
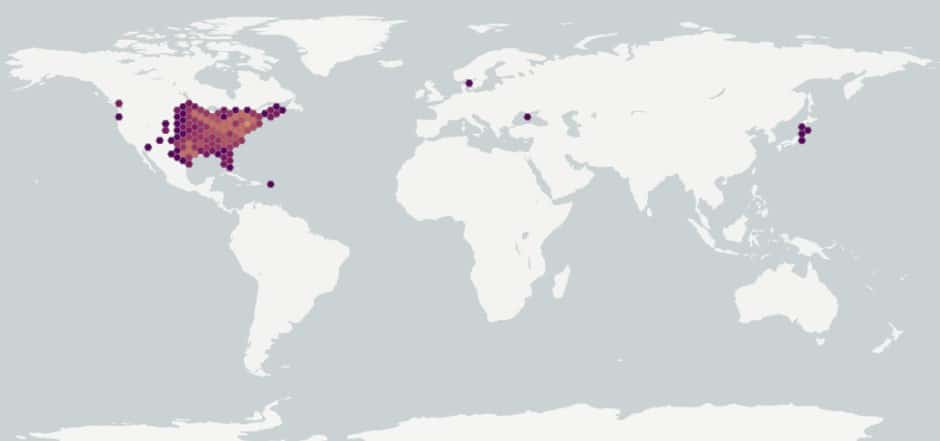
Distribution :
Répartition :
This species is native to North America, introduced to eastern Asia and northern Europe (GBIF 2017; USDA-ARS 2017). It is widespread in the United States, except for Washington, Oregon, Nevada and California, where it is not present (USDA-NRCS 2017).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Eastern black nightshade grows in cultivated fields, gardens, shores, thickets, open forests, roadsides and disturbed areas (Darbyshire 2003).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Annual
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Seed
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Eastern black nightshade, along with American black nightshade (S. americanum) and black nightshade (S. nigrum) represent the Canadian species of the ‘nightshade complex’ and are difficult to distinguish due to similar characteristics (Bassett and Munro 1985).
.Identification
Identification
-
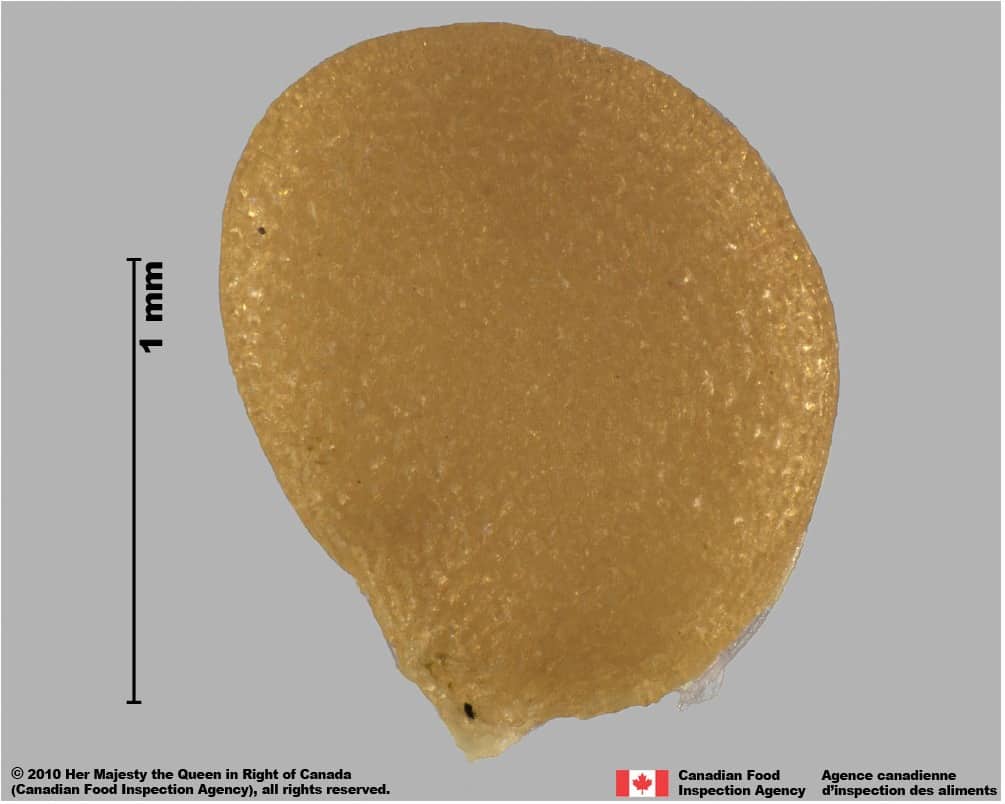
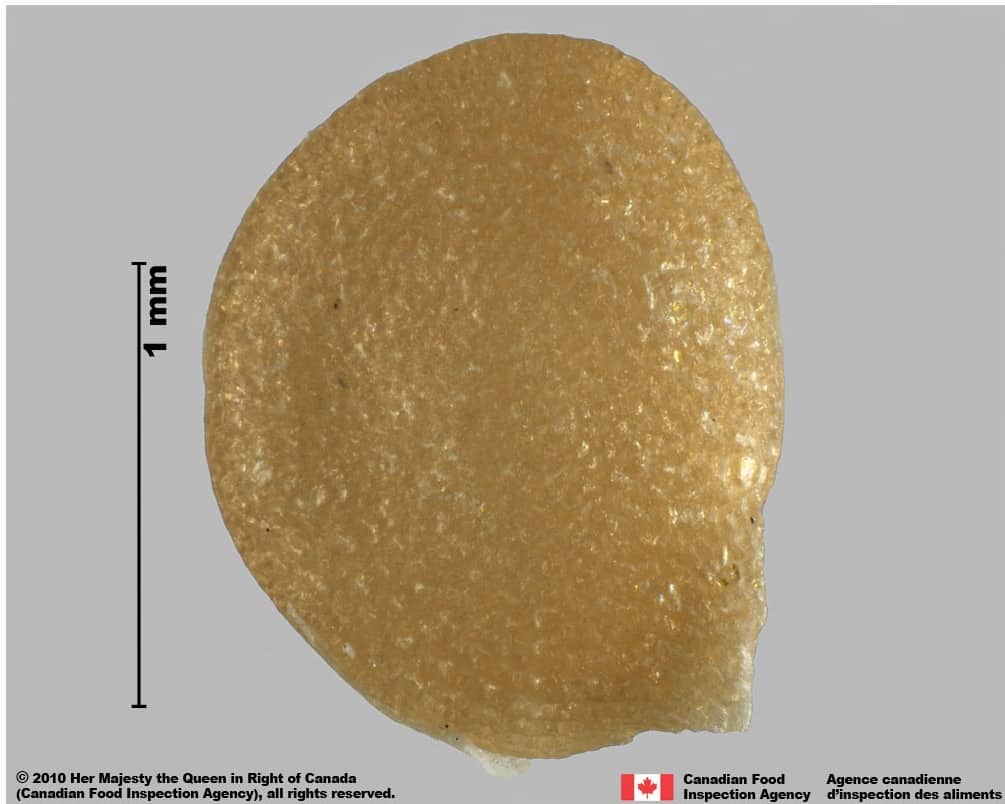
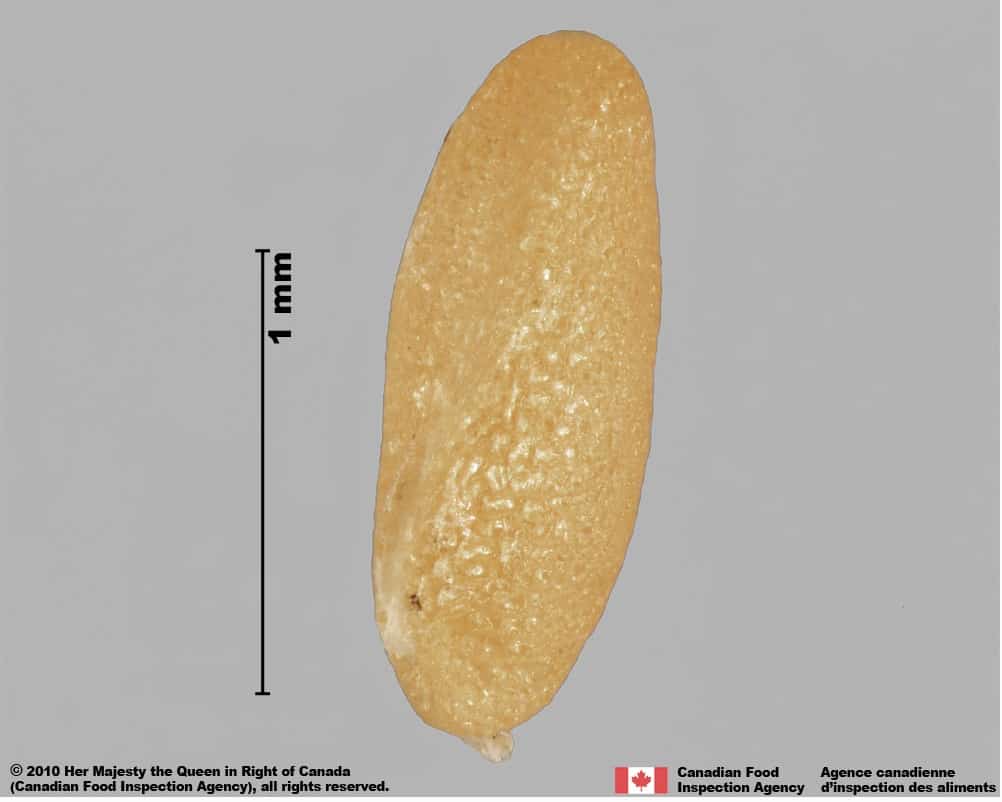
Seed
Size
- Seed length: 1.3 – 1.6 mm (average 1.4 mm); width: 0.9 – 1.3 mm (average 1.1 mm)
Shape
- Seed is round to oval shape with a hilum end tapered to a short ‘beak’, flattened
Surface Texture
- Seed surface is strongly reticulated with small, straight or wavy-edged interspaces
- The reticulation near the hilum has elongated cells
Colour
- Seed is light yellow, slightly shiny
Other Features
- Hilum is a thin slit along the margin
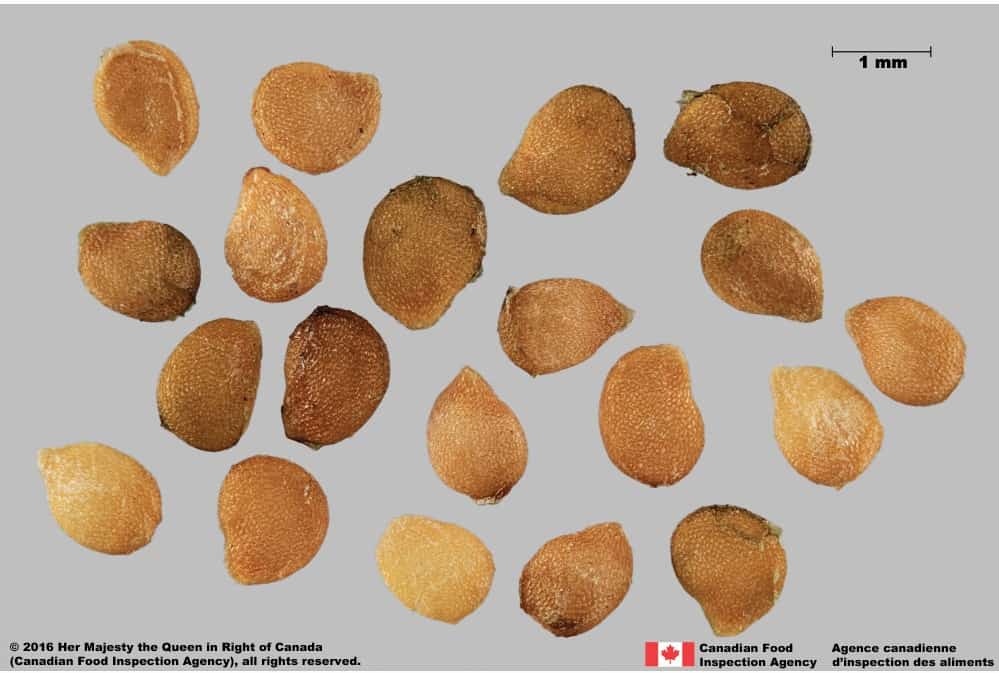

Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seeds







Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
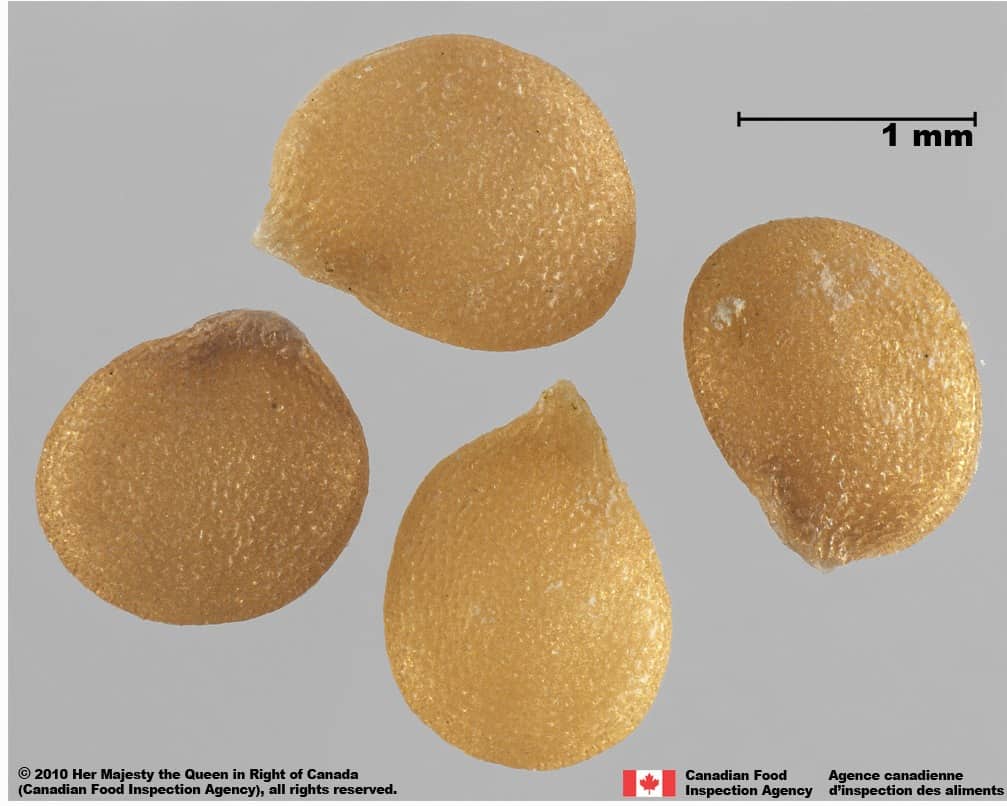
Solanum nigrum (black nightshade)
Black nightshade seeds have a similar flattened shape, tapered ‘beak’ at the hilum, yellow colour, and small-celled surface reticulation that elongates at the hilum.
Black nightshade seeds are generally larger than eastern black nightshade (average length: 1.7 mm; width: 1.3 mm), oval-shaped, with more shallow interspaces in the centre of the seeds. The interspaces of eastern black nightshade are a uniform depth across the seed. The ‘beak’ near the hilum appears more prominent than in eastern black nightshade seeds.
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces
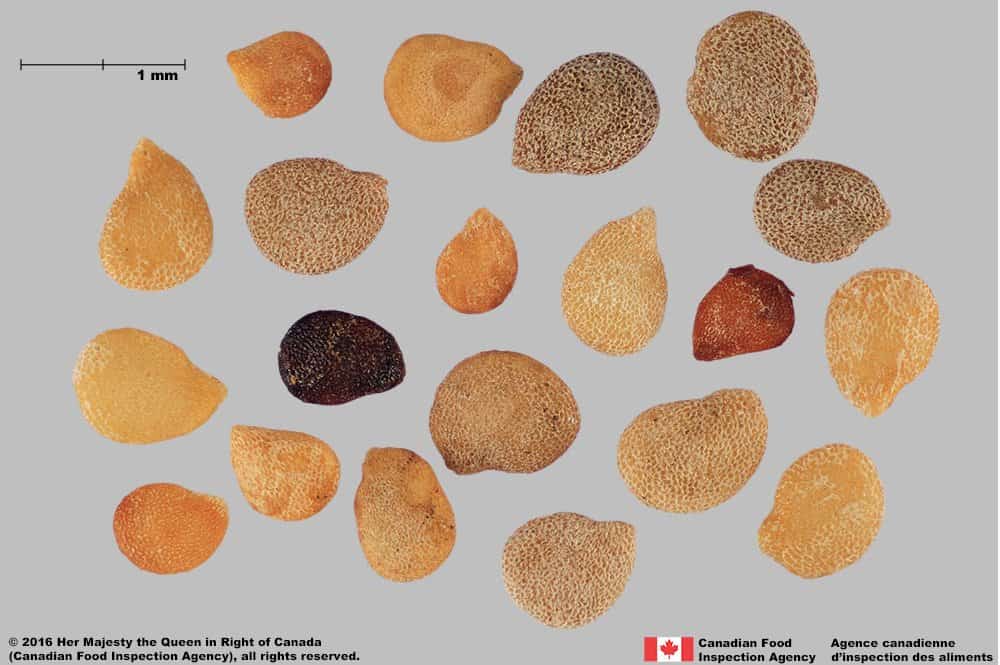

Solanum nigrum
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
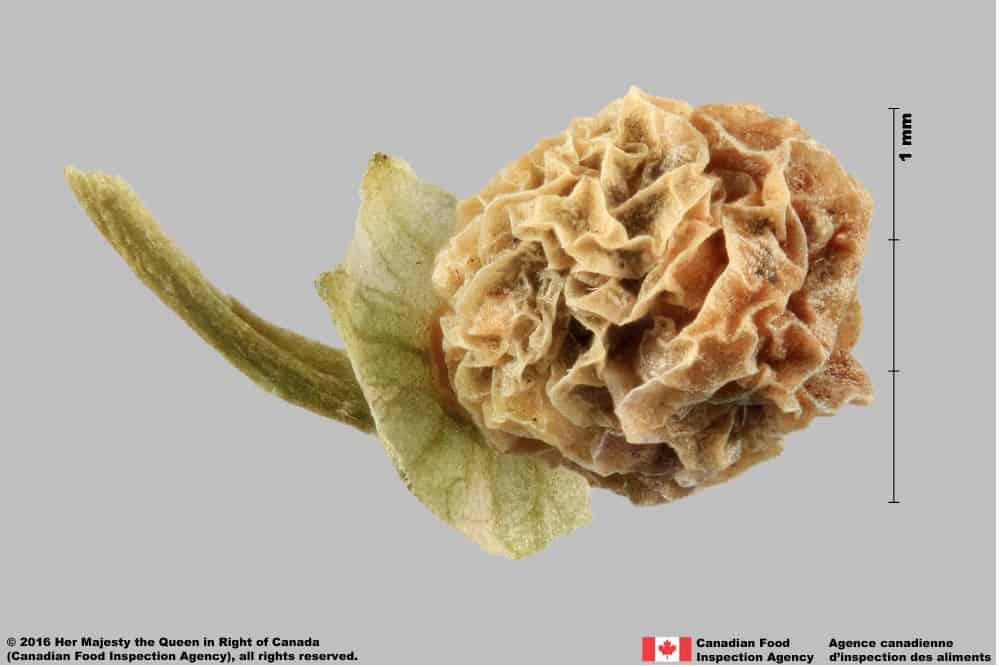
Solanum emulans (eastern black nightshade) berry
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Solanum emulans

Solanum emulans
Solanaceae
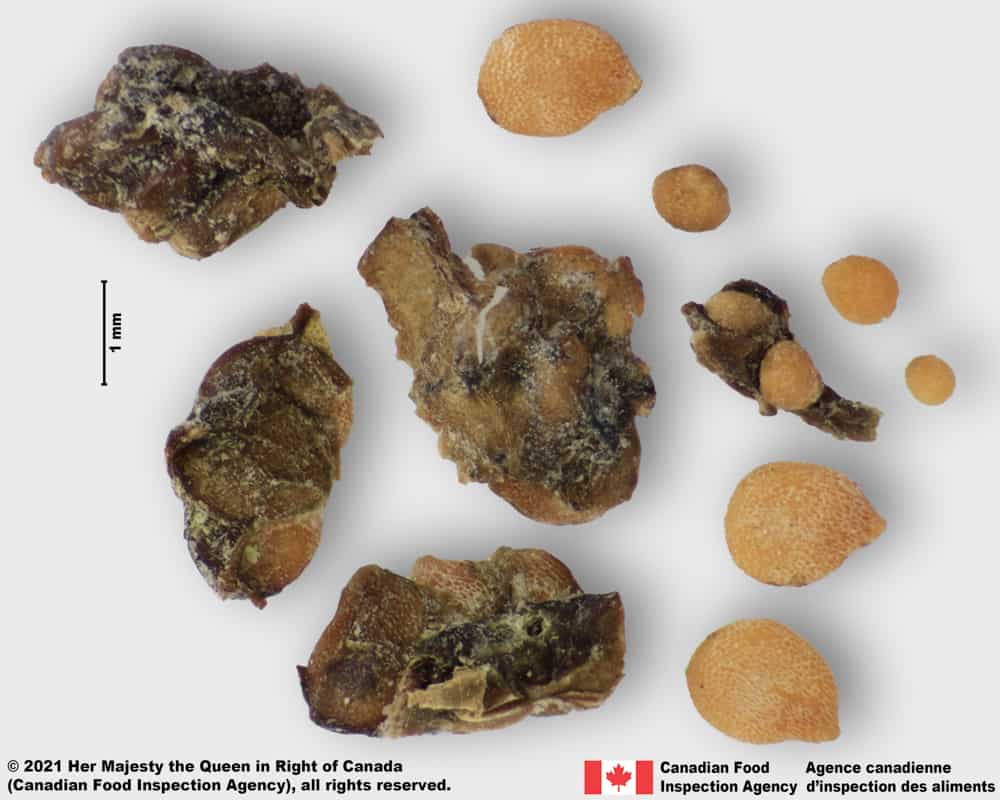
Solanum emulans crushed berry with seeds and stone cells
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Solanum nigrum

Solanum nigrum
Solanaceae
Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Solanum nigrum

Solanum nigrum
Solanaceae
Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) seeds
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Solanum nigrum
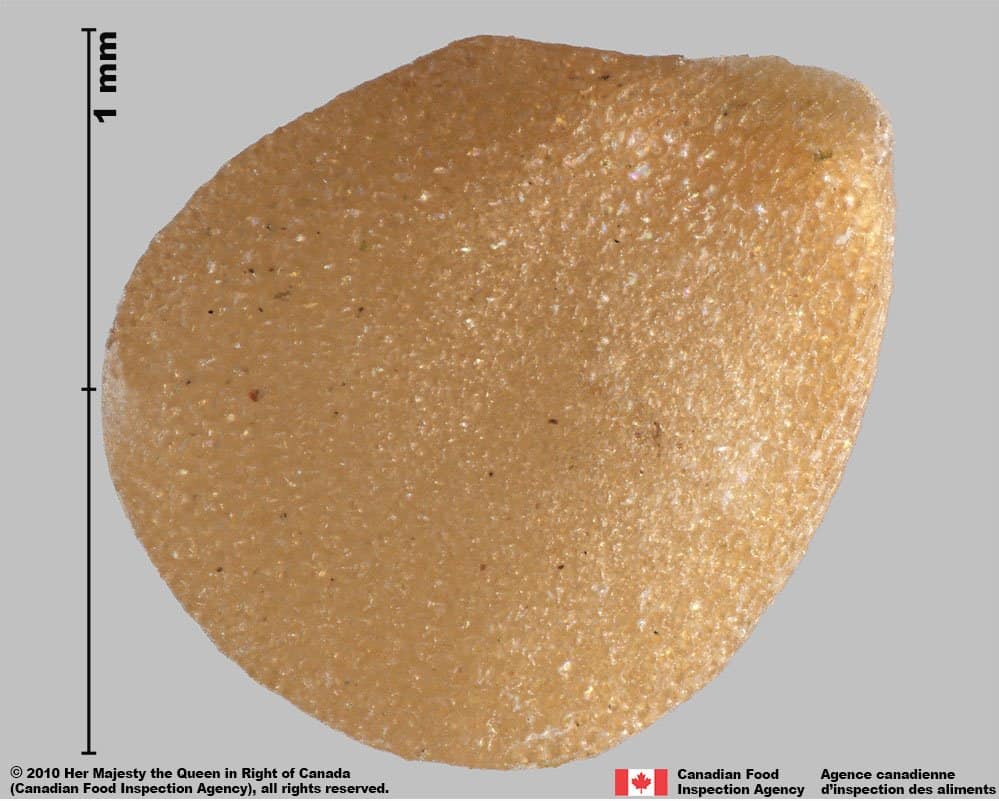

Solanum nigrum
Solanaceae
Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) seed
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Solanum nigrum
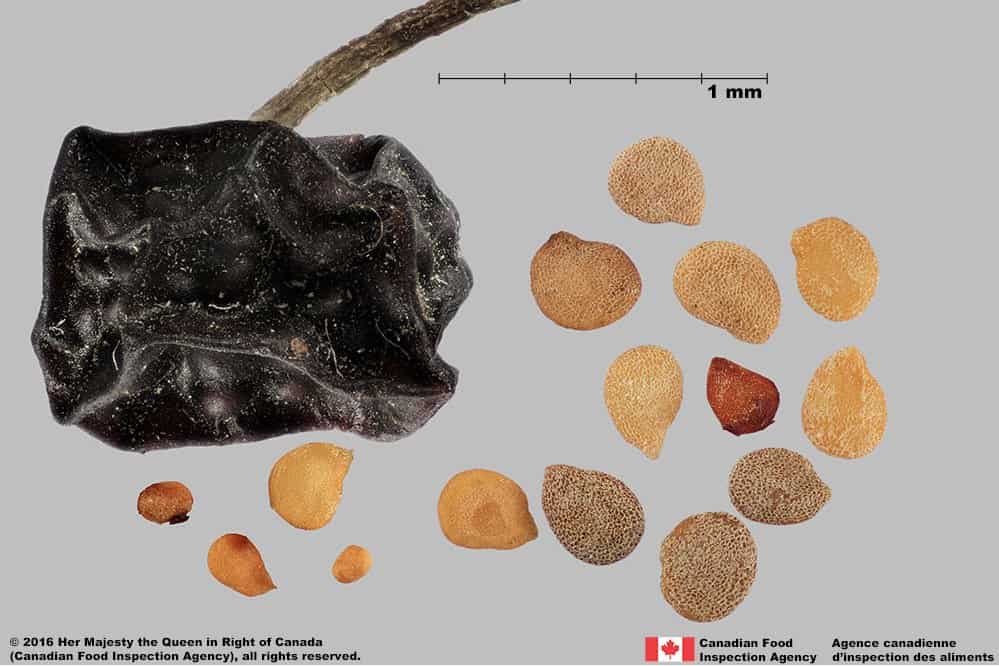

Solanum nigrum
Solanaceae
Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) berry and seeds
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Bassett, I.J. and Munro, D.B. 1985. The biology of Canadian weeds. 67. Solanum ptycanthum Dun., S. nigrum L. and S. sarrachoides Sendt. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 65:401-414.
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat 2017, GBIF Home Page. https://www.gbif.org Accessed April 25, 2017.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/3801688 Accessed December 29, 2022.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2017. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysearch Accessed April 25, 2017.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2017. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. https://plants.usda.gov/home Accessed April 25, 2017.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2022. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. http://plants.usda.gov Accessed December 29, 2022