Zygophyllum fabago
Overview
Aperçu
Regulation :
Remarques Réglementation:
- CFIA Weed Seeds Order - Class 1: Prohibited Noxious Weed Seeds
- List of Pests Regulated by Canada
- USA Federal Noxious Weed Seed List
Regulation Notes:
Prohibited Noxious, Class 1 in the Canadian Weed Seeds Order (2016) under the Seeds Act. All imported and domestic seed must be free of Prohibited Noxious weed seeds.
Distribution :
Répartition :
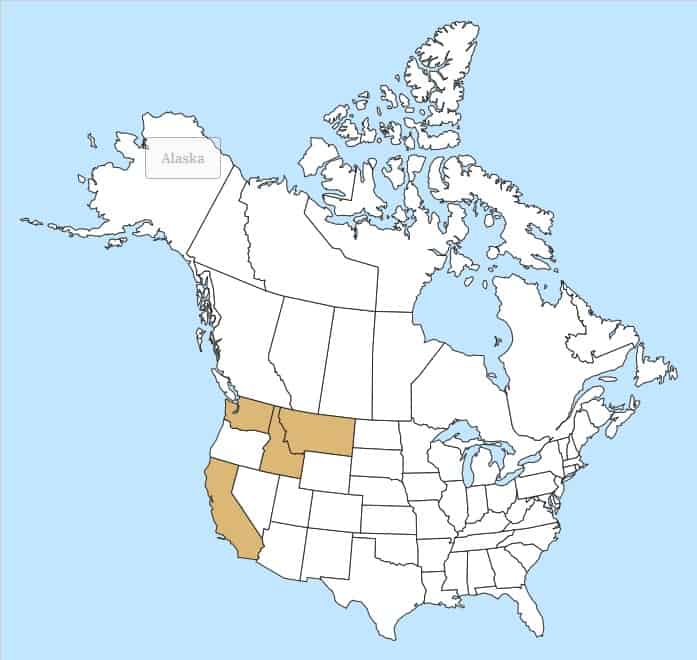
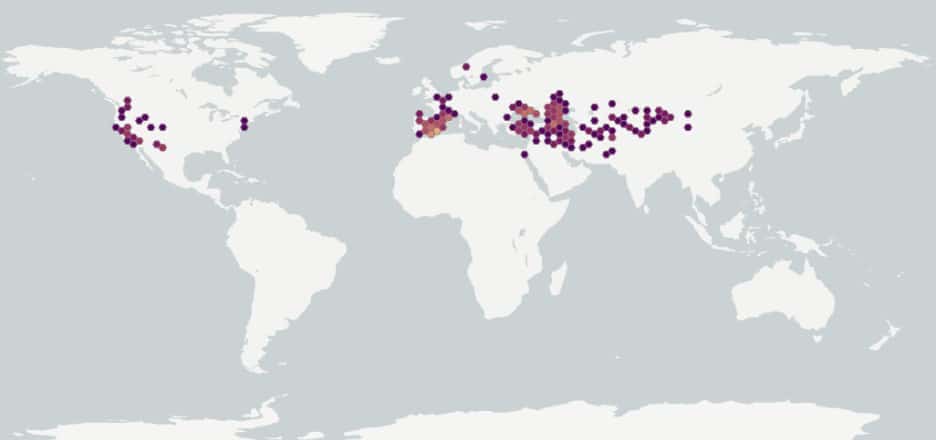
Native to eastern Europe, the Middle East and Central Asia. Introduced to Australia, southern Europe, as well as to most of the western United States (Davison and Wargo 2001; USDA-NRCS 2021). The species is absent from Canada (Brouillet et al. 2010+).
Habitat and Crop Association :
Habitat et Cultures Associées :
Dry rangelands, grasslands and disturbed areas, including roadsides, corrals and gravel pits (Davison and Wargo 2001). Z. fabago prefers dry habitats where it competes with native species (Davison and Wargo 2001).
Economic Use, cultivation area, and Weed Association :
Utilisation économique, zone de culture et association de mauvaises herbes :
Duration of Life Cycle :
Durée du cycle vital:
Perennial
Dispersal Unit Type :
Type d’unité de dispersion :
Seed
General Information
RENSEIGNEMENTS GÉNÉRAUX
Zygophyllum fabago seeds and plant parts are a traditional medicine in Iran, Turkey, China and other central Asian countries (Feng et al. 2008; Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019). The species is thought to have been imported into the United States in contaminated alfalfa seed (Davison and Wargo 2001). The species usually spreads by seed, but can also generate new plants from pieces of its roots (Davison and Wargo 2001).
.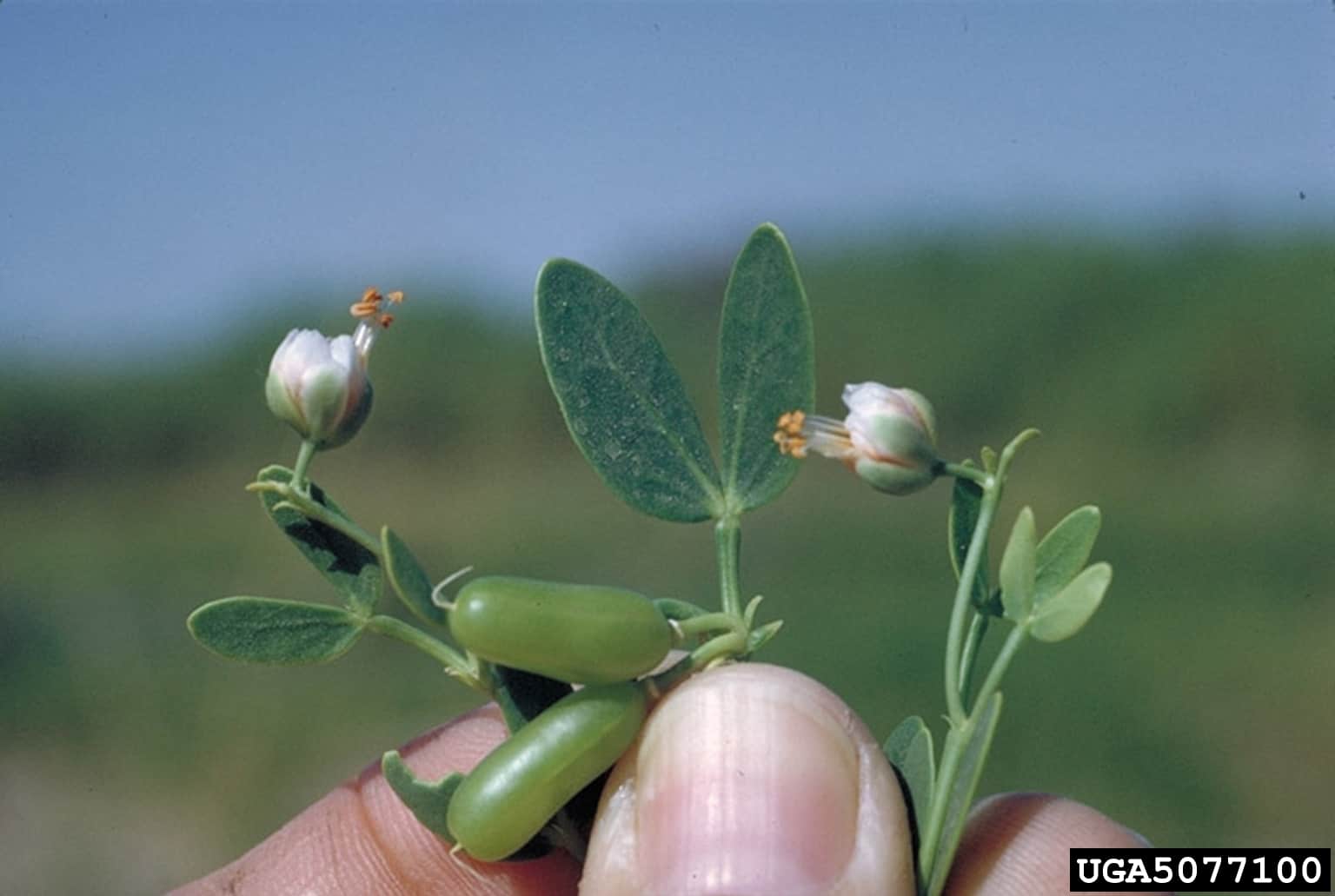
Zygophyllum fabago plant (Dell O. Clark, California Department of Food and Agriculture, Bugwood.org)
Identification
Identification
-
Capsule
Size
- Capsule length: 10 – 35 cm; width: 0.4 – 0.5 cm (FNA 1993+)
Shape
- Capsule is oblong shaped or cylindrical with 5 longitudinal ridges (FNA 1993+; Beier et al. 2003)
Surface Texture
- Capsule surface smooth (UKRBIN 2021)
Colour
- Capsule straw yellow when mature (UKRBIN 2021)
-
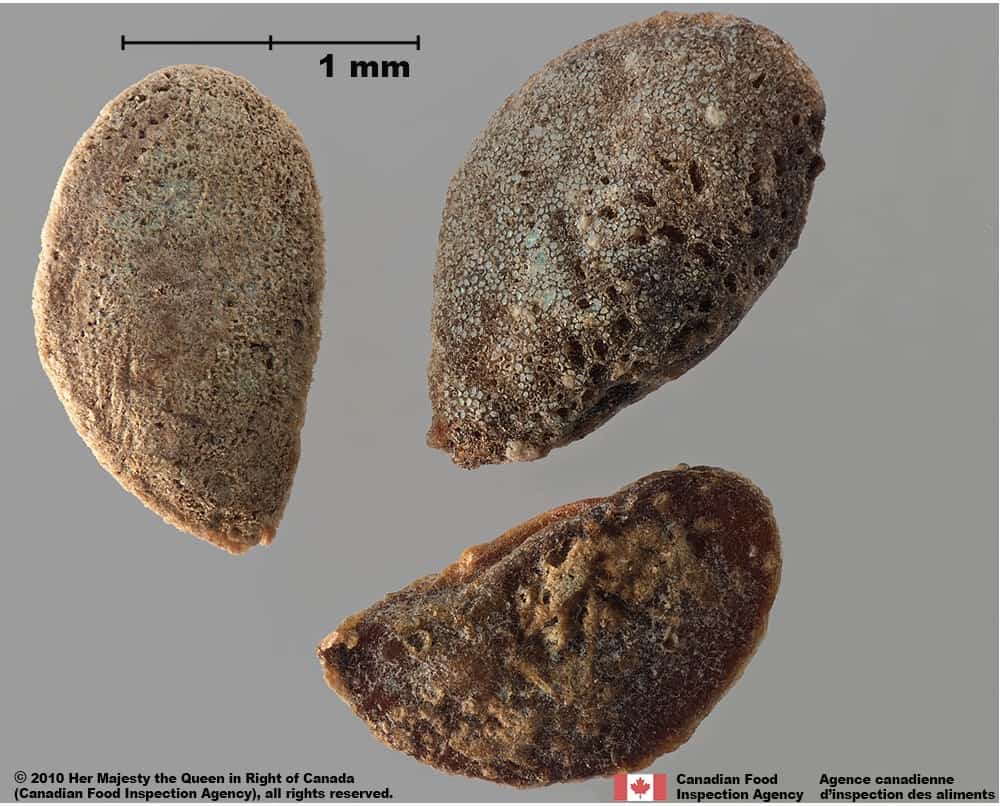
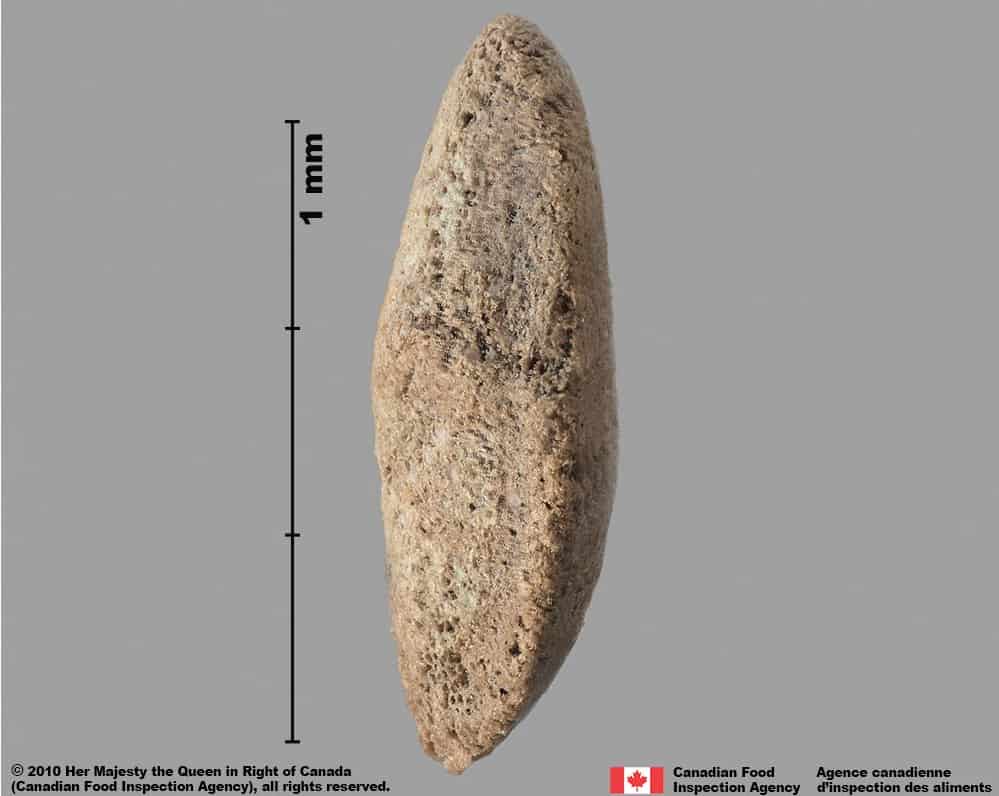
Seed
Size
- Seed length*: 3.4 mm – 5.9 mm; width: 1.6 – 3.9 mm
*Note: minimum and maximum of 20 seeds in a normal range of this species using image measurement (ISMA 2020)
Shape
- Seed shape is variable: oval, egg-shaped, D-shaped, kidney-shaped or irregular shaped, flattened in edge view
Surface Texture
- Seed surface is generally covered with a layer of dense papillate tubercles (Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019), the surface may be obscured by dried mucilage and appear bubbled or pitted rather than tuberculate
Colour
- The thick tissue layer covering the seed surface is grey or yellowish-white coloured
- Seed under the thick tissue layer is translucent red coloured
Other Features
Hilum and Hilum area
- Hilum is not visible
Other Features
- Seeds produce mucilage when wetted (Beier et al. 2003)
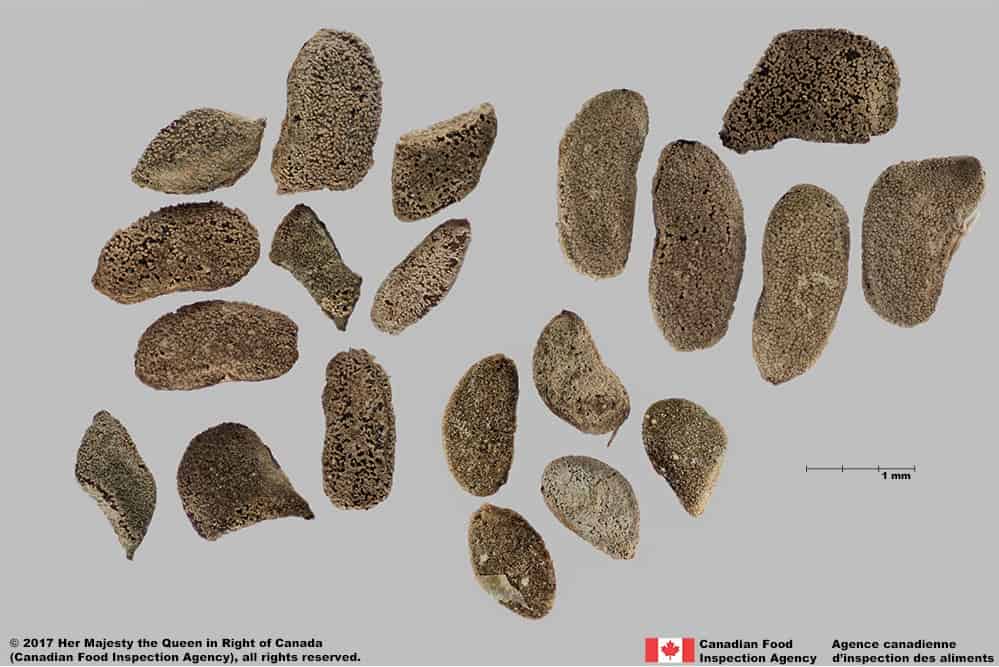

Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seeds





-
Embryo
Size
- Embryo partially fills the seed (Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019)
Shape
- Embryo is spatulate (Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019)
Endosperm
- Endosperm is hard and oily
Other Features
- The embryo is in axial position (Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019)
- The embryo contains chlorophyll while in the seed (Mohajel Kazemi et al. 2019)
Identification Tips
CONSEILS POUR L’IDENTIFICATION
Z. fabago seeds are variable in shape and flattened with a highly textured, mucilaginous seed coat. A review of the other species of Zygophyllum species indicate that the seeds generally have a different size, shape, colour and a smooth surface compared to Z. fabago (eFloras 2021; Tropicos 2021).

Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seed





Additional Botany Information
AUTRES RENSEIGNEMENTS BOTANIQUES
Flowers/Inflorescence
- Flower diameter: 6 – 7 mm, cup-shaped with white petals (FNA 1993+)
- Petals are red or orange at the base towards the inside of the flower, stamens are long and hang outside of the flower (FNA 1993+)
Vegetative Features
- Compound leaves are thick, fleshy, comprised of two leaflets and have opposite arrangement (WSNWCB 2022)
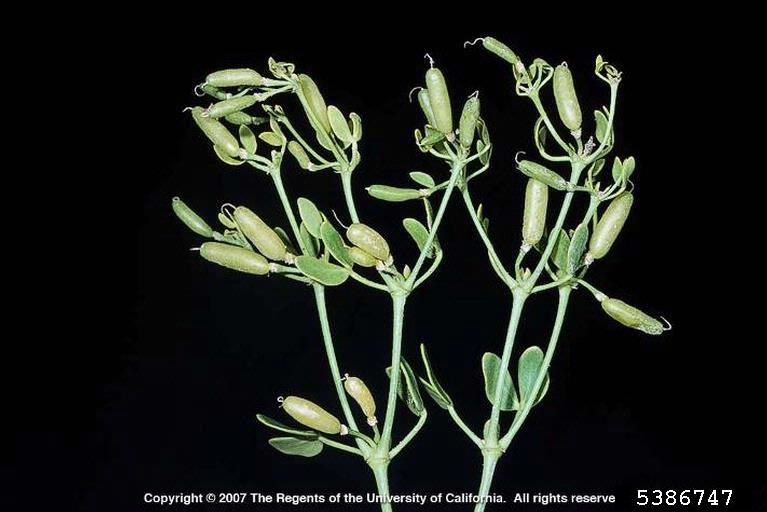

Zygophyllum fabago fruit (Joseph M. DiTomaso, University of California – Davis, Bugwood.org)


Similar Species
ESPÈCES SEMBLABLES
Similar species are based on a study of seed morphology of various species, and those with similar dispersal units are identified. The study is limited by physical specimen and literature availability at the time of examination, and possibly impacted by the subjectivity of the authors based on their knowledge and experience. Providing similar species information for seed identification is to make users aware of similarities that could possibly result in misidentification.
- Species of Zygophyllum are widely distributed in China, Pakistan, Central Asia, India, South Africa and the Mediterranean area (eFloras 2021; Tropicos 2021). These species may possibly be encountered in commodities originating from the areas mentioned above.
- Zygophyllum macropterum Boriss. seeds are larger (length: 5–9 mm; width: 2–3 mm), oblique teardrop-shaped and yellow or grayish green coloured (eFloras 2021)
- Z. eurypterum Boiss. & Buhse seeds are D- or C-shaped and black coloured and smooth textured (Tropicos 2021)
- Z. propinquum Decne seeds are oval shaped, compressed in edge view with a warty tuberculate surface (Tropicos 2021)
- Z. simplex Linn. seeds are oblong-shaped (Tropicos 2021)
- Z. atriplicoides Fisch. & Mey. seeds are larger (length 6 – 7 mm) and brown coloured (Tropicos 2021)
Click to select species
Cliquez pour sélectionner les espèces
Comparison Window
Fenêtre de comparaison
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Zygophyllum fabago

Zygophyllum fabago
Zygophyllaceae
Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Zygophyllum fabago

Zygophyllum fabago
Zygophyllaceae
Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seeds
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Zygophyllum fabago

Zygophyllum fabago
Zygophyllaceae
Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seed
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Zygophyllum fabago

Zygophyllum fabago
Zygophyllaceae
Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seed, side view
MAIN SPECIES
ESPÈCES PRINCIPALES
Zygophyllum fabago

Zygophyllum fabago
Zygophyllaceae
Syrian bean-caper (Zygophyllum fabago) seed, close up of surface
Need ID Help?
Besoin d’aide pour l’identification?
Reference(s)
Référence(s)
Beier, B. A., Chase, M. W. and Thulin, M., 2003. Phylogenetic relationships and taxonomy of subfamily Zygophylloideae (Zygophyllaceae) based on molecular and morphological data. Phylogenetic relationships Plant Systematics and Evolution 240 :11-39.
Brouillet, L., Coursol, F., Meades, S. J., Favreau, M., Anions, M., Bélisle, P. and Desmet, P. 2010+. VASCAN, the database of vascular plants of Canada. http://data.canadensys.net/vascan/ Accessed April 29, 2021.
Davison, J. and Wargo, M. 2001. Syrian beancaper: Another new noxious weed threatens Nevada. Cooperative extension. FS-01-46. University of Nevada, Reno, USA.
eFloras. 2020. Electronic Floras. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA., http://www.efloras.org Accessed November 17, 2021.
Feng, Y-L., Wu, B., Li, H-R., Li, Y-Q., Xu, Z., Yang, S-L., and Kitanaka, S. 2008. Triterpenoidal Saponins from the Barks of Zygophyllum fabago L. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 56: 858—860.
Flora of North America (FNA) Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico [Online]. 22+ vols. New York and Oxford. http://beta.floranorthamerica.org. Accessed December 29, 2022.
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Secretariat. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15468/39omei Accessed via https://www.gbif.org/species/3189902 Accessed December 29, 2022.
Government of Canada (GC). 2016. Canadian Weed Seeds Order. https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2016-93/page-2.html (English) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/fra/reglements/DORS-2016-93/page-2.html (French)
International Seed Morphology Association (ISMA). 2020. Method for Seed Size Measurement. Version 1.0. ISMA Publication Guide. https://www.idseed.org/authors/details/method_for_seed_size_measurement.html
Mohajel Kazemi ,E., Kazemian, M., Majidzadeh, F., Aliasgharpour, M., Movafeghi, A. 2019. Study of seed coat microsculpture organization during seed development in Zygophyllum fabago (Zygophyllaceae)
Tropicos. 2021. Missouri Botanical Garden. https://tropicos.org Accessed November 17, 2021.
UKRBIN, 2021. Zygophyllum fabago, Ukrainian Biodiversity Information Network https://ukrbin.com/show_image.php?imageid=124289 Accessed November 17, 2021.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Agricultural Research Services (USDA-ARS). 2021. Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomysimple.aspx Accessed April 29, 2021.
U.S. Department of Agriculture-Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2021. The PLANTS Database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC USA. http://plants.usda.gov Accessed April 29, 2021.
Washington State Noxious Weed Control Board (WSNWCB) 2022. https://www.nwcb.wa.gov/weeds/syrian-bean-caper Accessed February 17, 2022.