Elymus repens
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 2: Primary Noxious Weed Seeds
Regulation Notes:
Distribution :
Répartition :
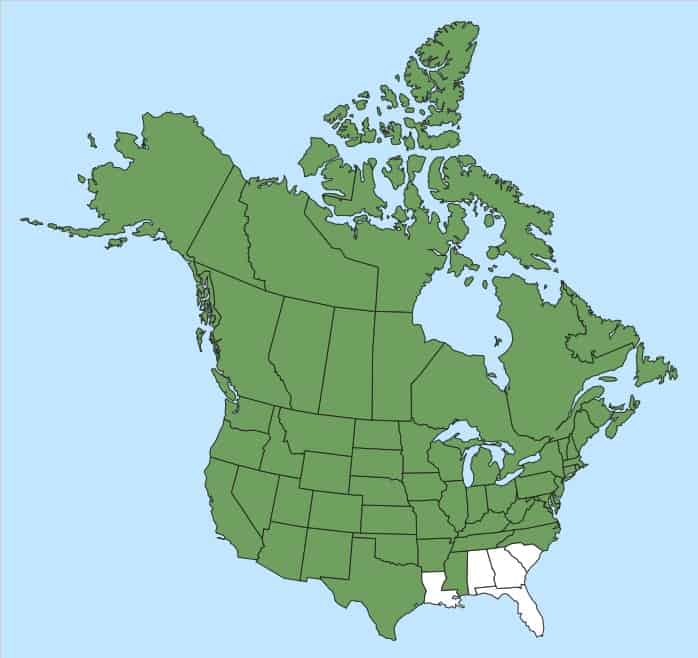
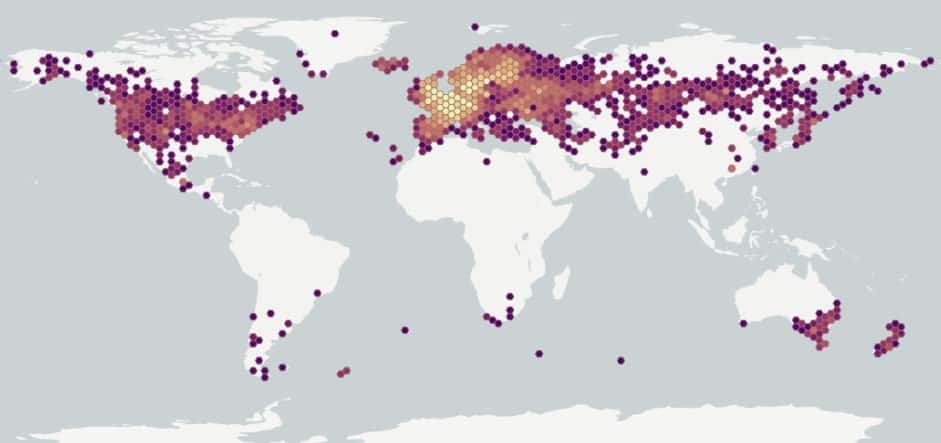
Exact native range obscure; however, likely native to northern Africa, Europe, temperate Asia, northern India and Pakistan. Introduced in other parts of Africa, North America, Argentina, Chile, Australia and New Zealand (USDA-ARS 2021). Occurs throughout the United States, except for some regions in the southeast (Kartesz 2015). Occurs in every province and territory in Canada (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Cultivated fields, pastures, old fields, cattle yards, river flats, roadsides, railway lines, and other disturbed areas (Darbyshire 2003; CABI 2021). A weed of all cultivated crops (Royer and Dickinson 1999).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Perennial
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Floret
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Elymus repens seed production is relatively low, from 25-400 per stem (Timling 2000). Seed can remain viable in the soil for up to 5 years (Timling 2000). E. repens also reproduces rapidly by rhizomes, which can be spread in soil (CABI 2021).
.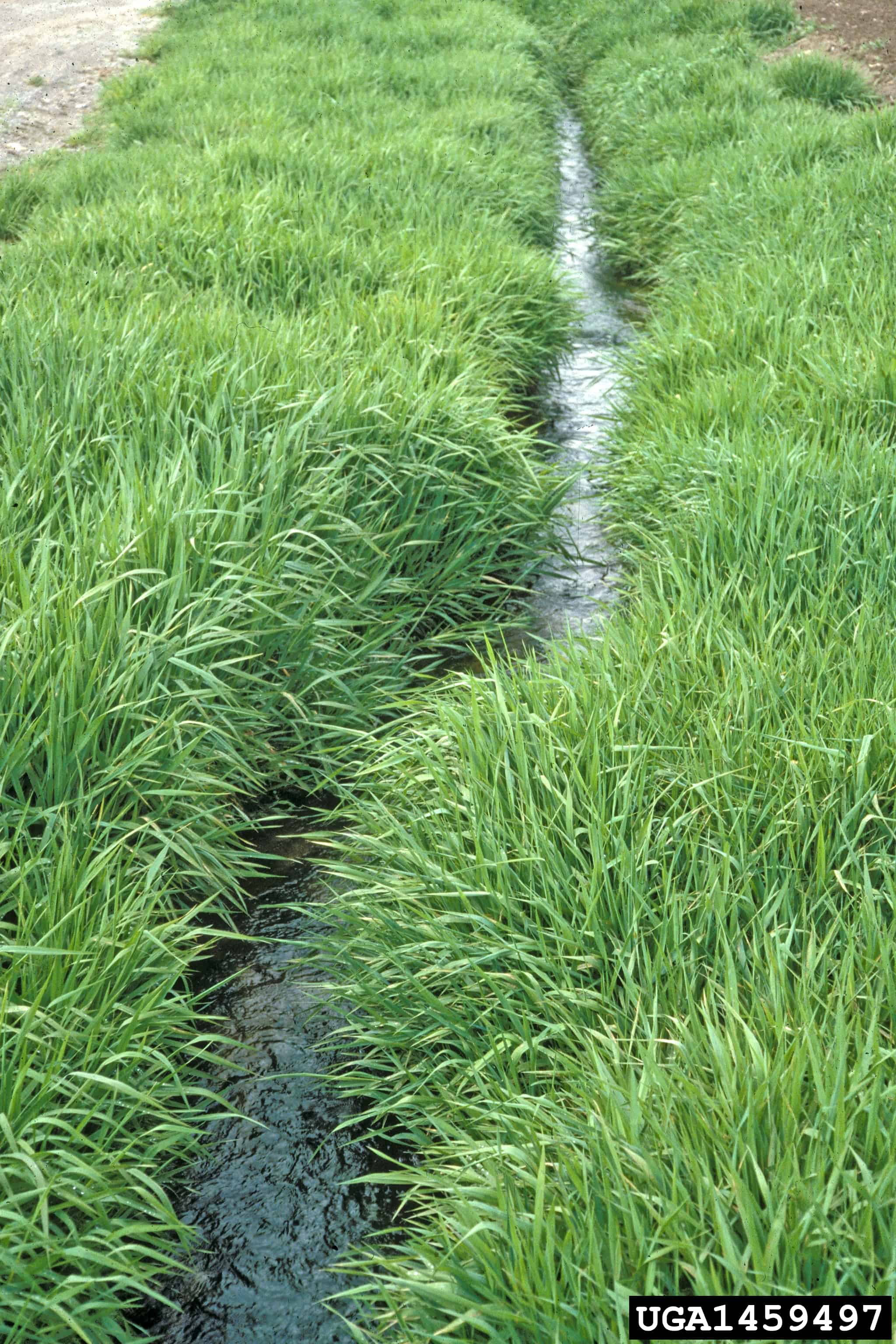
Elymus repens infestation (Steve Dewey, Utah State University, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
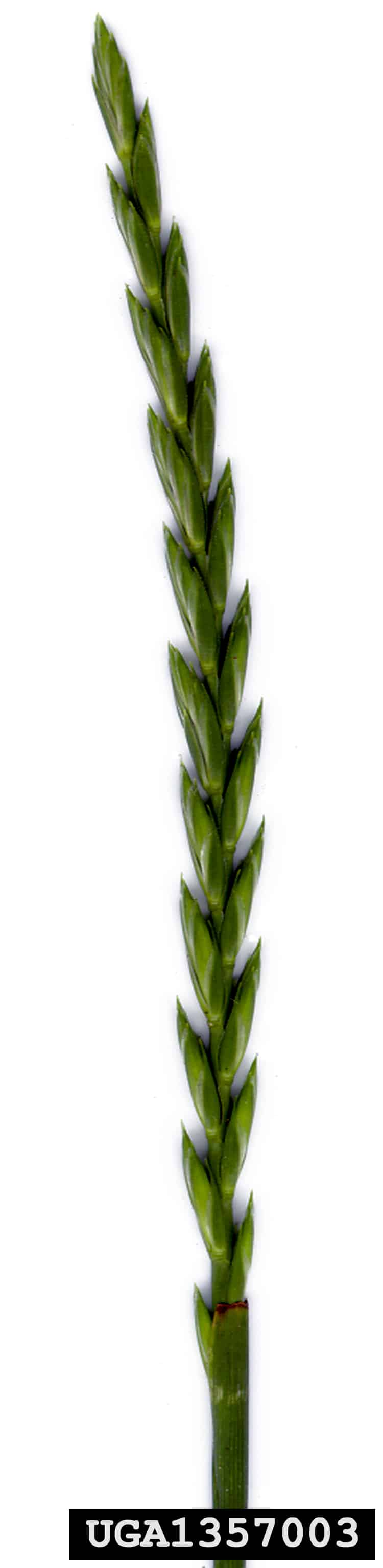
Spikelet
Size
- Spikelet length 10.0 – 27.0 mm (Barkworth et al. 2007)
Shape
- Spikelet oval or wedge-shaped
Surface Texture
- Spikelet surface is smooth textured with longitudinal ridges
Colour
- Spikelet is shiny straw-yellow coloured
Other Features
Glume awn
- Glumes are unawned or awned to 3.0 mm (Barkworth et al. 2007)
Other features
- Spikelet has 4 – 7 florets (Barkworth et al. 2007)
- Base of spikelet is truncate
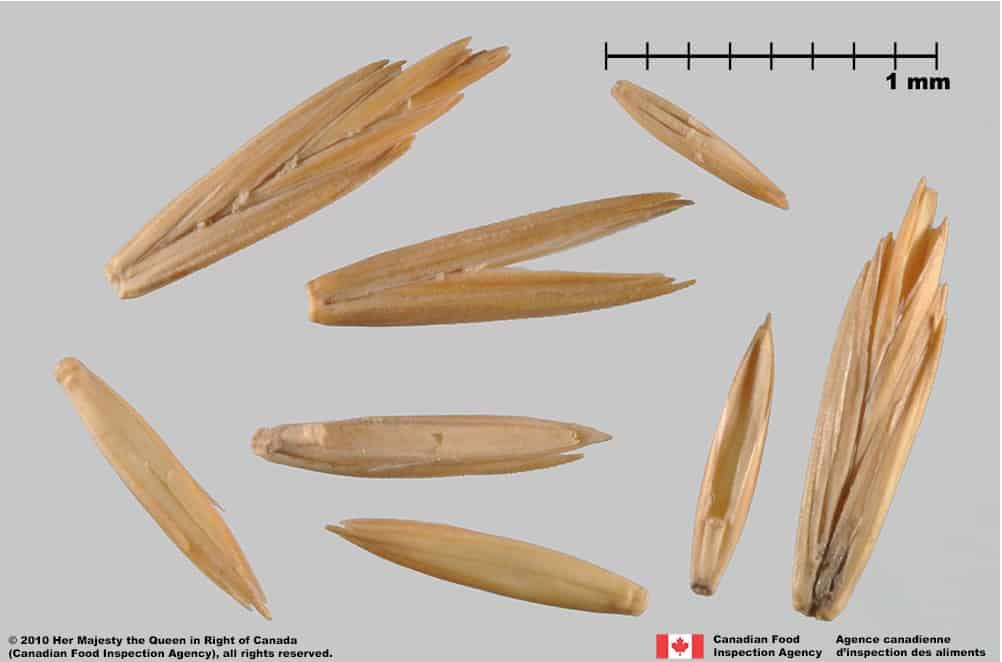

Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) spikelets and florets

-
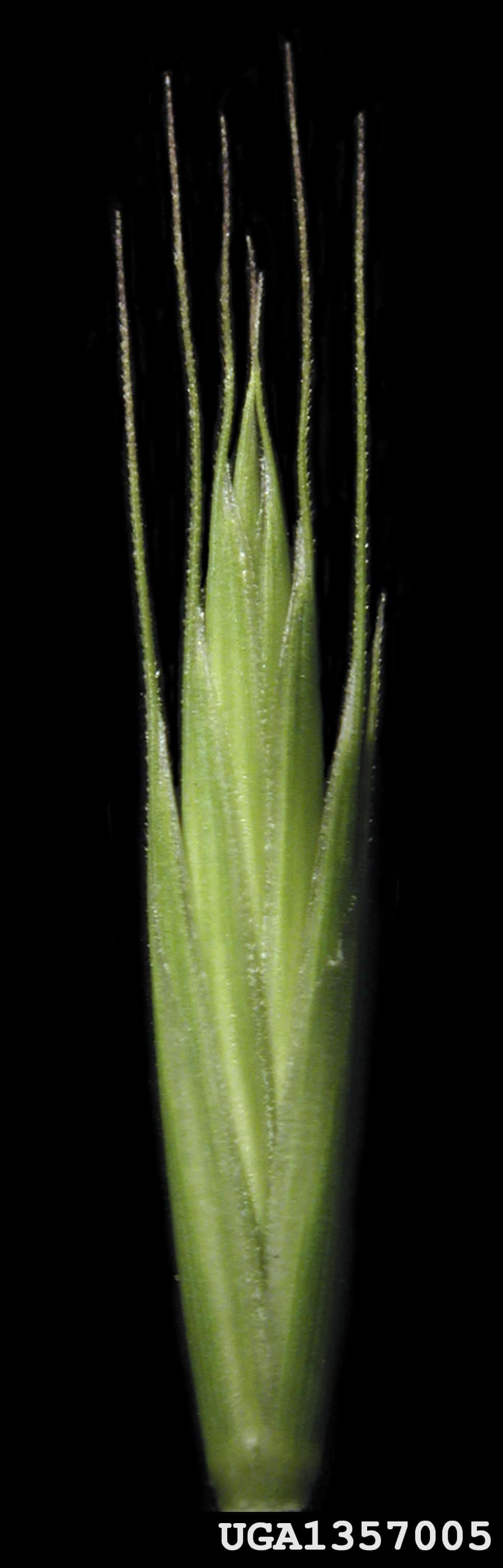
Floret
Size
- Floret length*: 7.1 – 11.0 mm; width: 1.3 – 1.6 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 florets in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Floret is narrow oval shaped, with a concave palea
Surface Texture
- Floret surface is smooth or sparsely granular textured
Colour
- Floret is shiny straw-yellow coloured
Other Features
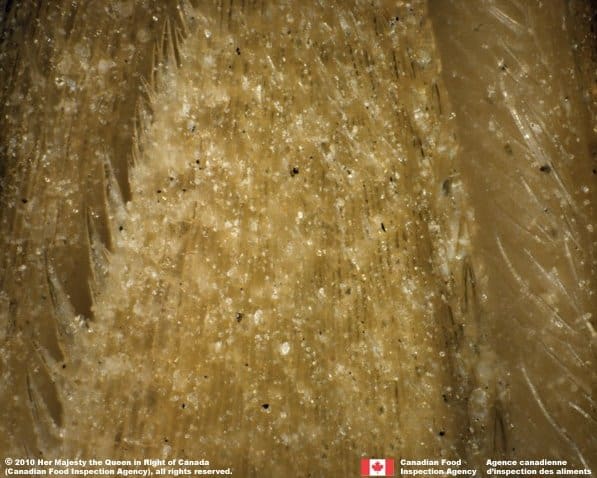
Lemma awn
- Lemma generally unawned, but may have a short awn 0.2 – 4.0 mm long (Barkworth et al. 2007)
Callus and Rachilla
- The rachilla has parallel sides
- Rachilla is from a U-shaped sinus
- No hairs across the callus
Other Features
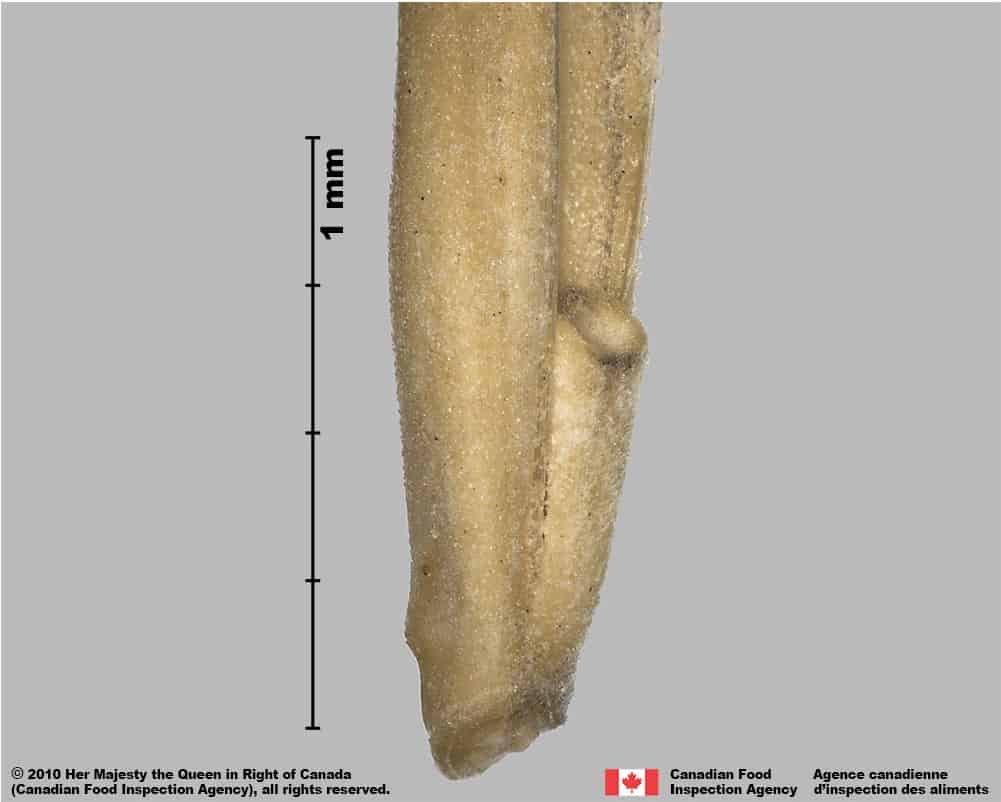
- A distinctive bump is on the lemma above the callus
- The palea teeth are short, generally spaced apart and have a wide base
- The lemma surface is generally smooth, and the palea and rachilla are generally more granular

Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) spikelets and florets
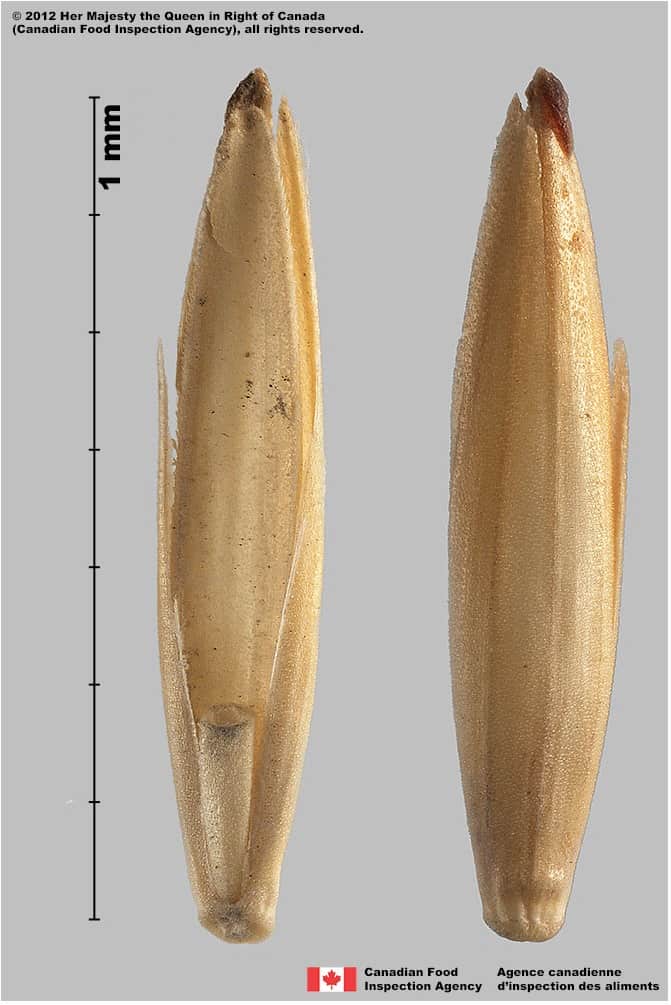
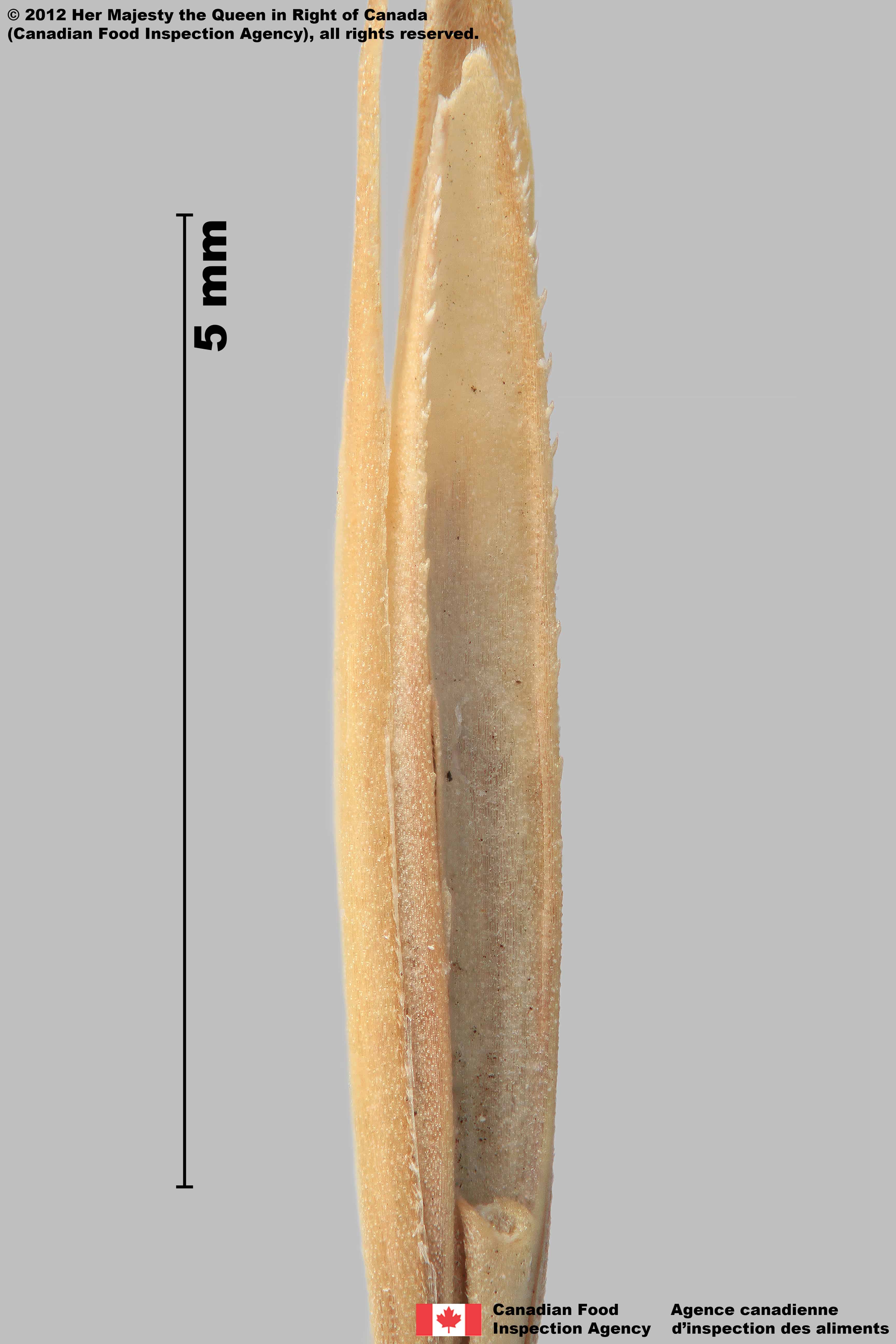
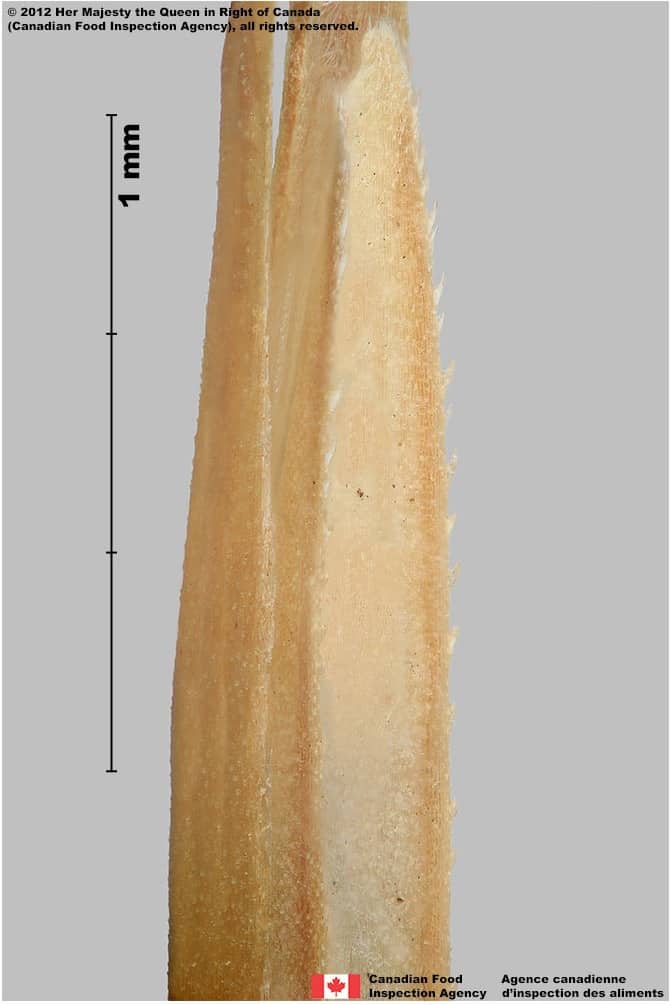






-
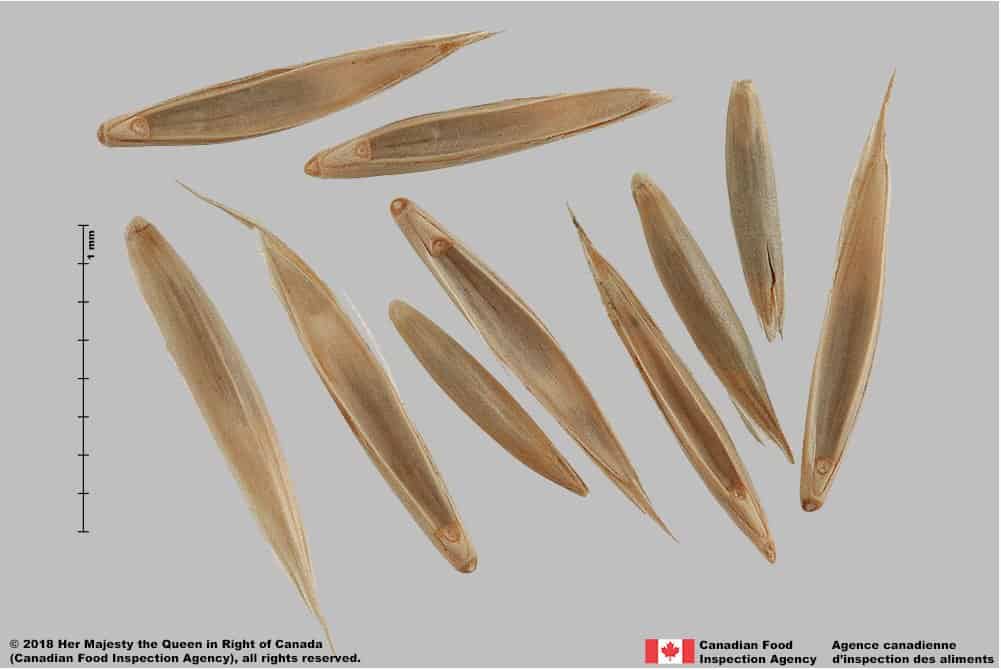
Caryopsis
Size
- Caryopsis length*: 3.8 – 5.0 mm; width: 1.0 – 1.6 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 caryopses in a normal range of this species using specimen measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Caryopsis is long oblong shaped with a pointed embryo end
Surface Texture
- Caryopsis surface is smooth textured
Colour
- Caryopsis is light brown, reddish brown or purplish coloured
Other Features
- Hilum is a long, black line on the side of the caryopsis opposite the embryo
-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo is a rudimentary size compared to the caryopsis
Shape
- Embryo is oval or wedge-shaped, in a lateral position at one end of the caryopsis
Endosperm
- Endosperm is hard and opaque white coloured
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
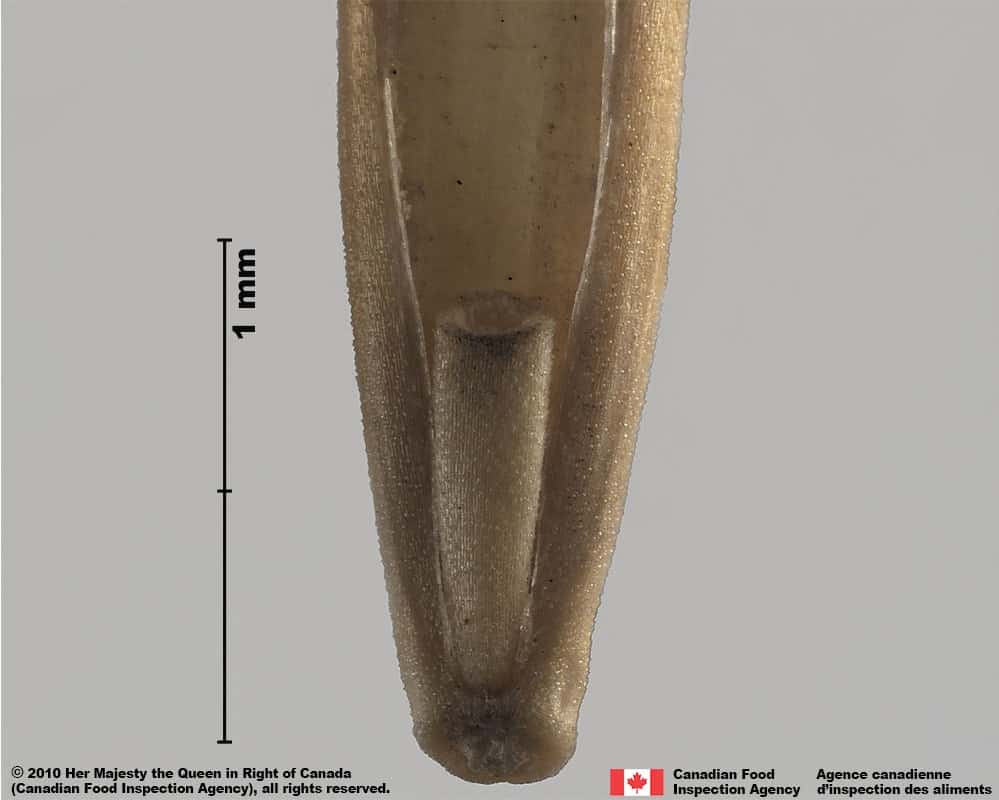
Florets of Elymus repens look similar to other Elymus species and Pascopyrum smithii and generally need magnification to see the distinguishing features. The florets can be distinguished by a combination of: a shiny straw-yellow lemma, a parallel-sided rachilla, U-shaped sinus, large palea teeth and no hair on the callus.

Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, palea view L, lemma view R





Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
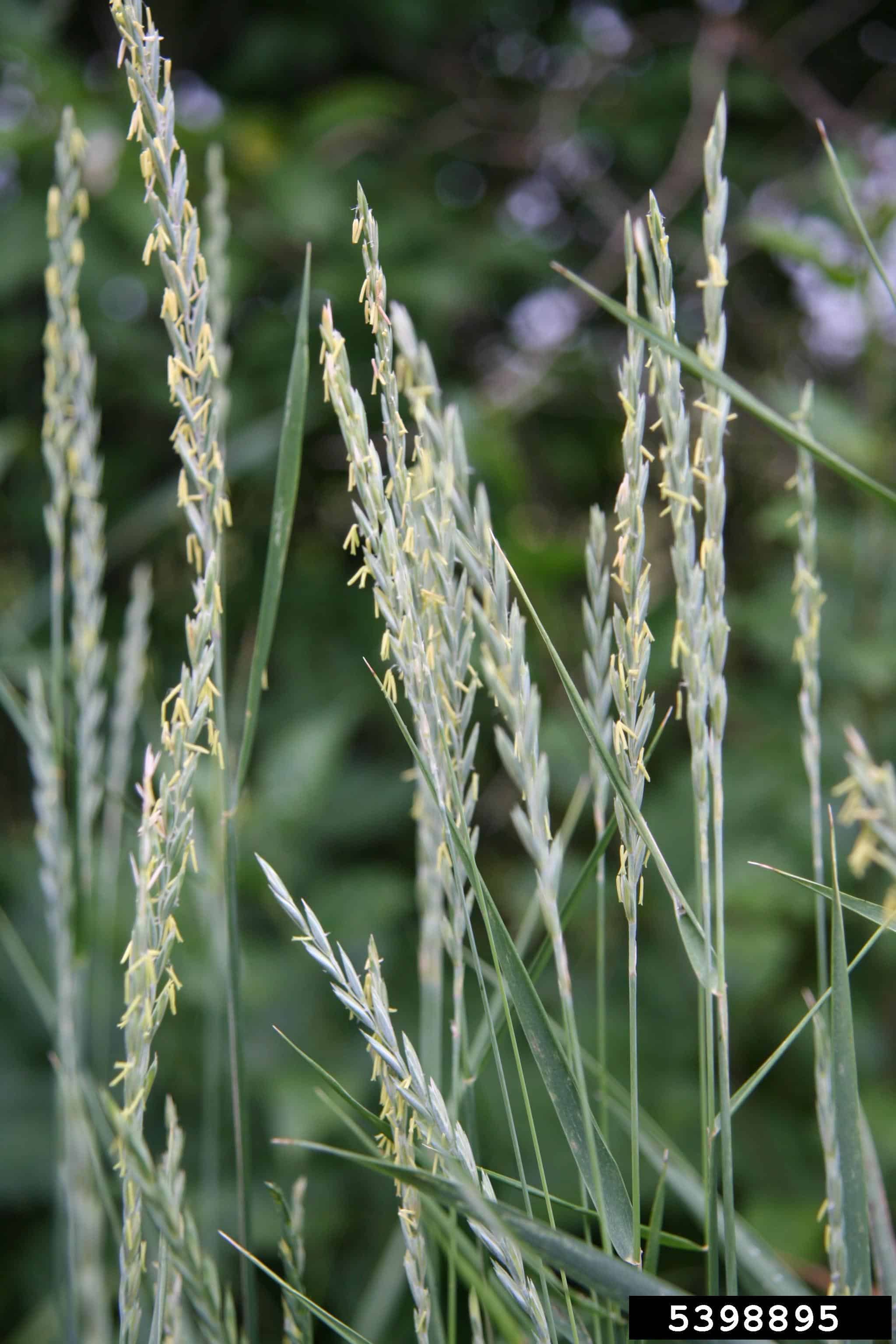

Elymus repens (Robert Vidéki, Doronicum Kft., Bugwood.org)




Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
Pascopyrum smithii (Rydb.) Barkworth & D. R. Dewey (western wheatgrass)
P. smithii florets are generally larger (length*: 7.6 – 13.0 mm; width: 1.2 – 1.8 mm), have a transverse groove at the base of the lemma, two lines of hairs on the callus and a mix of long and short teeth on the palea edge compared to E. repens. The rachilla is wedge-shaped from a V-shaped sinus. The lemma and palea may be covered in a white, waxy coating.
Elymus trachycaulus (Link) Gould ex Shinners subsp. trachycaulus (slender wheatgrass)
E. trachycaulus subsp. trachycaulus florets are a similar size (length*: 7.0 – 11.4 ; width: 1.2 – 1.7 mm), tend to be shiny light straw-yellow coloured, and one side of lemma is straight and the other is curved giving it a slightly twisted shape compared to E. repens. The callus is pointed with a line of hairs across it. Palea teeth are fine and close together, the rachilla is generally hairy, and the sinus is V-shaped.
*Note: minimum and maximum of 10 florets in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces

Pascopyrum smithii

Elymus trachycaulus
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) spikelets and florets
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, palea view L, lemma view R
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Elymus repens
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, palea teeth
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, close-up of palea teeth
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, close-up of rachilla
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Elymus repens

Elymus repens
Poaceae
Quackgrass (Couchgrass) (Elymus repens) floret, side view, close-up of rachilla
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) florets
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii
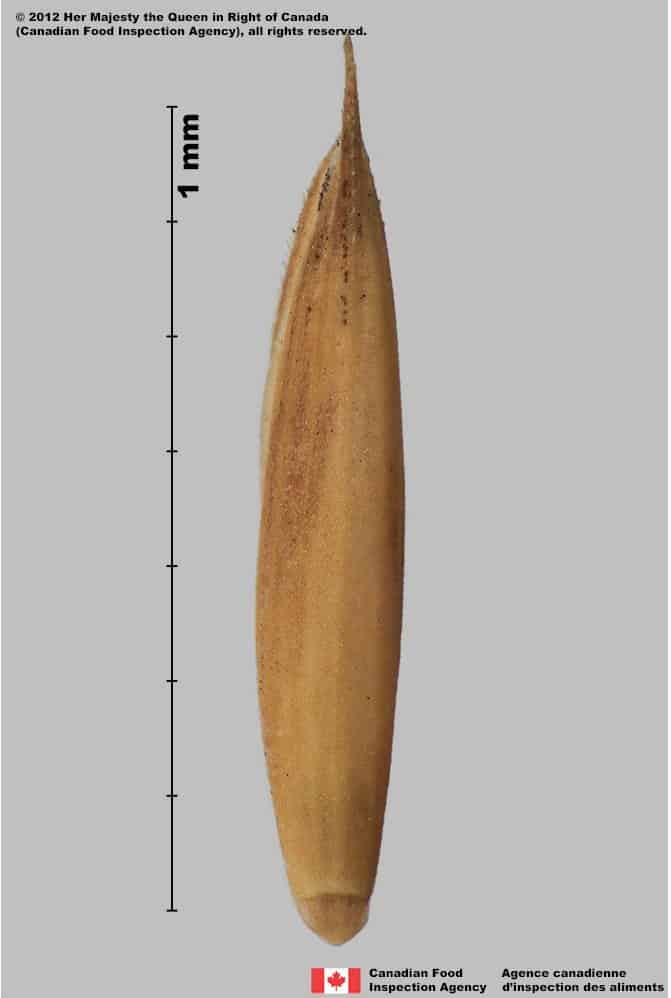

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) floret, lemma view
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii
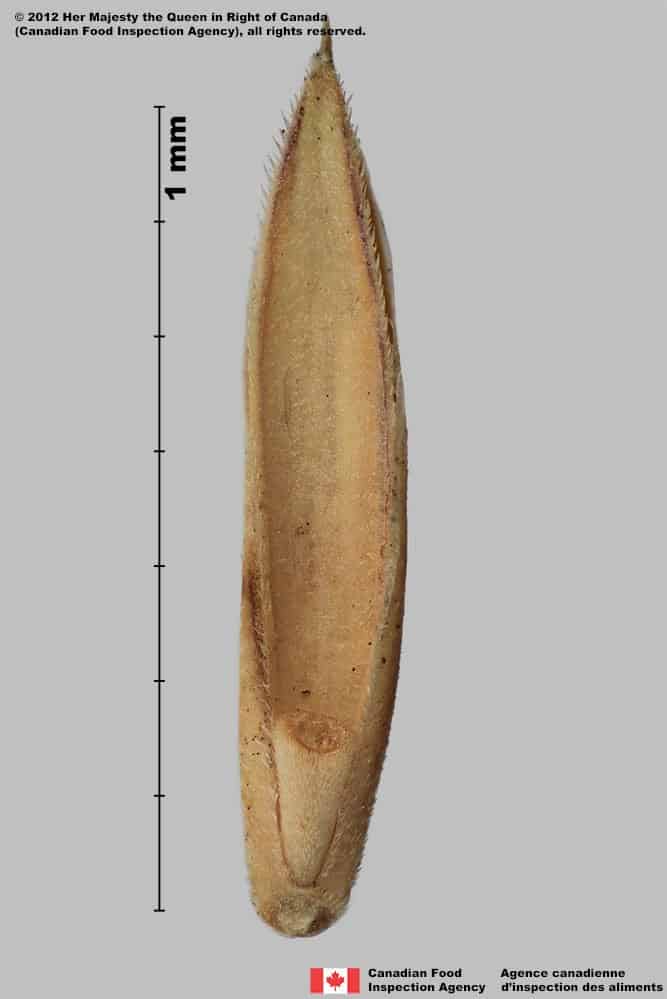

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) floret, palea view
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii
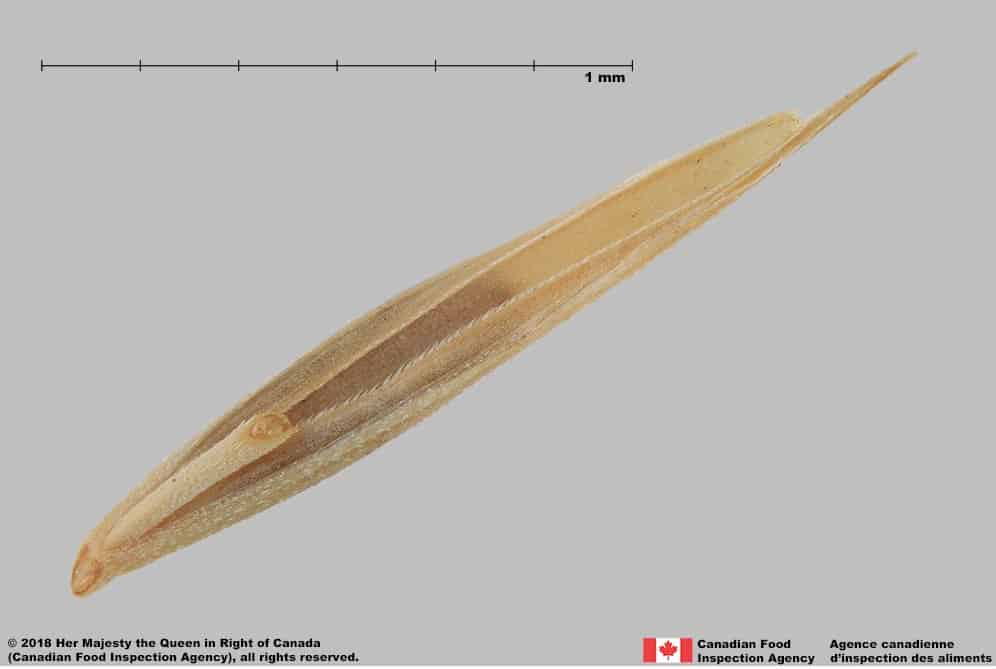

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) floret
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii
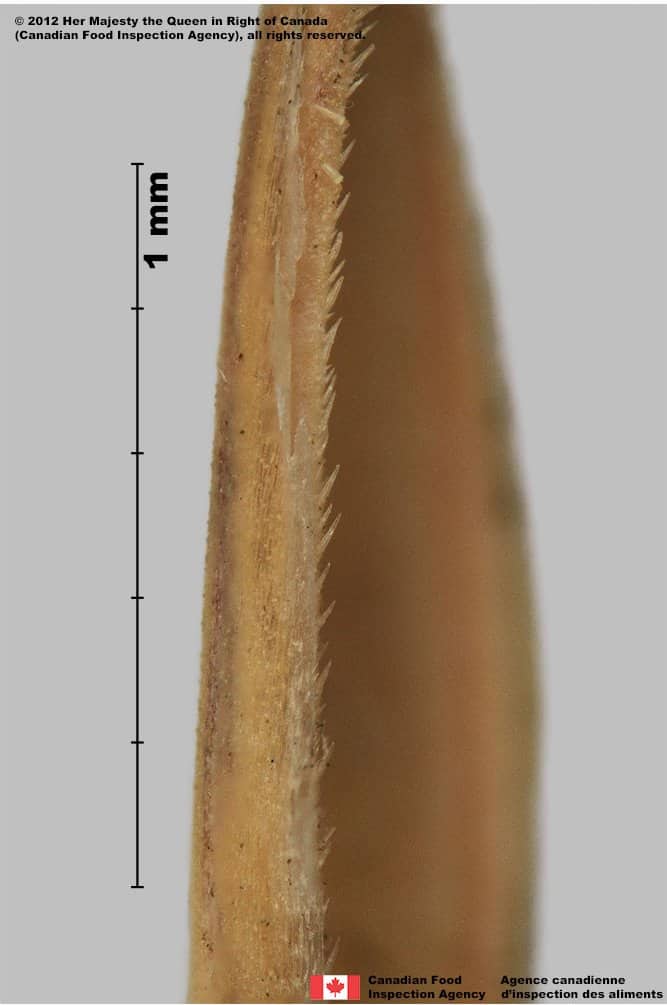

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) floret, palea teeth
SIMILAR SPECIES
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Pascopyrum smithii

Pascopyrum smithii
Poaceae
Western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) floret, callus (lemma view)
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Barkworth, M. E., Capels, K. M., Long, S. and Piep, M. B., (eds.) 2007. Volume 24. Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Poaceae, Part 1. Oxford University Press, New York, New York.
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed April 1, 2021.
Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International (CABI). 2021. Invasive Species Compendium, CAB International, Wallingford, UK. https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/journal/cabicompendium Accessed April 1, 2021.
Darbyshire, S. J. 2003. Inventory of Canadian Agricultural Weeds. Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Research Branch. Ottawa, ON.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/5290299 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide. https://www.idseed.org/authors/details/method_for_seed_size_measurement.html
Kartesz, J. T. 2015. The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). North American Plant Atlas. Chapel Hill, N.C., www.bonap.org/MapSwitchboard.html Accessed April 1, 2021.
Royer, F. and Dickinson, R. 1999. Weeds of Canada and the Northern United States. The University of Alberta Press/Lone Pine Publishing, Edmonton, Alberta.
Timling, I. 2000. Elytrigia repens as an invasive species during salt marsh restoration at the Baltic Sea. Restoration and Reclamation Review, Vol. 6 No. 2, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, MN., http://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/59716 Accessed May 30, 2016.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2021. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysimple.aspx Accessed April 1, 2021.